
Unit 25 Nuclear Chemistry
Assessment
•
Lan Vu
•
Chemistry
•
9th Grade - University
•
6 plays
•
Easy
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
443 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
a) are positively charged.
b) consist of two protons and four neutrons.
c) can penetrate any thickness of matter
d) All of the above
2.
Multiple Choice
nuclear decay
nuclear mass
isotopes
radon
3.
Multiple Choice
gives up two protons and two neutrons.
maintains the same number of protons and neutrons.
loses a proton and gains a neutron.
gains a proton and loses a neutron.
4.
Multiple Choice
remains the same
decreases by one.
increases by one.
increases by two.
5.
Multiple Choice
mass energy
magneticism
fusion
fission
6.
Multiple Choice
electrons
protons
nuclei
neutrons
7.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
beta particle
gamma ray
uranium
8.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
gamma ray
beta particle
uranium
9.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
electroscope
beta particle
gamma ray
10.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
gamma rays
beta particles
X rays
11.
Multiple Choice
alpha, beta, gamma
X ray, beta, gamma
alpha, gamma, beta
X ray, gamma, beta
12.
Multiple Choice
calculating the ages of fossils
fueling nuclear reactions
determining medical problems
treating brain tumors
13.
Multiple Choice
a chain reaction
fission
a chemical reaction
fusion
14.
Multiple Choice
to calculate the age of the Earth's oldest rocks
to calculate the age of a piece of bone
to identify the elements that make up a rock
to identify the elements that make up a bone
15.
Multiple Choice
(a) a different isotope of the same element.
(b) an entirely different element.
Both (a) and (b)
Neither (a) nor (b)
16.
Multiple Choice
In a pressurized water reactor( PWR) _____________
Light or heavy water is used as both coolant and moderator.
The coolant water boils in the reactor core.
Water is used at high pressure
Both (a) and (c).
17.
Multiple Choice
The reason for providing the thermal shielding is to _________________
Absorb the fast neutrons
Protect the operating personnel from exposure to radiations
Prevent the reactor wall from getting heated
All of the above
18.
Multiple Choice
The nuclear energy is measured as........
MeV
MW
Curie
None of the above
19.
Multiple Choice
Which is the most commonly used moderator?
Graphite
Sodium
Deuterium
Heavy water
20.
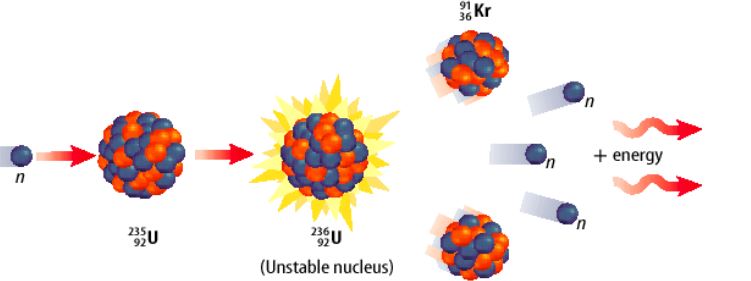
Multiple Choice
U238 will undergo fission by
Slow neutrons alone
fast neutrons alone
Either fast or slow neutrons
medium energy neutrons
21.
Multiple Choice
The best capable alternative source which can meet the future energy demand is
thermal power plant
nuclear power plant
hydroelectric power plant
geothermal power plant
22.
Multiple Select
How much coal is required to generate energy equivalent to the energy generated by 1 kg of uranium?
30000 tonnes of high grade coal
300 tonnes of high grade coal
10000 tonnes of high grade coal
3000 tonnes of high grade coal
23.
Fill in the Blank
The Famous nobel lecturette speaking in the audio clip is _________.
24.
Multiple Choice
a) are positively charged.
b) consist of two protons and four neutrons.
c) can penetrate any thickness of matter
d) All of the above
25.
Multiple Choice
nuclear decay
nuclear mass
isotopes
radon
26.
Multiple Choice
gives up two protons and two neutrons.
maintains the same number of protons and neutrons.
loses a proton and gains a neutron.
gains a proton and loses a neutron.
27.
Multiple Choice
electrons
protons
nuclei
neutrons
28.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
beta particle
gamma ray
uranium
29.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
gamma ray
beta particle
uranium
30.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
electroscope
beta particle
gamma ray
31.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
gamma rays
beta particles
X rays
32.
Multiple Choice
alpha, beta, gamma
X ray, beta, gamma
alpha, gamma, beta
X ray, gamma, beta
33.
Multiple Choice
Inside the electrons
Inside the neutrons
Inside the atomic nucleus
Inside the electron shells
34.
Multiple Choice
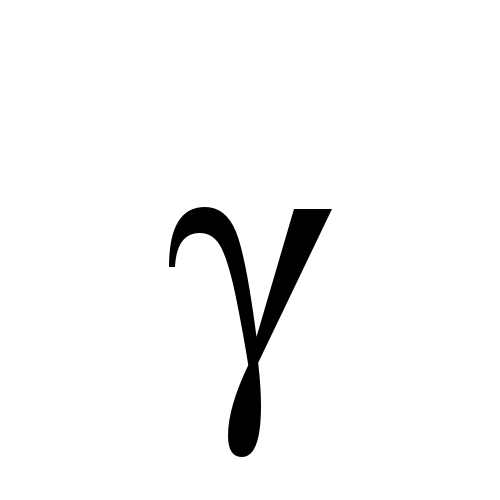
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
electron
35.
Multiple Choice
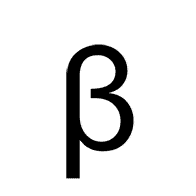
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
neutron
36.
Multiple Choice
Actinium-234
Thorium-233
Protactinium-234
Radium-230
37.
Multiple Choice

5224X
5023X
5024X
5025X
38.
Multiple Choice

5023Y
4622Y
5025Y
5024Y
39.
Multiple Choice
5022Y
4622Y
4820Y
5426Y
40.
Multiple Choice
What type of decay is shown here
23892U ---> 23490Th + 42He.
alpha
beta
gamma
41.
Multiple Choice
What type of nuclear decay is shown here
13756Ba →→ 13756Ba + γ rays
alpha
beta
gamma
42.
Multiple Choice
Finish this equation
20983Bi--> _______ + 20581Tl
42He
0-1e
y
43.
Multiple Choice
Identify the type of nuclear decay shown here
21483Bi → 0-1e + 21484Po
alpha
beta
gamma
44.
Multiple Choice
finish the equation
22688Ra --> ____ + 22688Ra
42He
0-1e
y
45.
Multiple Choice
finish the equation
18173Ta --> ____ + 18174W
42He
0-1e
y
46.
Multiple Choice
Identify the type of nuclear decay shown here
21483Bi → 0-1e + 21484Po
alpha
beta
gamma
47.
Multiple Choice
What type of decay is shown here
23892U ---> 23490Th + 42He.
alpha
beta
gamma
48.
Multiple Choice
What type of nuclear decay is shown here
13756Ba →→ 13756Ba + γ rays
alpha
beta
gamma
49.
Multiple Choice
Finish this equation
20983Bi--> _______ + 20581Tl
42He
0-1e
y
50.
Multiple Choice
Identify the type of nuclear decay shown here
21483Bi → 0-1e + 21484Po
alpha
beta
gamma
51.
Multiple Choice
finish the equation
22688Ra --> ____ + 22688Ra
42He
0-1e
y
52.
Multiple Choice
finish the equation
18173Ta --> ____ + 18174W
42He
0-1e
y
53.
Multiple Choice
Which force holds protons and neutrons together in the atom nucleus?
electric force
gravity
strong nuclear force
weak nuclear force
54.
Multiple Choice
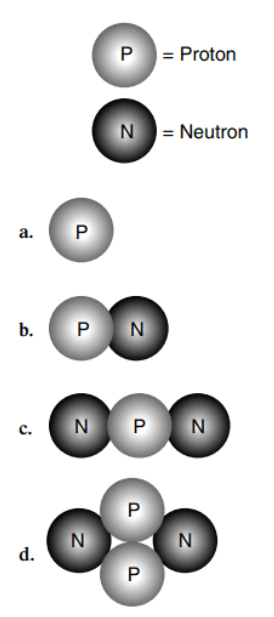
Which of these is an alpha particle?
A
B
C
D
55.
Multiple Choice
Carbon-14 and carbon-12 have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. These different forms of the same element are called
radioactive
isotopes
nuclei
tracers
56.
Multiple Choice
The mass number of a nucleus is equal to ______.
the number of protons plus the number of neutrons
the number of electrons
the number of protons
the number of neutrons
57.
Multiple Choice
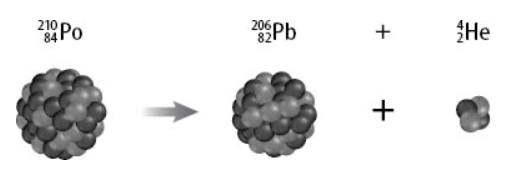
What type of nuclear decay is represented in this illustration?
beta decay
gamma radiation
alpha decay
nuclear fusion
58.
Multiple Choice
Which happens in a nucleus during gamma decay?
The number of protons increases.
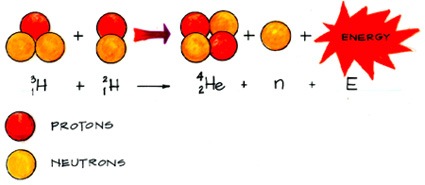
The number of neutrons increases.
The number of protons remains the same.
The total number of neutrons plus neutrons decreases.
59.
Multiple Choice
When a neutron turns into a proton in a nucleus, what sort of particle is emitted?
alpha
beta
gamma
photon
60.
Multiple Choice
Gamma rays _________.
have no mass and no charge
have mass but no charge
have no mass but have charge
have mass and charge
61.
Multiple Choice
What are found in the nucleus of an atom?
protons and electrons
electrons and neutrons
protons, neutrons, and electrons
protons and neutrons
62.
Multiple Choice
Protons do not repel each other in the nucleus because of the ______.
weak force
electric force
strong force
gravitational force
63.
Multiple Choice
In a radioactive nucleus, the electric force _____ the strong force.
balances
overpowers
is overpowered by
adds to
64.
Multiple Choice
Which of these is not a type of nuclear radiation?
alpha particles
beta particles
gamma rays
microwaves
65.
Multiple Choice
How does the alpha decay of a nucleus cause the nucleus to change?
Only the number of protons decreases.
Only the number of neutrons decreases.
The number of neutrons and the number of protons decrease.
The number of protons increases and the number of neutrons decreases.
66.
Multiple Choice
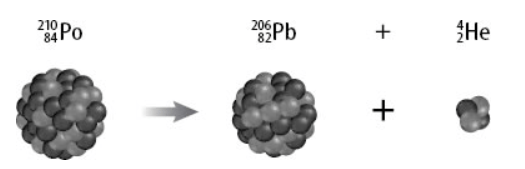
Which of these is a true statement about the products of the decay compared to polonium-210?
The charges are equal but the mass numbers are not equal.
The mass numbers are equal but the charges are not equal.
The mass numbers and charges are equal.
Neither the mass numbers nor the charges are equal.
67.
Multiple Choice
A hydrogen nucleus has only one proton. How many neutrons are in a hydrogen-3 nucleus?
0
1
2
3
68.
Multiple Choice
The three types of nuclear radiation in order of decreasing penetrating power are
alpha, beta, gamma
alpha, gamma, beta
beta, alpha, gamma
gamma, alpha, beta
69.
Multiple Choice
Thermonuclear bomb works on the principle of:
Fission
Fusion
Both A and B
None of the above
70.
Multiple Choice
Which article of clothing was oddly named for a nuclear testing site?
Bikini
Fedora
Cravat
Swimsuit
71.
Multiple Choice
Nuclear medicine is a medical Specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of Disease.
True
False
72.
Multiple Choice
What dangerous byproduct is produced by nuclear power plants?
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Radioactive waste
Smoke
73.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following country produces the most nuclear energy?
India
China
Russia
USA
74.
Multiple Choice
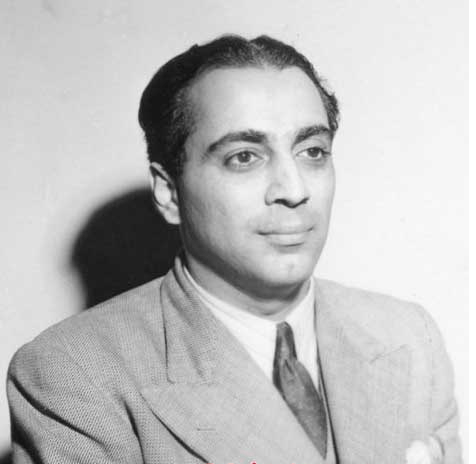

