
Gravity and Orbits
Assessment
•
Erica Fordiani
•
Science
•
6th - 8th Grade
•
116 plays
•
Hard
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
68 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
Two factors effecting the strength of gravity between 2 objects are...
weight and mass
distance and weight
mass and matter
mass and distance
2.
Multiple Choice
A(n) _____ is the curved path of an object around a point/object in space.
orbit
rotation
revolution
phase
3.
Multiple Choice
What prevents planets from drifting off into space and keeps it in the planets in our Solar System?
Gravity
Weight
Friction
Forward Motion
4.
Multiple Choice
What prevents planets from pulled into and crash into the Sun?
Gravity
Weight
Friction
Inertia (Forward Motion)
5.
Multiple Select
Which of the following is required for planets to stay in orbit around the Sun? (choose all that apply)
Gravity
Weight
Friction
Inertia (Forward Motion)
6.
Multiple Choice
Force
Motion
Weight
Gravity
7.
Multiple Choice

they are spherical, they have at least one moon and they have gravity
Orbit the sun, massive enough that their gravity controls all objects in the area and they are spherical
they have at least one moon, they are spherical and they were made by accretion
they are spherical, they orbit the sun and they have living organisms
8.
Multiple Choice
What is true about the distance between a planet and the sun and the planet’s revolution around the Sun?
The closer the planet is to the sun, the slower it orbits.
The farther the planet is to the sun, the faster it orbits.
The farther the planet is to the sun, the brighter the sun is.
The closer the planet is to the sun, the faster it orbits.
9.
Multiple Choice
A planet with a large orbit has...
a short day
a long day
a long year
a short year
10.
Multiple Choice
A planet with a short orbit has...
a short day
a long day
a long year
a short year
11.
Multiple Choice
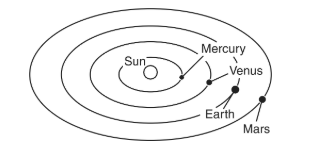
Which planet will take the least amount of time to revolve around the Sun?
Mercury
Venus
Earth
Mars
12.
Multiple Choice

Without gravity, the stars, planets and all objects in the universe would _______.
continue to orbit each other
move in a random direction
move in a straight line
stop moving
13.
Multiple Choice
What would happen to Earth if its forward motion stopped?
Earth would continue to orbit in our Solar System normally.
Earth would sit motionless and not moving.
Earth would drift off in space because nothing would hold it in the Solar System.
Earth would move toward the Sun and eventually crash into it.
14.
Multiple Choice
What would happen to Earth if the Sun's gravity dissappeared?
Earth would continue to orbit in our Solar System normally.
Earth would sit motionless and not moving.
Earth would drift off in space because nothing would hold it in the Solar System.
Earth would move toward the Sun and eventually crash into it.
15.
Multiple Choice
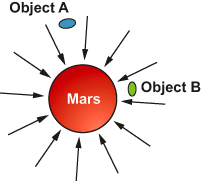
