
Electricity
Assessment
•
Marc Horton
•
Physics
•
9th - 11th Grade
•
23 plays
•
Easy
Student preview

12 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
The nucleus of an atom contains
Only electrons
Only neutrons
Electrons and neutrons
Protons and neutrons
2.
Multiple Choice
A battery sends a current through a metal wire.
Direct current is movement of charge
backwards and forwards
in many directions
in one direction
up and down
3.
Multiple Choice
A metal wire carries an electric current. The charge that flows in the wire is made up of
electrons
protons
positive ions
negative ions
4.
Multiple Choice

The graphs show how the current in a component changes with the voltage applied across the component.
Which graph matches the component
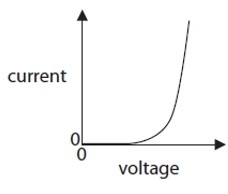
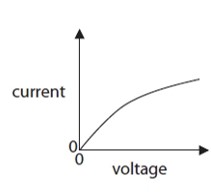
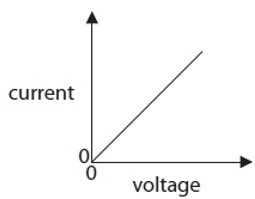
5.
Multiple Choice

The graphs show how the current in a component changes with the voltage applied across the component.
Which graph matches the component



Explore all questions with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

TYS 5105 C14 (Current of Electricity)
•
10th Grade

Forces and Motion 8
•
8th - 10th Grade

11B5 electricity quiz
•
11th Grade

Current Electricity
•
10th Grade

Current Electricity
•
10th Grade

SBA Mock Test 3 - Electricity & Circuits
•
9th - 10th Grade

4NA current of electricity
•
8th - 9th Grade

4NA Revision on DC Circuits and Practical Electricity
•
9th - 10th Grade