Identify the famous nuclear physicist.
P. K. Iyenger
Homi J. Bhaba
Niels Bohr
James Chadwick
75.
Multiple Choice
Identify the movie.
Krrish
PK
Parmanu
Mission Mangal
76.
Multiple Select
Which of the following is/are NOT true about Indian space research? (choose one or more)
ISRO was set up in 1962.
Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), SHAR is situated in Bangaluru
The first satellite launched in India was Aryabhatta.
Great scientist Dr. Vikram Sarabhai is known as the father of Indian space research.
77.
Fill in the Blank
The full form of GSLV is
78.
Multiple Select
Who is your favorite scientist?
A P J Abdul Kalam
C V Raman
S N Bose
Homi J Bhaba
Bikram Sarabhai
79.
Open Ended
Write down three (3) applications of radioactive elements.
Evaluate responses using AI:
OFF
80.
Fill in the Blank
The current chairman of ISRO
81.
Multiple Select
Who among the following were the former chairman of ISRO? (More than one option may be correct)
A. S. Kiran Kumar
Ajit Kumar Mohanty
K. Radhakrishnan
G. Satheesh Reddy
82.
Fill in the Blank
Dr Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre is located in
83.
Multiple Choice
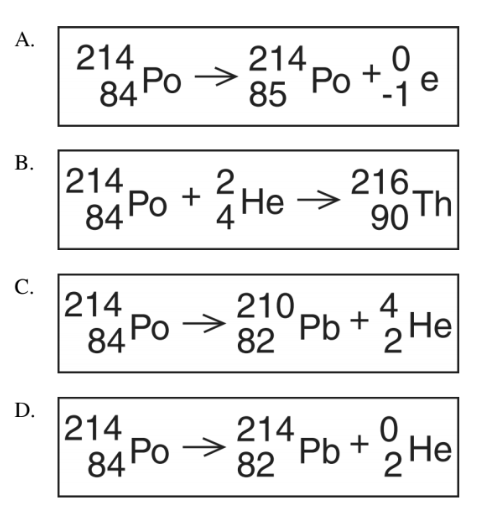
Which equation correctly represents the alpha decay of polonium-214?
A
B
C
D
84.
Multiple Choice
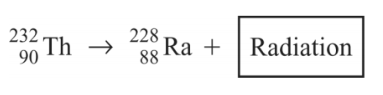
This equation shows the radioactive decay of thorium (Th). Which of the following particles is released in this reaction?
alpha
beta
neutron
gamma
85.
Multiple Choice
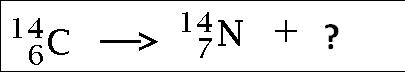
alpha particle
beta particle
gamma particle
neutron
86.
Multiple Choice

it's 88 because element X gains 2 protons
it's 218 because element X loses 2 protons and 2 neutrons
it's 220 because element X loses 2 neutrons
it's 226 because element X gains 2 protons and 2 neutrons
87.
Multiple Choice
(a) a different isotope of the same element.
(b) an entirely different element.
Both (a) and (b)
Neither (a) nor (b)
88.
Multiple Choice
nuclear decay
nuclear mass
isotopes
radon
89.
Multiple Choice
gives up two protons and two neutrons.
maintains the same number of protons and neutrons.
loses a proton and gains a neutron.
gains a proton and loses a neutron.
90.
Multiple Choice
mass energy
magneticism
fusion
fission
91.
Multiple Choice
electrons
protons
nuclei
neutrons
92.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
beta particle
gamma ray
uranium
93.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
electroscope
beta particle
gamma ray
94.
Multiple Choice
alpha, beta, gamma
X ray, beta, gamma
alpha, gamma, beta
X ray, gamma, beta
95.
Multiple Choice
a chain reaction
fission
a chemical reaction
fusion
96.
Multiple Choice
What type of nuclear decay is shown here
13756Ba →→ 13756Ba + γ rays
alpha
beta
gamma
97.
Multiple Choice
Identify the type of nuclear decay shown here
21483Bi → 0-1e + 21484Po
alpha
beta
gamma
98.
Multiple Choice
a) are positively charged.
b) consist of two protons and four neutrons.
c) can penetrate any thickness of matter
d) All of the above
99.
Multiple Choice
gives up two protons and two neutrons.
maintains the same number of protons and neutrons.
loses a proton and gains a neutron.
gains a proton and loses a neutron.
100.
Multiple Choice
electrons
protons
nuclei
neutrons
101.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
electroscope
beta particle
gamma ray
102.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
gamma rays
beta particles
X rays
103.
Multiple Choice
85209At = ___ + 24He
83205Bi
86209Rn
81207Tl
85208At
104.
Multiple Choice
614C = ___ + -10e
410Be
714N
210He
613C
105.
Multiple Choice
In alpha decay, the mass number...
increases by 2
decreases by 2
increases by 4
decreases by 4
106.
Multiple Choice
In alpha decay, the atomic number...
increases by 2
decreases by 2
increases by 4
decreases by 4
107.
Fill in the Blank
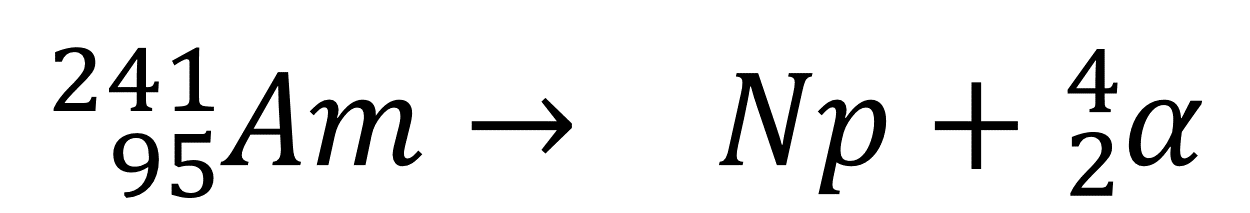
The mass number of Neptunium (Np) is _____.
108.
Fill in the Blank
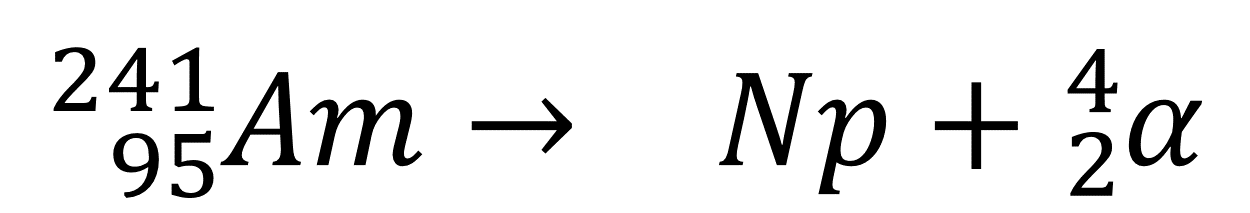
The atomic number of Neptunium (Np) is _____.
109.
Fill in the Blank
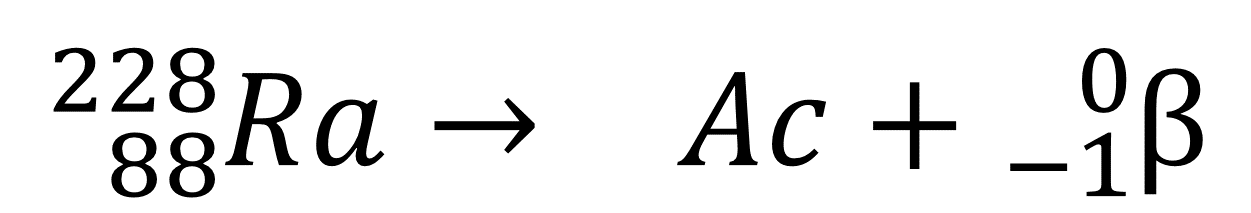
The atomic number of Actinium (Ac) is _____.
110.
Multiple Choice
In beta decay, the mass number
decreases by 4.
increases by 1.
stays the same.
decreases by 2.
111.
Multiple Choice
In beta decay, the atomic number
decreases by 2.
increases by 1.
stays the same.
decreases by 1.
112.
Multiple Choice
Oxygen-19 produces ________________ through beta decay.
nitrogen-19
fluorine-19
carbon-14
lead-208
113.
Multiple Choice
nuclear decay
nuclear mass
isotopes
radon
114.
Multiple Choice
gives up two protons and two neutrons.
maintains the same number of protons and neutrons.
loses a proton and gains a neutron.
gains a proton and loses a neutron.
115.
Multiple Choice
electrons
protons
nuclei
neutrons
116.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
electroscope
beta particle
gamma ray
117.
Multiple Choice
Carbon-14 and carbon-12 have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. These different forms of the same element are called
radioactive
isotopes
nuclei
tracers
118.
Multiple Choice
The mass number of a nucleus is equal to ______.
the number of protons plus the number of neutrons
the number of electrons
the number of protons
the number of neutrons
119.
Multiple Choice