Here is a model of the gravitational force of Mars. Objects A and B have the same mass but are different distances from Mars. Which statement explains how the gravitational force affects the two objects?
Object A and B will be affected equally by the gravitational force.
Object B will be more affected by the gravitational force because it is closer to Mars than Object A.
Object A will be more affected by the gravitational force because it is farther from Mars than Object B.
16.
Multiple Choice
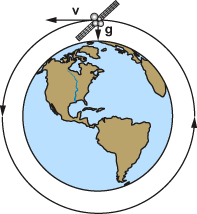
The satellite is orbiting Earth in the direction shown and is pulled toward Earth by gravity. What would happen if Earth's gravity suddenly disappeared?
The satellite would fall to Earth.
The satellite would stop moving.
The satellite would continue to orbit Earth.
The satellite would move into space in a straight line.
17.
Multiple Choice
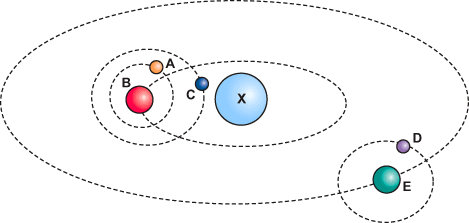
The dotted lines in the picture show orbital paths of objects. Which statement is true about all of the orbits shown?
All objects move in circular orbits.
The size of an object determines the size of its orbit.
The force of gravity is what holds each object in its orbit.
The size of both an object and the object it orbits are equal.
18.
Multiple Choice
Observe the path of Voyager 2 satellite . Why did the route of Voyager 2 change, without firing its thrusters, as it passed Jupiter?
Gravitational force between Jupiter and Voyager 2 pulled it into a new route.
Solar winds pushed Voyager 2 into a new path.
Jupiter blocked the sun’s gravitational pull on Voyager 2.
The gravity of Jupiter caused Voyager 2 to become its satellite.
Answer explanation
Large planets have enough mass to exert a significant pull on an object traveling near them. Scientists used the gravitational forces of the large planets to give Voyager a “boost” so that it moved faster.
19.
Multiple Select
Which of the following did engineers need to know to plan Voyager 2’s path through the solar system? Choose *ALL* that apply.
the positions of the planets
the masses of the planets
the mass of Voyager 2
Newton's laws of motion and the law of universal gravitation
Answer explanation
Designers needed to know the masses of all the planets, the mass of the spacecraft, and where the planets would be as Voyager 2 traveled. Additional knowledge of Newton’s laws of motion and the law of universal gravitation were needed to predict how the masses of planets would affect the satellite’s motion.
20.
Multiple Choice
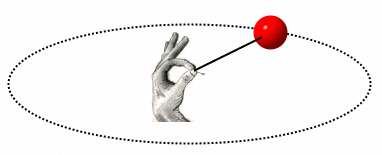
the longer the string means the larger the planet
the longer the string, the longer the orbit time of a planet
the shorter the string, the longer the orbit time of the planet
the shorter the string, the smaller the planet
21.
Multiple Choice
Do planets affect the sun? Why?
No. The Sun pulls on the planets and keep them in orbit.
Yes. Sun pulls on planets; planets pull on Sun.
22.
Multiple Choice
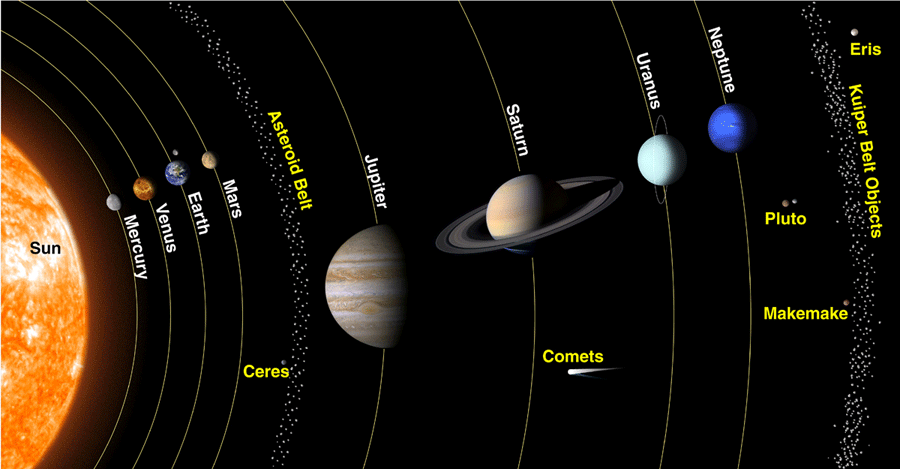
Mercury
Mars
Jupiter
Neptune
23.
Multiple Choice

