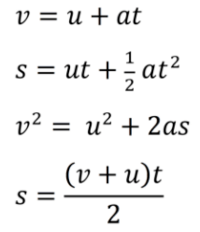
SUVAT Equations
Assessment
•

Adam Knights
•
Physics
•
5th - 9th Grade
•
438 plays
•
Medium
Student preview

15 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
A cyclist travelling at a speed of 4.2 m s-1 accelerates at 1.1 m s-2. In a time of 7.4 s, the distance travelled is
30 m
35 m
61 m
91 m
2.
Multiple Choice
A freely falling object on Earth has a speed of 5.0 m s-1. After falling a further 20 m, its speed it
15 m s-1
20 m s-1
25 m s-1
45 m s-1
3.
Multiple Choice
A bus is travelling at a speed of 9.0 m s-1. It then accelerates at a rate of 0.75 m s-2 for a time of 8.0 s. What therefore is its final speed?
6.0 m s-1
15 m s-1
17 m s-1
21 m s-1
4.
Multiple Choice
The acceleration of free fall on a certain planet is 8.0 m s-2. An object gets dropped from a height and hits the ground after 1.5 s. From what height must the object have been dropped?
6.0 m
9.0 m
11 m
12 m
5.
Multiple Choice
A ball is dropped from rest from a building 35.0 m high. If air resistance is neglected, then the ball will hit the ground with a speed of
8.4 m s-1
13.1 m s-1
18.5 m s-1
26.2 m s-1
Explore all questions with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

suvat equations quiz
•
9th Grade

F4 PHY CH2
•
8th Grade

Physics - Linear Motion
•
7th Grade

LINEAR MOTION(KINEMATIC FORMULA )
•
9th Grade

Physics Linear Motion
•
7th - 10th Grade

Motion
•
9th - 12th Grade

SUVAT
•
9th - 12th Grade

Mechanics SUVAT
•
9th - 11th Grade