What type of nuclear decay is represented in this illustration?
beta decay
gamma radiation
alpha decay
nuclear fusion
120.
Multiple Choice
How does the alpha decay of a nucleus cause the nucleus to change?
Only the number of protons decreases.
Only the number of neutrons decreases.
The number of neutrons and the number of protons decrease.
The number of protons increases and the number of neutrons decreases.
121.
Multiple Choice
A neutron changes into a proton and an electron releasing this type of particle.
alpha decay
beta decay
gamma decay
all of the above
alpha & beta decay
122.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
electroscope
beta particle
gamma ray
123.
Multiple Choice
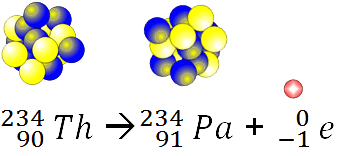
Alpha
beta
gamma
none
124.
Multiple Choice
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
125.
Multiple Choice
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
126.
Multiple Choice
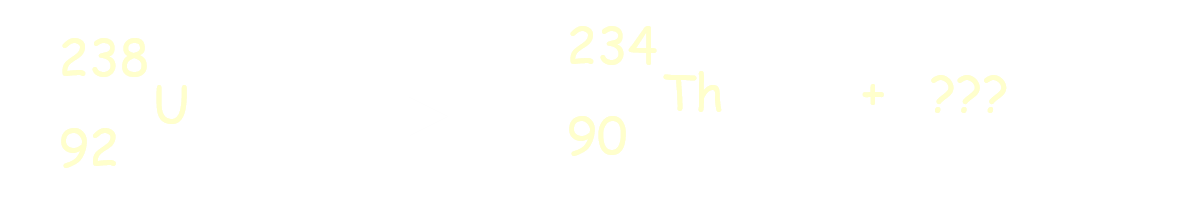
an alpha particle
a beta particle
gamma rays
visible light
127.
Multiple Choice
Fission reaction
Fusion reaction
Decomposition reaction
Decay
128.
Multiple Choice
Beta decay
Alpha decay
Nuclear fission
Nuclear fusion
129.
Multiple Choice
It is easy to implement.
It produces less energy than nuclear fission.
It produces more energy than nuclear fission.
It has the ability to occur easily in everyday life.
130.
Multiple Choice
fission
fusion
131.
Multiple Choice
fusion
fission
half-life
gamma radiation
132.
Multiple Choice
Fusion
Half-life
Fission
Fusion or fission
133.
Multiple Choice

Fission reaction
Fusion reaction
Decomposition reaction
Decay
134.
Multiple Choice
Underwater
All around us
In the radioactive waste
On the sun
135.
Multiple Choice
Nuclear power plants
Radio active decay
Atomic Bomb
On the surface of the sun
136.
Multiple Choice
heavy ions fuse together
very light nuclei fuse together
uranium splits into two fragments
uranium emits a neutron
137.
Multiple Choice
Mass number
Atomic number
Atomic mass
Number of protons
138.
Multiple Choice
a) are positively charged.
b) consist of two protons and four neutrons.
c) can penetrate any thickness of matter
d) All of the above
139.
Multiple Choice
gives up two protons and two neutrons.
maintains the same number of protons and neutrons.
loses a proton and gains a neutron.
gains a proton and loses a neutron.
140.
Multiple Choice
remains the same
decreases by one.
increases by one.
increases by two.
141.
Multiple Choice
electrons
protons
nuclei
neutrons
142.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
beta particle
gamma ray
uranium
143.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
gamma ray
beta particle
uranium
144.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
electroscope
beta particle
gamma ray
145.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
gamma rays
beta particles
X rays
146.
Multiple Choice
it is a fossil fuel
it leaves behind radioactive waste
it emits large amounts of pollution into the atmosphere
there are no disadvantages
147.
Multiple Choice
Uranium releases electrons to create electricity
When a nuclear fission reaction occurs, the electrons emitted can strike other nuclei in the sample, and cause them to split
When a nuclear fission reaction occurs, the neutrons emitted can strike other nuclei in the sample, and cause them to split
Protons and neutrons change to electrons because the nuclei are so big
148.
Multiple Choice
The ability to absorb energy
The ability to release tremendous amounts of energy
The ability to produce more energy than nuclear fusion
There are no beneficial aspects of nuclear fission
149.
Multiple Choice
What type of decay is shown here
23892U ---> 23490Th + 42He.
alpha
beta
gamma
150.
Multiple Choice
What type of nuclear decay is shown here
13756Ba →→ 13756Ba + γ rays
alpha
beta
gamma
151.
Multiple Choice
Finish this equation
20983Bi--> _______ + 20581Tl
42He
0-1e
y
152.
Multiple Choice
Identify the type of nuclear decay shown here
21483Bi → 0-1e + 21484Po
alpha
beta
gamma
153.
Multiple Choice
finish the equation
22688Ra --> ____ + 22688Ra
42He
0-1e
y
154.
Multiple Choice
88226Ra = ___ + 24He
86222Rn
89226Ac
84224Po
88225Ra
155.
Multiple Choice
85209At = ___ + 24He
83205Bi
86209Rn
81207Tl
85208At
156.
Multiple Choice
2760Co = ___ + -10e
2556Mn
2860Ni
2358V
2759Co
157.
Multiple Choice
146C --> 0-1e + ________
145B
146C
147N
42He
158.
Multiple Choice
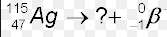
Ag-115
Cd-115
Pd-115
Not Listed
159.
Multiple Choice
gives up two protons and two neutrons.
maintains the same number of protons and neutrons.
loses a proton and gains a neutron.
gains a proton and loses a neutron.
160.
Multiple Choice
electrons
protons
nuclei
neutrons
161.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
beta particle
gamma ray
uranium
162.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
electroscope
beta particle
gamma ray
163.
Multiple Choice
(a) a different isotope of the same element.
(b) an entirely different element.
Both (a) and (b)
Neither (a) nor (b)
164.
Multiple Choice
56
26
30
33
165.
Multiple Choice
What type of decay is shown here
23892U ---> 23490Th + 42He.
alpha
beta
gamma
166.
Multiple Choice
Finish this equation
20983Bi--> _______ + 20581Tl
42He
0-1e
y
167.
Multiple Choice
Identify the type of nuclear decay shown here
21483Bi → 0-1e + 21484Po
alpha
beta
gamma
168.
Multiple Choice
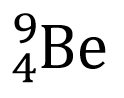
This element is also called
Beryllium-4
Beryllium-5
Beryllium-9
Beryllium-13
169.
Multiple Choice
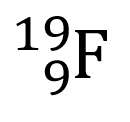
How many protons and neutrons are in the nucleus of the atom shown?
9 protons and 19 neutrons
19 protons and 9 neutrons
10 protons and 9 neutrons
9 protons and 10 neutrons
170.
Multiple Choice
Solve this equation for alpha decay.
2760Co = ___ + 24He
2556Mn
2860Ni
2358V
2759Co
171.
Multiple Choice
The beta decay of Nitrogen-16 will produce
Nitrogen-14
Boron-12
Fluorine-20
Oxygen-16
172.
Multiple Choice
The Alpha decay of Zinc-66 will produce
Gallium-67
Zinc-65
Nickel-58
Nickel-62
173.
Multiple Choice
finish the equation
18173Ta --> ____ + 18174W
42He
0-1e
y
174.
Multiple Choice
30
16
12
15
175.
Multiple Choice
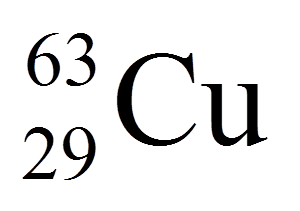
29
34
63
92
176.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the correct isotope for the following ion: Protons = 82; Neutrons = 125; Electrons = 80
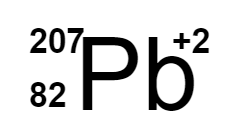

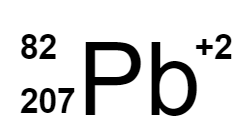

177.
Multiple Choice
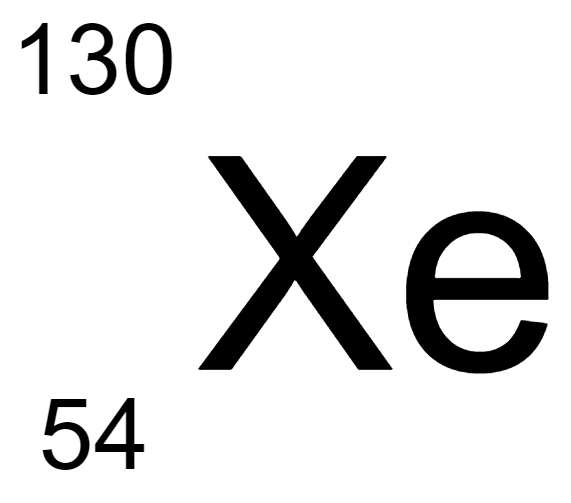
Determine the isotope notation:
Xenon-54
Xenon-130
Xenon-76
Xenon-184
178.
Multiple Choice
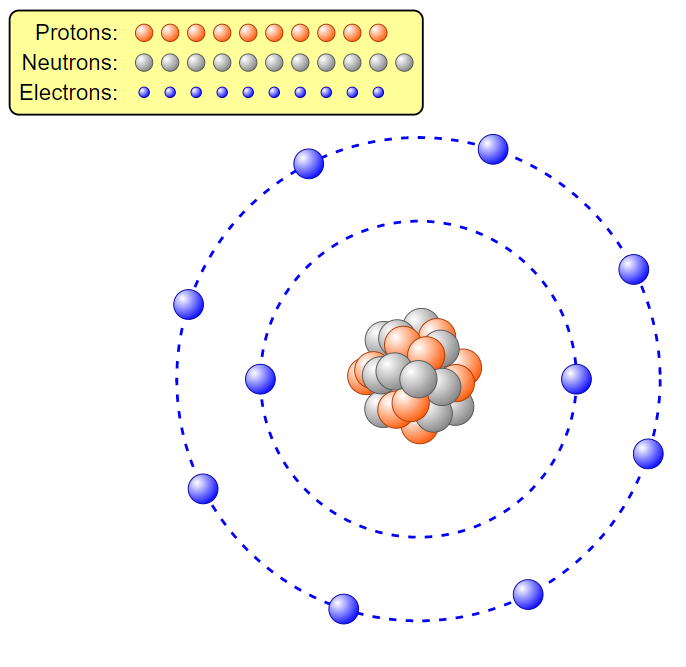
Is this an atom or an ion:
atom
ion
179.
Multiple Choice

