
Forces and Equilibrium
Assessment
•
Mr. Low
•
Physics
•
10th Grade
•
34 plays
•
Hard
Student preview

35 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
State the principle of moments
A When a system is in equilibrium, the sum of the total clockwise moment is equal to the sum of the total anti-clockwise moment about the same pivot.
B When a system is in equilibrium, the sum of the total clockwise moment is greater the sum of the total anti-clockwise moment about the same pivot.
C When a system is in equilibrium, the sum of the total clockwise moment is less than the sum of the total anti-clockwise moment about the same pivot.
D When a system is in equilibrium, the sum of the total clockwise moment is equal to the sum of the total anti-clockwise moment about the different pivot.
2.
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows a man lifting a heavy rock using a steel bar. He pushes downwards on the end of the bar with a force F. Which pivot positions allows the force F to be as small as possible?

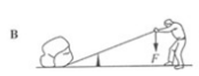
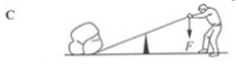

3.
Multiple Choice

80,000Nm
100,000Nm
120,000Nm
140,000Nm
4.
Multiple Choice

Two masses of mass 10.0 and 6.0 kg are hung from massless strings at the end of a light rod. The rod is virtually weightless. A pivot (fulcrum) is placed off center and the system is free to rotate. If the 6.0 kg mass is 4.0 m away from the pivot, how far away is the 10.0 kg mass if the system is not rotating?
0.42 m
2.4 m
4.8 m
4.2 m
5.
Multiple Choice

Assuming the system is in equilibrium, calculate the missing distance d
3.4 m
2.8 m
4.4 m
1.6 m
Explore all questions with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Forces and Equilibrium
•
10th Grade

Force, Friction, and Equilibrium
•
10th Grade

Forces and Moments
•
9th - 11th Grade

Forces Speed and Moments
•
9th - 11th Grade

High School Forces
•
9th - 11th Grade

Moments and equilibrium
•
10th - 11th Grade

force and moments of force
•
10th Grade

moments of forces
•
9th - 11th Grade