Determine the correct nuclear symbol:
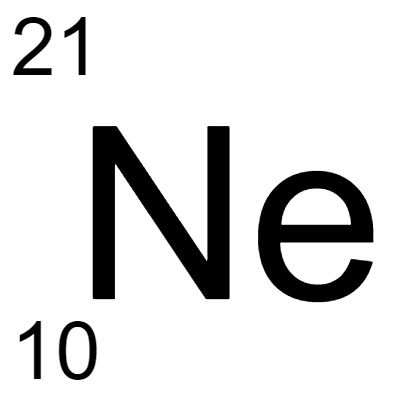
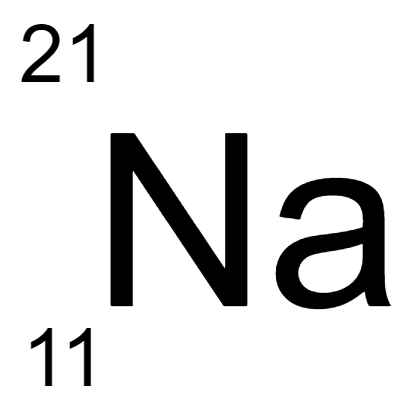
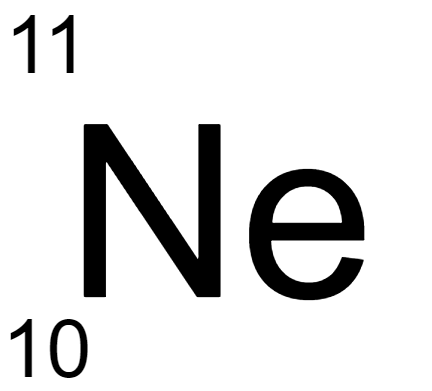
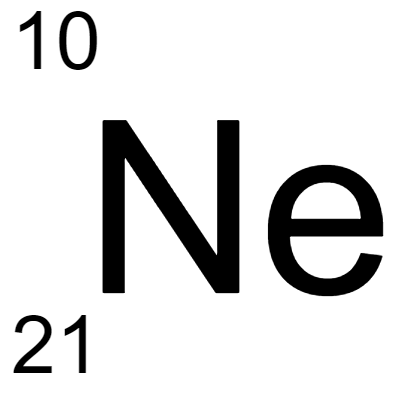
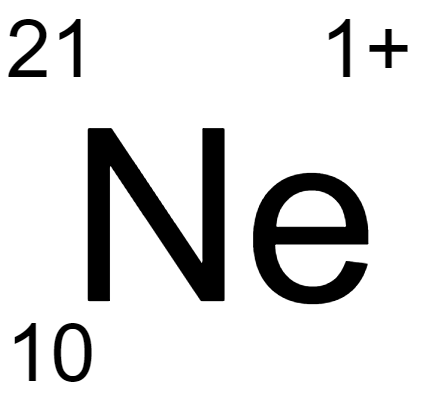
180.
Multiple Choice

8
3
4
5
181.
Multiple Choice

19
8
11
10
182.
Multiple Choice
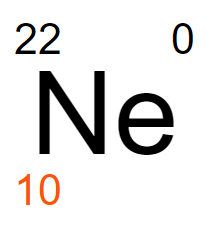
Which isotope notation is correct for the atom shown?
Neon-22
Neon-10
Neon-12
Neon-0
183.
Multiple Choice
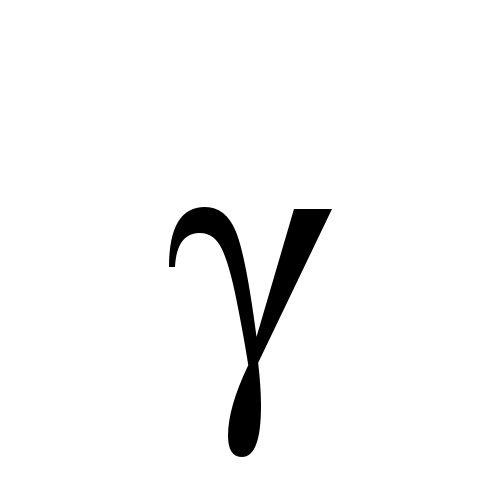
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
184.
Multiple Choice
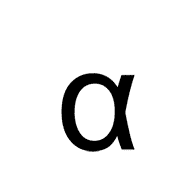
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
185.
Multiple Choice
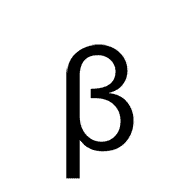
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
186.
Multiple Choice
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
187.
Multiple Choice
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
188.
Multiple Choice
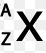
number of neutrons
atomic number
number of electrons
mass number
189.
Multiple Choice

Fission reaction
Fusion reaction
Decomposition reaction
Decay
190.
Multiple Choice

Beta decay
Alpha decay
Nuclear fission
Nuclear fusion
191.
Multiple Choice
nuclear decay
nuclear mass
isotopes
radon
192.
Multiple Choice
electrons
protons
nuclei
neutrons
193.
Multiple Choice
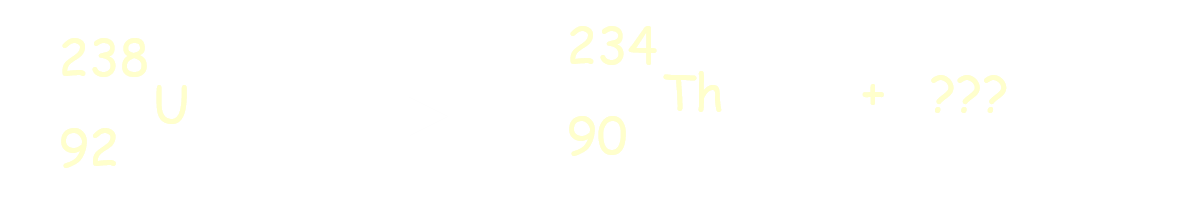
an alpha particle
a beta particle
gamma rays
visible light
194.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
electroscope
beta particle
gamma ray
195.
Multiple Choice
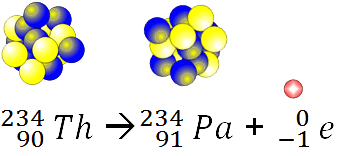
Alpha
beta
gamma
none
196.
Multiple Choice
85209At = ___ + 24He
83205Bi
86209Rn
81207Tl
85208At
197.
Multiple Choice
614C = ___ + -10e
410Be
714N
210He
613C
198.
Multiple Choice
Gamma rays have
no mass
a huge mass
a small mass
an average mass
199.
Multiple Choice

The nucleus is held together by the ___________________________force.
The Strong Nuclear Force
The Weak Nuclear Force
Electromagnetism
Gravity
200.
Multiple Choice
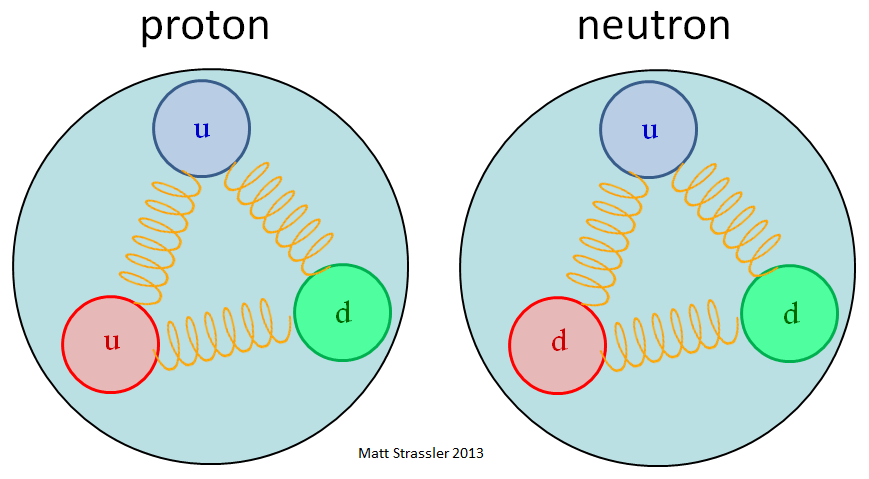
During beta-particle emission, a neutron splits into a____________________.
proton and electron
neutron and electron
neutron and proton
201.
Multiple Choice
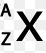
In a correctly written symbol what would be located in the "Z" position?
number of neutrons
atomic number
number of electrons
mass number
202.
Multiple Choice
How is the alpha particle written in a nuclear equation?
42He
24He
0-1e
00γ
203.
Multiple Choice
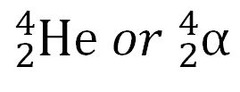
alpha particle
beta particle
neutron
gamma ray
204.
Multiple Choice

3
4
6
10
205.
Multiple Choice
nuclear energy
binding energy
radioacitve energy
electromagnetic energy
206.
Multiple Choice
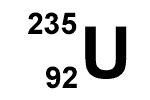
235
92
327
143
207.
Multiple Choice
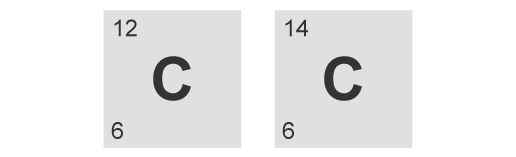
Different atomic numbers
Different number of protons
Different number of neutrons
Different number of electrons
208.
Multiple Choice
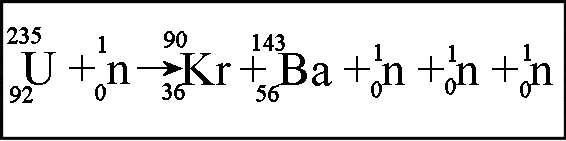
alpha decay
beta decay
fission
fusion
209.
Multiple Choice
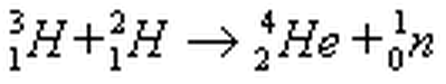
alpha decay
beta decay
fission
fusion
210.
Multiple Choice
18
20
21
41
211.
Multiple Choice
finding radioactive elements that have longer half-lives
finding ways of storing radioactive wastes
finding compounds to cool heated water
finding non-radioactive elements for reactors
212.
Multiple Choice
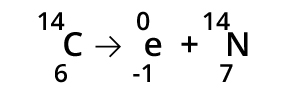
fusion
fission
alpha
beta
213.
Multiple Choice
skin
paper
aluminum
thick lead
214.
Multiple Choice
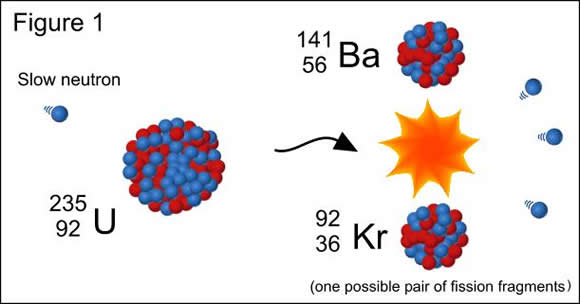
fission
fusion
alpha decay
beta decay
215.
Multiple Choice
the number of neutrons.
the number of electrons.
the mass number.
the average atomic mass.
216.
Multiple Choice
It has too many electrons.
It has an atomic number greater than 83
It has more neutrons than protons
It has more protons than neutrons
217.
Multiple Choice
The atomic number decreases by 4
The atomic number increases by 1
The atomic number decreases by 2.
The atomic number stays the same.
218.
Multiple Choice
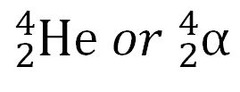
alpha particle
beta particle
neutron
gamma ray
219.
Multiple Choice

3
4
6
10
220.
Multiple Choice
nuclear energy
binding energy
radioacitve energy
electromagnetic energy
221.
Multiple Choice
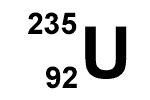
235
92
327
143
222.
Multiple Choice

Different atomic numbers
Different number of protons
Different number of neutrons
Different number of electrons
223.
Multiple Choice
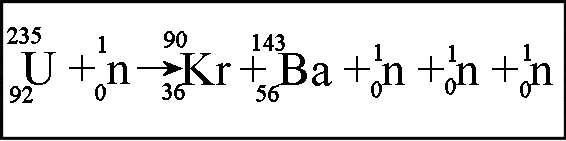
alpha decay
beta decay
fission
fusion
224.
Multiple Choice
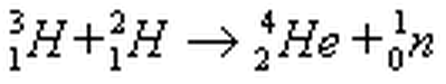
alpha decay
beta decay
fission
fusion
225.
Multiple Choice
18
20
21
41
226.
Multiple Choice
finding radioactive elements that have longer half-lives
finding ways of storing radioactive wastes
finding compounds to cool heated water
finding non-radioactive elements for reactors
227.
Multiple Choice
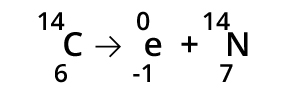
fusion
fission
alpha
beta
228.
Multiple Choice
skin
paper
aluminum
thick lead
229.
Multiple Choice

fission
fusion
alpha decay
beta decay
230.
Multiple Choice
the number of neutrons.
the number of electrons.
the mass number.
the average atomic mass.
231.
Multiple Choice
It has too many electrons.
It has an atomic number greater than 83
It has more neutrons than protons
It has more protons than neutrons
232.
Multiple Choice
The atomic number decreases by 4
The atomic number increases by 1
The atomic number decreases by 2.
The atomic number stays the same.
233.
Multiple Choice
146C --> 0-1e + ________
145B
146C
147N
42He
234.
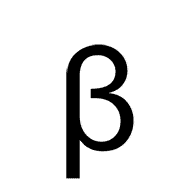
Multiple Choice
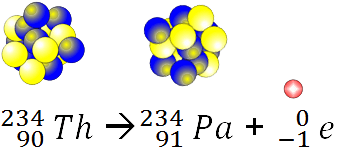
Alpha
beta
gamma
none
235.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
electroscope
beta particle
gamma ray
236.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
gamma rays
beta particles
X rays
237.
Multiple Choice
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
238.
Multiple Choice
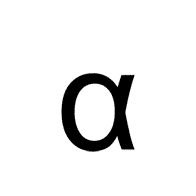
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
239.
Multiple Choice
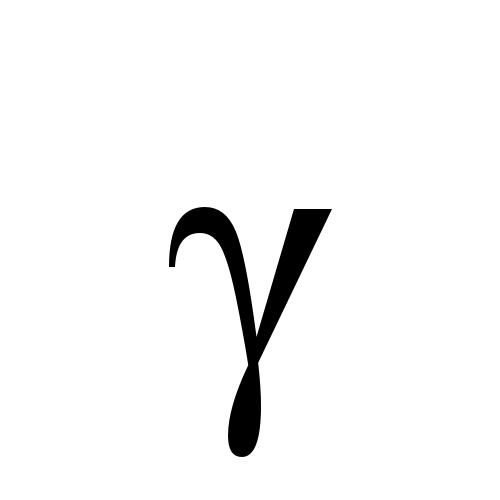
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
240.
Multiple Choice
42He
0-1e
0+1 e
10n
241.
Multiple Choice
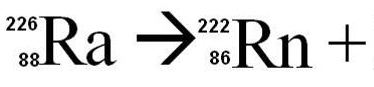
alpha
beta
gamma
none
242.
Multiple Choice
94Be + 11H → _____ + 42He
105B
105Ne
63Li
63C
243.
Multiple Choice
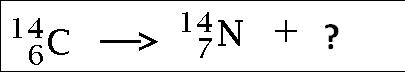
alpha particle
beta particle
gamma particle
neutron
244.
Multiple Choice

alpha particle
beta particle
gamma particle
245.
Multiple Choice
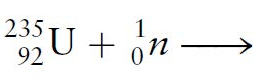
23692U
23693U
23492Np
23493Np
246.
Multiple Choice
Complete the nuclear reaction
85209At = ___ + 24He
83205Bi
86209Rn
81207Tl
85208At
247.
Multiple Choice
Complete the nuclear reaction
2760Co = ___ + -10e
2556Mn
2860Ni
2358V
2759Co
248.
Multiple Choice
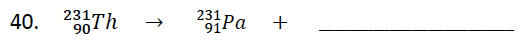
Complete the nuclear reaction
42He
0-1 e
00γ
178O
249.
Multiple Choice
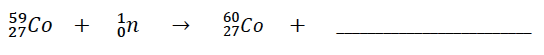
Complete the nuclear reaction
42He
0-1 e
00Y
178O
250.
Multiple Choice
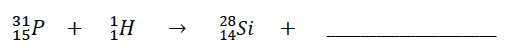
42He
0-1 e
00Y
178O
251.
Multiple Choice
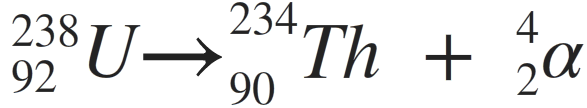
This is the correct equation for U-238 decay.
true
false
252.
Multiple Choice
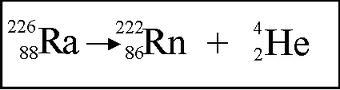
This is the correct equation for the decay of Ra.
true
false
253.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following nuclear emissions is only energy?
Alpha particle
Beta particle
Gamma ray
254.
Multiple Choice
146C --> 0-1e + ________
145B
146C
147N
42He
255.
Multiple Choice
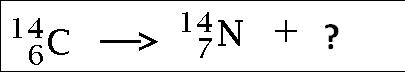
What particle completes this reaction?
Alpha particle
Beta particle
Gamma ray
Neutron
256.
Multiple Choice
Which is the missing isotope that will balance the following nuclear equation?
94Be + 11H → _____ + 42He
105B
105Ne
63Li
63C
257.
Multiple Choice
Balance the following equation:
146C --> 0-1e + ________
145B
146C
147N
42He
258.
Multiple Choice
Which is the symbol for an alpha particle?
42He
0-1e
0+1 e
10n
259.
Multiple Choice
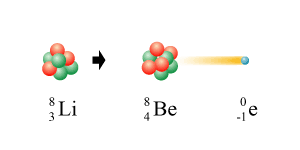
Which type of nuclear decay is this equation?
Alpha decay
Beta decay
Gamma radiation
260.
Multiple Choice
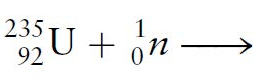
Balance the nuclear equation.
23692U
23693U
23492Np
23493Np
261.
Multiple Choice

This is the symbol for a(n)
Alpha particle
Beta particle
Gamma ray
262.
Multiple Choice
The following is an example of which type of decay?
24395Am → 23993Np + 42He
Alpha decay
Beta decay
Gamma decay
263.
Multiple Choice
The least penetrating form of radiation is
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
264.
Multiple Choice
The most penetrating form of radiation is
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
265.
Multiple Choice
An alpha particle is a(n)
Helium nucleus
Pure energy
Electron
266.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does the symbol -10e represent?
Alpha particle
Beta particle
Gamma ray
267.
Multiple Choice
146C --> 0-1e + ________
145B
146C
147N
42He
268.
Multiple Choice
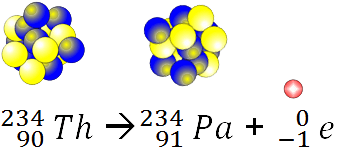
Alpha
beta
gamma
none
269.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
electroscope
beta particle
gamma ray
270.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
gamma rays
beta particles
X rays
271.
Multiple Choice

Alpha
Beta
Gamma
272.
Multiple Choice
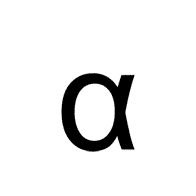
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
273.
Multiple Choice
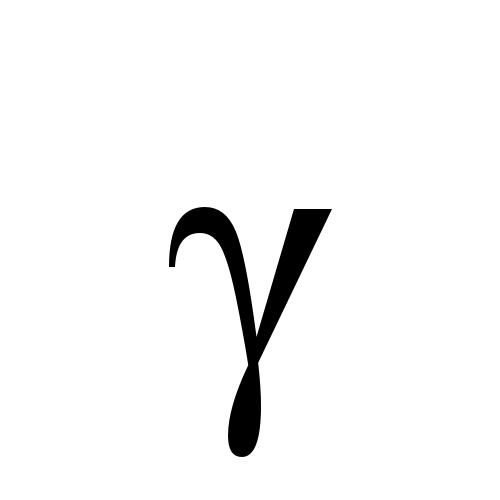
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
274.
Multiple Choice
42He
0-1e
0+1 e
10n
275.
Multiple Choice

alpha
beta
gamma
none
276.
Multiple Choice
94Be + 11H → _____ + 42He
105B
105Ne
63Li
63C
277.
Multiple Choice
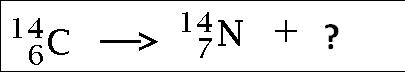
alpha particle
beta particle
gamma particle
neutron
278.
Multiple Choice

alpha particle
beta particle
gamma particle
279.
Multiple Choice
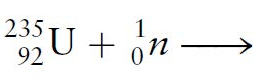
23692U
23693U
23492Np
23493Np
280.
Multiple Choice
Complete the nuclear reaction
85209At = ___ + 24He
83205Bi
86209Rn
81207Tl
85208At
281.
Multiple Choice
Complete the nuclear reaction
2760Co = ___ + -10e
2556Mn
2860Ni
2358V
2759Co
282.
Multiple Choice
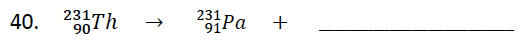
Complete the nuclear reaction
42He
0-1 e
00γ
178O
283.
Multiple Choice
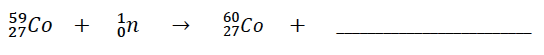
Complete the nuclear reaction
42He
0-1 e
00Y
178O
284.
Multiple Choice
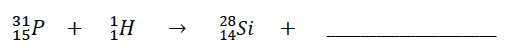
42He
0-1 e
00Y
178O
285.
Multiple Choice
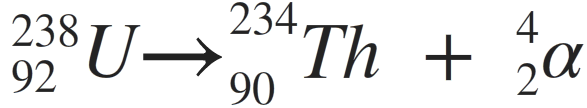
This is the correct equation for U-238 decay.
true
false
286.
Multiple Choice
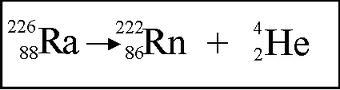
This is the correct equation for the decay of Ra.
true
false
287.
Multiple Choice
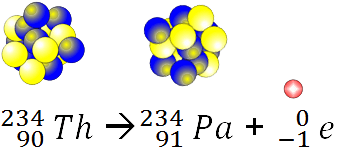
Alpha
beta
gamma
none
288.
Multiple Choice
150
148
146
289.
Multiple Choice
alpha particle
gamma rays
beta particles
X rays
290.
Multiple Choice

alpha
beta
gamma
none
291.
Multiple Choice
20985At = ___ + 42He
20583Bi
20986Rn
20781Tl
20885At
292.
Multiple Choice
22688Ra = ___ + 42He
22286Rn
22689Ac
22484Po
22588Ra
293.
Multiple Choice
6027Co = ___ + 0-1e
5625Mn
6028Ni
5823V
5927Co
294.
Multiple Choice
146C = ___ + 0-1e
104Be
147N
102He
136C
295.
Multiple Choice
24395Am → 23993Np + 42He
alpha decay
beta decay
gamma decay
296.
Multiple Choice
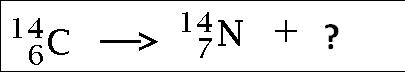
alpha particle
beta particle
gamma particle
neutron
297.
Multiple Choice
Isotopes of an element have a different number of...
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
Mass
298.
Multiple Choice
Potassium-39 has how many neutrons?
19
18
20
21
299.
Multiple Choice
How do you calculate mass number?
Mass x percent
Protons + Electrons
Protons + Neutrons
Neutrons + Protons + Electrons
300.
Multiple Choice
The three main types of nuclear radiation are alpha, beta, and gamma. Which of the following lists these types of radiation from highest penetrating power to lowest penetrating power?
alpha, gamma, beta
beta, alpha, gamma
beta, gamma, alpha
gamma, beta, alpha
301.
Multiple Choice
In the symbol 20682Pb what does 82 stand for?
Mass number
Atomic number
Atomic mass
Number of protons
302.
Multiple Choice
Balance the following nuclear decay equation:
146C --> 0-1e + ________
145B
146C
147N
42He
303.
Multiple Choice
What does the symbol -10e represent
alpha particle
beta particle
gamma ray
the zero element
304.
Multiple Choice
What is the half-life of an isotope if 125 g of a 500 g sample of the isotope remains after 3.0 years?
1.5 yrs
2.5 yrs
3.5 yrs
4.5 yrs
305.
Multiple Choice
Select the correct isotope symbol for an atom with 12 protons and 13 neutrons
Mg-12
Mg-13
Mg-25
Mg-24.305
306.
Multiple Choice
Select the correct isotope symbol for an atom with 76 protons and 114 neutrons
Osmium-114
Osmium-76
Osmium-190
Osmium-190.23
307.
Multiple Choice
1.25mg
1.25g
10g
10mg
308.
Multiple Choice
3.0g
0.25mg
0.3g
0.25g
309.
Multiple Choice
1 half-life
2 half-lives
3 half-lives
4 half-lives
310.
Multiple Choice
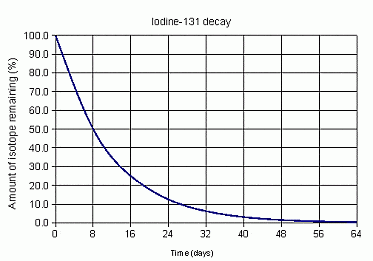
32 days
8 days
16 days
24 days
311.
Multiple Choice
1/2
1/3
1/16
1/8
312.
Multiple Choice
25,000
50,000
12,500
0
313.
Multiple Choice
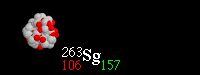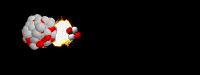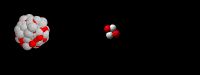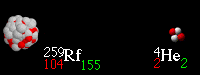
beta decay
alpha decay
314.
Multiple Choice
How many grams are left after 1 half life?
100 grams
25 grams
2 grams
50 grams
315.
Multiple Choice
The % of the parent isotope remaining after 1 Half Life.
50%
25%
12.5%
6.25%
316.
Multiple Choice
The % of the parent isotope remaining after 2 Half Lives.
50%
25%
12.5%
6.25%
317.
Multiple Choice
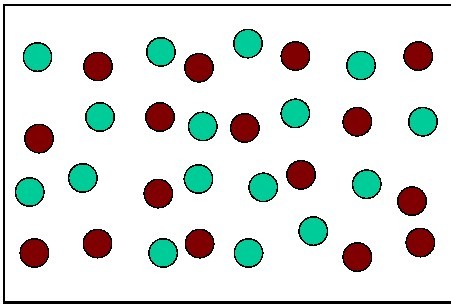
The diagram shows 32 atoms.
16 of the Red are parent isotopes
16 of the Green are daughter isotopes
How many half-lives have occurred?
0
1
2
3
318.
Multiple Choice
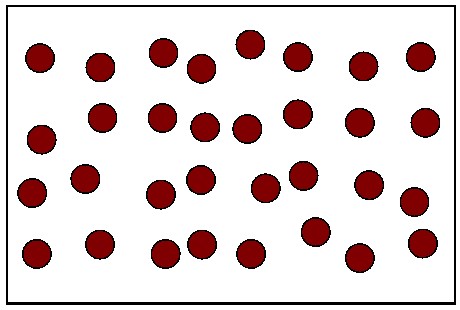
The diagram shows 32 atoms
32 of the Red are the parent isotope
0 of the atoms are daughter isotopes
How many half-lives have occurred?
0
1
2
3
319.
Multiple Choice
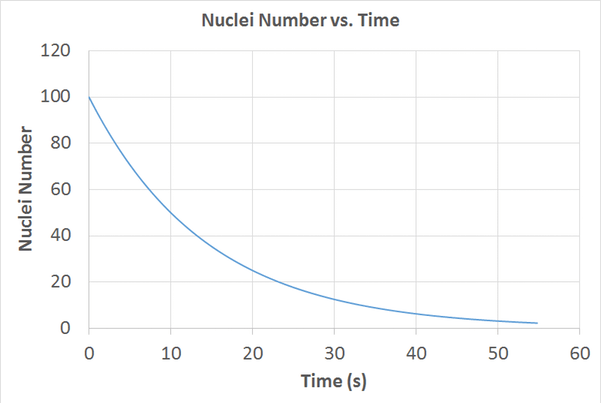
What is the Half life of this isotope?
5 seconds
10 seconds
15 seconds
20 seconds
320.
Multiple Choice
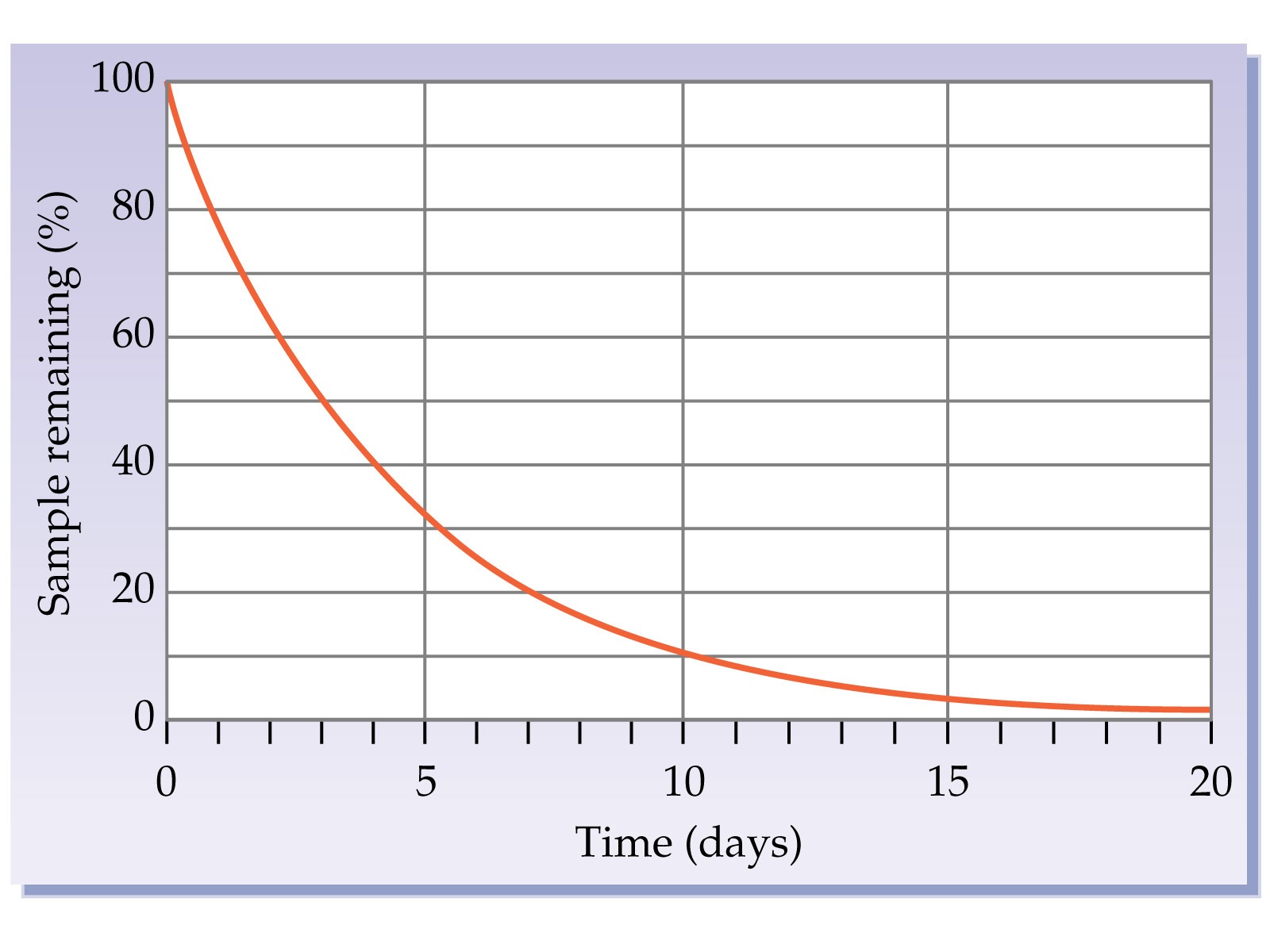
What is the Half Life of this isotope?
3 days
5 days
8 days
10 days
321.
Multiple Choice
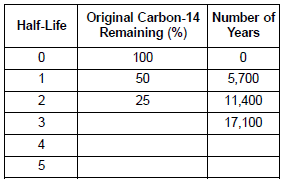
After 22,800 years, approximately what percentage of the original carbon-14 remains?
15%
12.5%
6.25%
3.125%
322.
Multiple Choice
the number of protons
the number of protons and neutrons
the number of neutrons
the number of protons and electrons
323.
Multiple Choice
the number of protons
the number of protons and neutrons
the number of neutrons
the number of protons and electrons
324.
Multiple Choice
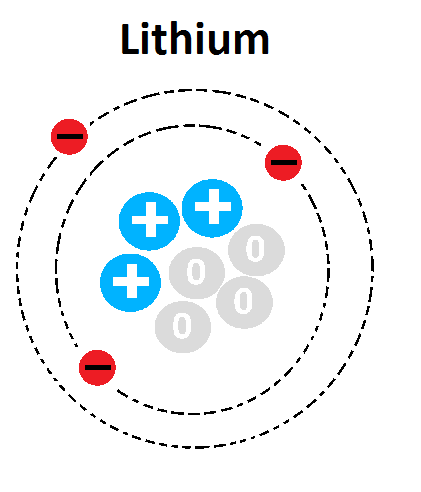
1
3
4
7
325.
Multiple Choice
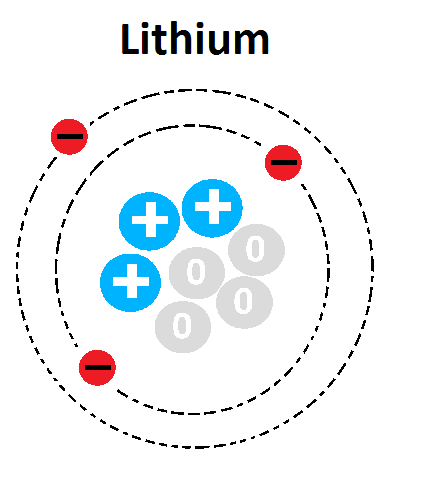
What is the mass number of this atom?
1
3
4
7
326.
Multiple Choice
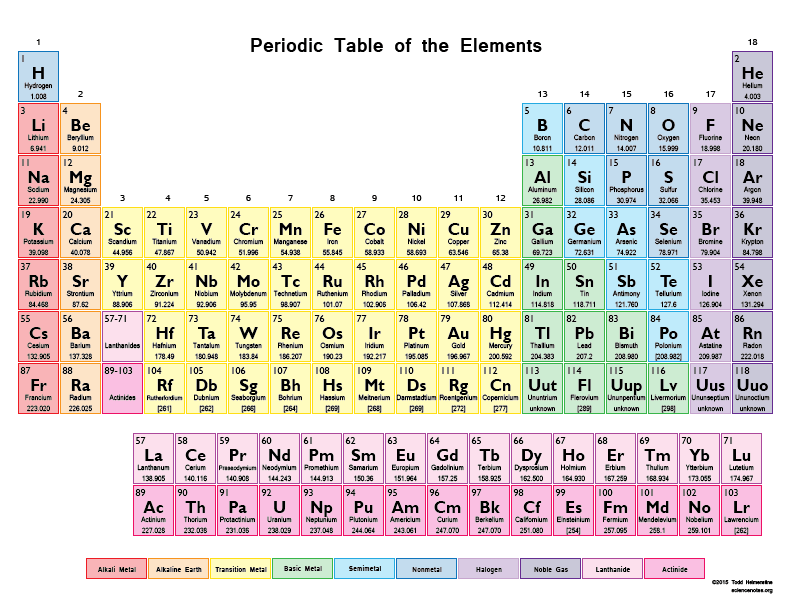
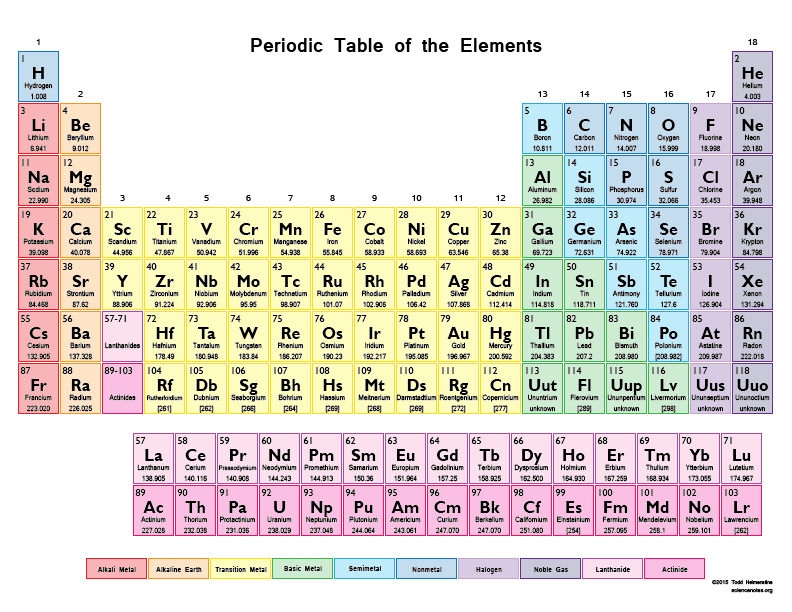
What is the atomic number of Barium, Ba? (enlarge the periodic table)
20
38
56
88
327.
Multiple Choice
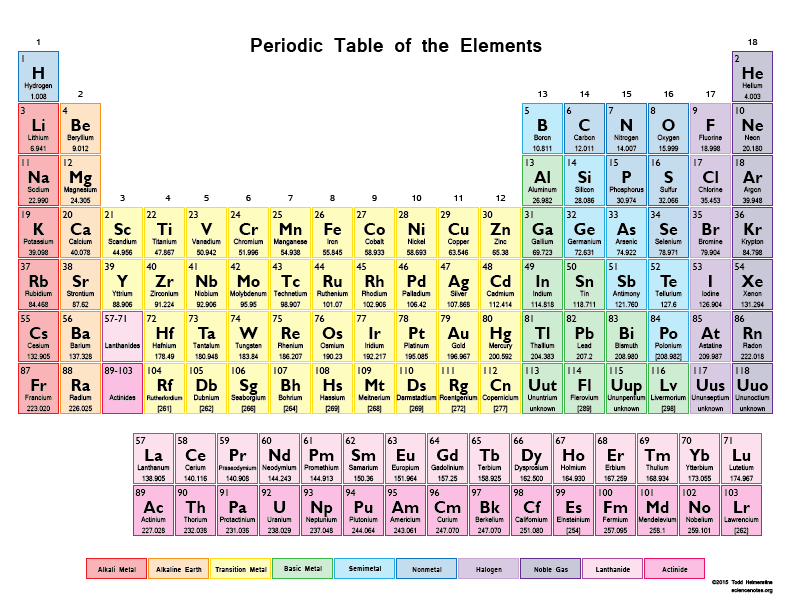
How many protons are in a sodium atom, Na? (tap to enlarge the periodic table)
Sodium has 1 proton.
Sodium has 3 protons.
Sodium has 11 protons
328.
Multiple Choice
Atoms of the same element which have a different number of neutrons are called _________________.
ions
isotopes
quarks
molecules
329.
Multiple Choice
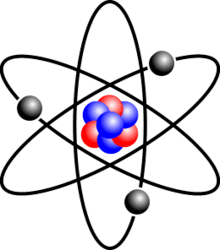
Which subatomic particle has a negative charge in the atom?
proton
neutron
electron
quark
330.
Multiple Choice
How many neutrons does C-14 contain? (tap to enlarge the image)
6
7
14
8
331.
Multiple Choice
How many neutrons does an atom of the isotope Neon-22 have? (tap to enlarge the image)
12
10
22
20
332.
Multiple Choice
How many electrons are in an atom with an atomic number of 50?
5
8
50
2
333.
Multiple Choice
ALL atoms of the same element have:
same number of proton
same number of nucleon
different number of neutron
different number of electron
334.
Multiple Choice

neutrons & mass number
atomic number and neutrons
atomic number and electrons
protons, atomic number, and mass number
335.
Multiple Choice
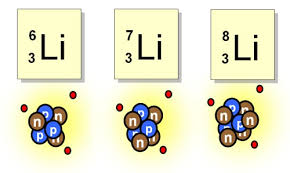
Li-6
Li-7
Li-8
they have the same # of neutrons
336.
Multiple Choice
protons, electrons, and atomic mass
protons, electrons, and atomic number
neutrons and electrons
neutrons and atomic mass
337.
Multiple Choice
6
7
14
8
338.
Multiple Choice
I and II
III and IV
I and IV
I and III
339.
Multiple Choice
53
36
89
125
340.
Multiple Choice
204
206
207
208
341.
Multiple Choice

14
7
15
18
342.
Multiple Choice

True
False
343.
Multiple Choice
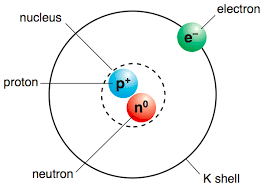
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons
Protons only
Protons and Electrons
Protons and Neutrons
344.
Multiple Choice
the atomic number
the number of neutrons
the energy levels
the periodic table groups
345.
Fill in the Blank
If an atom has 12 neutrons and 11 protons, what is its atomic mass?
346.
Multiple Choice

8
3
4
5
347.
Multiple Choice

48
22
26
70
348.
Multiple Choice
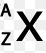
number of neutrons
atomic number
number of electrons
mass number
349.
Multiple Choice
2 amu
3 amu
4 amu
5 amu
350.
Multiple Choice
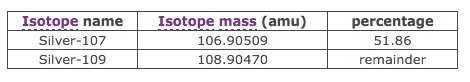
106.38649amu
111.91896amu
107.8677amu
121
351.
Multiple Choice
9.012, Beryllium
12.011, Carbon
6.941, Lithium
10.812, Boron
352.
Multiple Choice
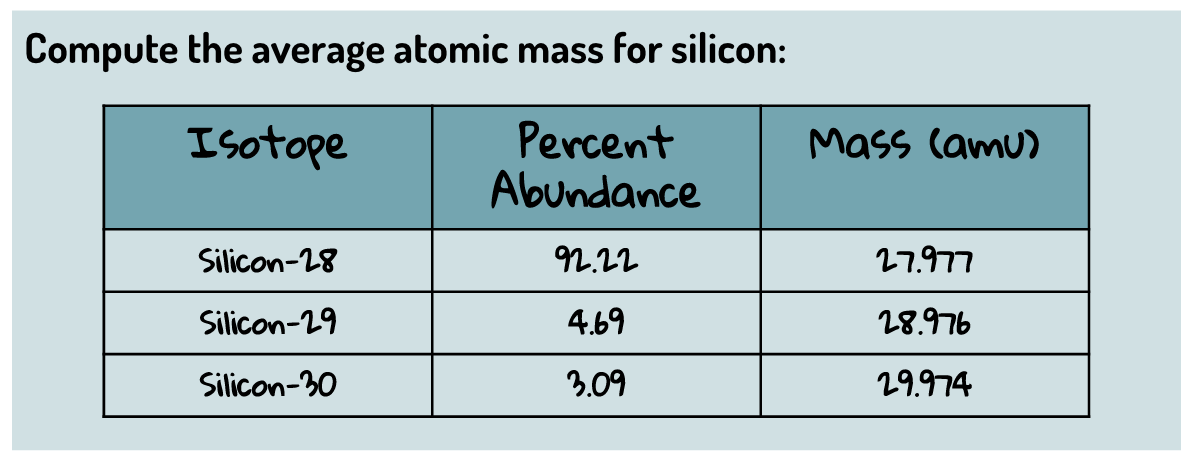
27.977
28.09
28.976
The average mass cannot be determined from provided information.
353.
Multiple Choice
16
8
15.999
0
354.
Multiple Choice

8
3
4
5
355.
Multiple Choice
6
7
14
8
356.
Multiple Choice
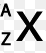
number of neutrons
atomic number
number of electrons
mass number
357.
Multiple Choice
protons, electrons, and atomic mass
protons, electrons, and atomic number
neutrons and electrons
neutrons and atomic mass
358.
Multiple Choice

neutrons & mass number
atomic number and neutrons
atomic number and electrons
protons, atomic number, and mass number
359.
Multiple Choice
protons and neutrons are the same
protons and electrons are the same
neutrons and electrons are the same
neutrons balance the protons and electrons
360.
Multiple Choice
Q.Isotopes must have the same number of protons but different numbers of ________
electron rings
charges
neutrons
electrons
361.
Multiple Choice
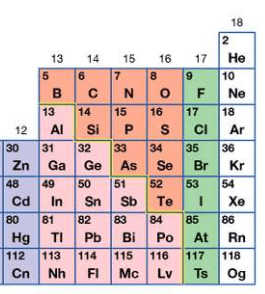
How many neutrons are in an atom of Nitrogen-16?
9
7
16
20
362.
Multiple Choice
Which statement is true?
The galaxies are moving toward us.
The galaxies are moving away from us.
The universe remains static or unchanged in motion.
None of the above
363.
Multiple Choice
Which elements are most
abundant in the visible
universe?
Hydrogen and Carbon
Carbon and Helium
Hydrogen and Oxygen
Hydrogen and Helium
364.
Multiple Choice
Most scientists believe the Big Bang Theory explains which of the following questions?
How our planets and moons formed
How our universe began
How the sun turns hydrogen into helium
How fast light travels through space
365.
Multiple Choice
Which description is considered most accurate regarding what actually happened during the Big Bang?
Two galaxies collided causing an immense explosion as stars crashed into one another
All of what would become the universe was concentrated in a single small point, or singularity, which rapidly expanded into what is now stars, planets, galaxies, matter, and energy.
All matter emerged from a massive black hole at the center of the universe.
Parts of the sun were ripped off by massive internal explosions and were thrown into space where they cooled to become other things, like plants, comets, and other galaxies.
366.
Multiple Choice
the big bang.
humans came along.
stars began doing fusion.
the redshift was discovered.
367.
Multiple Choice
1/2
1/3
1/16
1/8
368.
Multiple Choice
1.25mg
1.25g
10g
10mg
369.
Multiple Choice
3.0g
0.25mg
0.3g
0.25g
370.
Multiple Choice
1 half-life
2 half-lives
3 half-lives
4 half-lives
371.
Multiple Choice

32 days
8 days
16 days
24 days
372.
Multiple Choice
The % of the parent isotope remaining after 1 Half Life.
50%
25%
12.5%
6.25%
373.
Multiple Choice
The % of the parent isotope remaining after 2 Half Lives.
50%
25%
12.5%
6.25%
374.
Multiple Choice

The diagram shows 32 atoms
32 of the Red are the parent isotope
0 of the atoms are daughter isotopes
How many half-lives have occurred?
0
1
2
3
375.
Multiple Choice

The diagram shows 32 atoms.
16 of the Red are parent isotopes
16 of the Green are daughter isotopes
How many half-lives have occurred?
0
1
2
3
376.
Multiple Choice

What is the Half life of this isotope?
5 seconds
10 seconds
15 seconds
20 seconds
377.
Multiple Choice
energy
jello
protons
neutrons
378.
Multiple Choice
0.25g
2.5g
25g
80g
379.
Multiple Choice
1.25mg
1.25g
10g
10mg
380.
Multiple Choice
3.0g
0.25mg
0.3g
0.25g
381.
Multiple Choice
1 half-life
2 half-lives
3 half-lives
4 half-lives
382.
Multiple Choice
100.0g
50.0g
12.5g
8.5g
383.
Multiple Choice
1/2
1/3
1/16
1/8
384.
Multiple Choice
312.5%
31.25%
.3125%
3.125%
385.
Multiple Choice
The amount of time it takes for some of the nuclei in a sample of the isotope to decay
The amount of time it takes for half the electrons in a sample of the isotope to decay
The amount of time it takes for half the nuclei in a sample of the isotope to decay
the amount of time it takes to double the nuclei in a sample of the isotope to decay
386.
Multiple Choice
9.7x106 atoms remain
97.0x106 atoms remain
0.97x106 atoms remain
9.7x105 atoms remain
387.
Multiple Choice
0.334 seconds
3.34 seconds
1.77 seconds
13.4 seconds
388.
Multiple Choice
Fission
Fusion
389.
Multiple Choice
It is easy to implement.
It produces less energy than nuclear fission.
It produces more energy than nuclear fission.
It has the ability to occur easily in everyday life.
390.
Multiple Choice
fusion
fission
decay
gamma radiation
391.
Multiple Choice
fission
fusion
392.
Multiple Choice
fusion
fission
half-life
gamma radiation
393.
Multiple Choice
Fusion
Half-life
Fission
Fusion or fission
394.
Multiple Choice

Fission reaction
Fusion reaction
Decomposition reaction
Decay
395.
Multiple Choice
Underwater
All around us
In the radioactive waste
On the sun
396.
Multiple Choice
Helium and Hydrogen atoms
Hydrogen atoms
Hydrogen and Lithium atoms
Hydrogen and Carbon atoms
397.
Multiple Choice
Nuclear power plants
Radio active decay
Atomic Bomb
On the surface of the sun
398.
Multiple Choice
heavy ions fuse together
very light nuclei fuse together
uranium splits into two fragments
uranium emits a neutron
399.
Multiple Choice
fission
fusion
radioactive decay
K-capture
400.
Multiple Choice
it is a fossil fuel
it leaves behind radioactive waste
it emits large amounts of pollution into the atmosphere
there are no disadvantages
401.
Multiple Choice
Uranium releases electrons to create electricity
When a nuclear fission reaction occurs, the electrons emitted can strike other nuclei in the sample, and cause them to split
When a nuclear fission reaction occurs, the neutrons emitted can strike other nuclei in the sample, and cause them to split
Protons and neutrons change to electrons because the nuclei are so big
402.
Multiple Choice
The ability to absorb energy
The ability to release tremendous amounts of energy
The ability to produce more energy than nuclear fusion
There are no beneficial aspects of nuclear fission
403.
Multiple Choice
true
false
404.
Multiple Choice
Fission
Fusion
Radioactive Decay
405.
Multiple Choice
many steps or mini-reactions in the process
long chains of elements form in a row
406.
Multiple Choice

Yes
No
Just our sun
Only large stars
407.
Multiple Choice

To win the Nobel prize
To make energy for people to use
To destroy the world
To know more about stars
408.
Multiple Choice
fission
fusion
409.
Multiple Choice
fusion
fission
half-life
gamma radiation
410.
Multiple Choice
Fusion
Half-life
Fission
Fusion or fission
411.
Multiple Choice
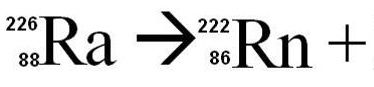
alpha
beta
gamma
none
412.
Multiple Choice
+2
0
+4
-1
413.
Multiple Choice
+1
-1
0
+2
414.
Multiple Choice
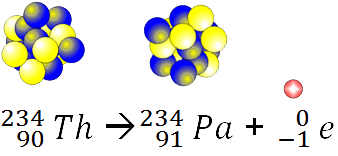
Alpha decay
beta decay
gamma decay
positron emission
415.
Multiple Choice

Fission reaction
Fusion reaction
Decomposition reaction
Decay
416.
Multiple Choice
Underwater
All around us
In the radioactive waste
On the sun
417.
Multiple Choice
Helium and Hydrogen atoms
Hydrogen atoms
Hydrogen and Lithium atoms
Hydrogen and Carbon atoms
418.
Multiple Choice
Nuclear power plants
Radio active decay
Atomic Bomb
On the surface of the sun
419.
Multiple Choice
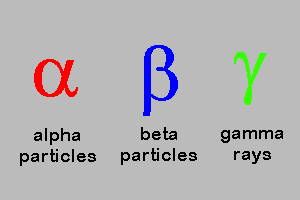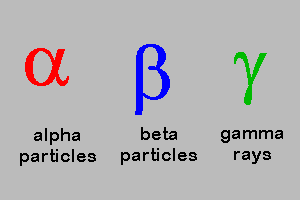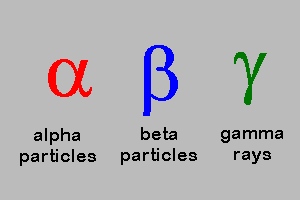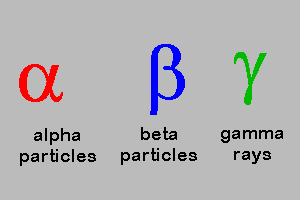
Alpha , Beta, Gamma
Beta , Gamma , Alpha
Gamma, Beta, Alpha
Gamma, Alpha, Beta
420.
Multiple Choice
Scars
Less risk of cancer
Skin burns
Nausea
421.
Multiple Choice
carbon
cobalt
uranium
titanium
422.
Multiple Choice
Little Girl,Dragon breath
Little boy,Fat man
Big Women,Tiger
Little boy,Fat Father
423.
Multiple Choice
True
False
424.
Multiple Choice
Fission
Fusion
425.
Multiple Choice
It is easy to implement.
It produces less energy than nuclear fission.
It produces more energy than nuclear fission.
It has the ability to occur easily in everyday life.
426.
Multiple Choice
fusion
fission
decay
gamma radiation
427.
Multiple Choice
fission
fusion
428.
Multiple Choice
fusion
fission
half-life
gamma radiation
429.
Multiple Choice
Fusion
Half-life
Fission
Fusion or fission
430.
Multiple Choice
Underwater
All around us
In the radioactive waste
On the sun
431.
Multiple Choice
Nuclear power plants
Radio active decay
Atomic Bomb
On the surface of the sun
432.
Multiple Choice
fission
fusion
radioactive decay
K-capture
433.
Multiple Choice
true
false
434.
Multiple Choice

To win the Nobel prize
To make energy for people to use
To destroy the world
To know more about stars
435.
Multiple Choice
The type of radioactive particle that can be stopped by a sheet of paper is the ____.
alpha particle
uranium
beta particle
gamma ray
436.
Multiple Choice
The most penetrating type of radiation is the _______.
beta particle
gamma ray
uranium
alpha particle
437.
Multiple Choice
One type of radioactive device that indicates the intensity of radiation with a clicking sound that increases in frequency as more radiation is present is a(n) ____.
bubble chamber
cloud chamber
electroscope
Geiger counter
438.
Multiple Choice
Can be stopped by aluminum foil; has no mass and negative charge.
beta particle
alpha partcle
gamma ray
half-life
439.
Multiple Choice
Powerful radiation that can cause biological damage.
beta particle
alpha particle
gamma ray
carbon dating
440.
Multiple Choice
Using the decay of an isotope to find the age of a once-living object [fossil].
carbon dating
alpha particle
gamma ray
half-life
441.
Multiple Choice
A helium nucleus; low energy.
gamma ray
carbon dating
half-life
alpha particle
442.
Multiple Choice
Time necessary for 50% of a radioactive sample to decay.
carbon dating
half-life
alpha particle
gamma ray
443.
Multiple Choice
Who was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize for her work with radioactivity?
Lise Meitner
Marie Curie
Jane Goodall
Judy Blume

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Balancing Nuclear Reactions
•
9th - 12th Grade

Nuclear Fusion and Fission
•
10th Grade - University

Nuclear Reactions
•
10th Grade

Nuclear Power Plants
•
9th - 12th Grade

Nuclear Equations
•
10th - 12th Grade

Isotopes & Radioactivity
•
9th - 12th Grade

Nuclear Review
•
9th - 12th Grade

Radioactivity and Atomic Structure
•
11th Grade