Mercury
Mars
Jupiter
Neptune
24.
Multiple Select
Which variables affect gravity?
mass
speed
distance
volume
weight
25.
Multiple Select
Which of the following is required for planets to stay in orbit around the Sun? (choose all that apply)
Gravity
Weight
Friction
Inertia (Forward Motion)
26.
Multiple Choice
brighter objects tend to orbit duller ones
duller objects tend to orbit brighter ones
lighter objects tend to orbit heavier ones
heavier objects tend to orbit lighter ones
27.
Multiple Choice

it's moving too slowly around it
it's moving fast enough around it
it's too heavy too pull in
it's too far away
28.
Multiple Choice
circular
elliptical
spiral
conical
29.
Multiple Choice
The early solar system was made up of mostly what?
hydrogen, helium and dust
hydrogen, oxygen and dust
hydrogen, iron and dust
carbon, hydrogen and dust
30.
Multiple Choice
Gravitational forces are always
Attractive
Pushing
repulsive
objects
31.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the formation of the solar system?
The Sun ejected rocky material which formed the planets due to magnetic attraction forces.
A rotating disk of gas and dust was drawn together by the force of gravity.
One very large planetary body broke apart into several smaller planets.
Several stars of different masses cooled and formed the planets and the Sun.
32.
Multiple Choice
Why do some planets have moons in our solar system?
They are close to the sun
They have enough gravity to hold a moon in orbit
They are special
All planets have moons
33.
Multiple Choice
What force played a major role in the formation of the solar system?
Magnetism
Push
Pull
Gravity
34.
Multiple Choice
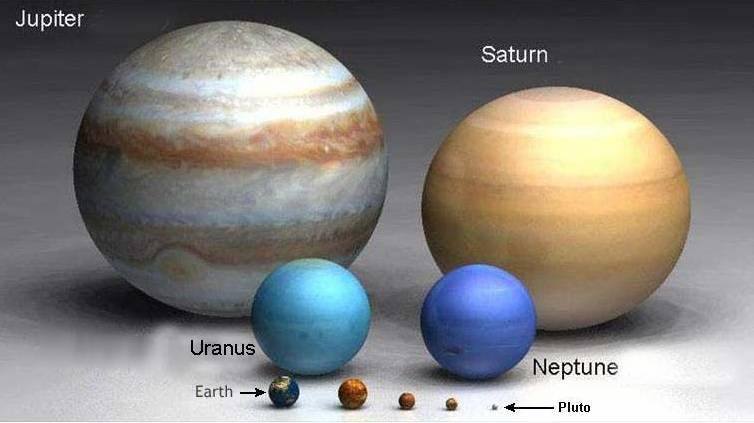
Which planet would have the largest gravitational pull?
Venus
Mars
Jupiter
Neptune
35.
Multiple Choice
How does changing the distance between objects affect the force of gravity?
Decreasing distance increases gravity
Increasing distance increases gravity
Mr. Deem knows, but he's not telling
Distance does not affect gravity
36.
Multiple Choice
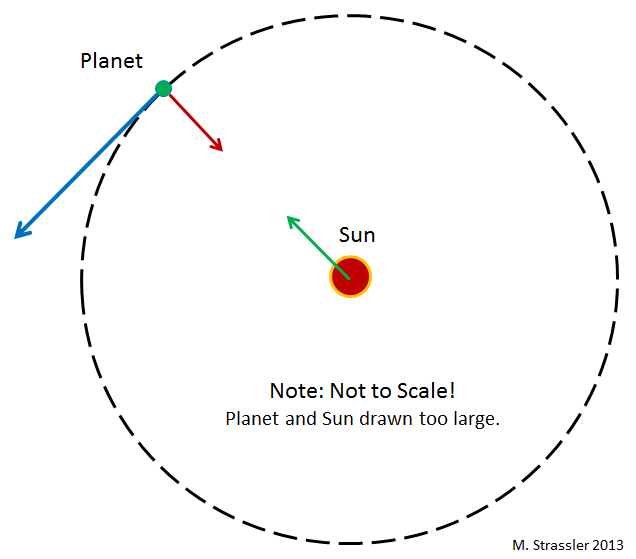
Match the term: The tendency of an object to resist a change in its motion
acceleration
inertia
mass
frame of reference
37.
Multiple Choice

Suppose that this person left go of the chain. As soon as he releases the chain the balls inertia would....
make the ball immediately stop and fall straight to the ground.
keep the ball moving in a circle around him.
result in the ball flying off in a straight line away from the person.
either a, b, or c -- depending on whether the person continues to push it
38.
Multiple Choice
mass and distance
inertia and gravity
eccentricity and velocity
force and speed
39.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the formation of the solar system?
The sun ejected rocky material which later went on to form the planets.
A rotating disk of gas and dust was drawn together by the force of gravity.
One very large planetary body broke apart into several smaller planets.
Several stars of different masses cooled and formed the planets and the sun.
40.
Multiple Choice

When Sean was riding his bike and braked suddenly, he kept moving forward due to
gravity
friction
inertia
weight
41.
Multiple Choice

coffee
motion
inertia
gravity
42.
Multiple Choice

Which explains why the tablecloth trick works?
The dishes are stuck in place due to air resistance.
The tablecloth is an ilusion.
The dishes have inertia, and therefore stay on the table.
magic
43.
Multiple Choice
What is the relationship between heavy objects and inertia?
Only heavy objects have inertia.
Heavy objects have more inertia.
Heavy objects have less inertia.
Heavy objects have no inertia.
44.
Multiple Choice
at rest
moving
in one spot
inertia
45.
Multiple Choice
rest
a constant speed
school
inertia
46.
Multiple Choice
speed
mass
temperature
friction
47.
Multiple Choice
The amount of matter in an object is called ______________.
displacement
mass
friction
friction
48.
Multiple Choice
gravity and orbit
gravity and inertia
gravity and mass
gravity and weight
49.
Multiple Choice

What two forces affect gravity?
mass and inertia
mass and distance
mass and force
mass and weight
50.
Multiple Choice
As distance between objects increases, the pull of gravity...
increases
decreases
Stays the same
51.
Multiple Choice
Pounds
weight
Force
Mass
52.
Multiple Select

You travel to the Moon. Which of the following is true? (choose ALL that are true)
Your mass stays the same
Your weight stays the same
Your mass is different
Your weight is different
53.
Multiple Choice
the sun has more mass
the sun is a star
the Earth is heavier
the sun is in the middle of the milky way
54.
Multiple Choice
What is weight?
how much fat is on your body
how strong you are
how strongly your body is being pulled down by gravity
when you have to stand in line
55.
Multiple Choice
Inertia tells us that we need ____________ to get an object moving or to make it stop.
a force
gravity
friction
strength
56.
Multiple Choice
What would happen to Earth if there were no inertia?
Earth would crash into the sun
Earth would fly out to space
Earth would collapse
Earth would orbit the moon
57.
Multiple Choice
accelerating
free-falling
orbiting
attaining escape velocity
58.
Multiple Choice
9 minutes
90 minutes
9 hours
90 hours
59.
Multiple Choice
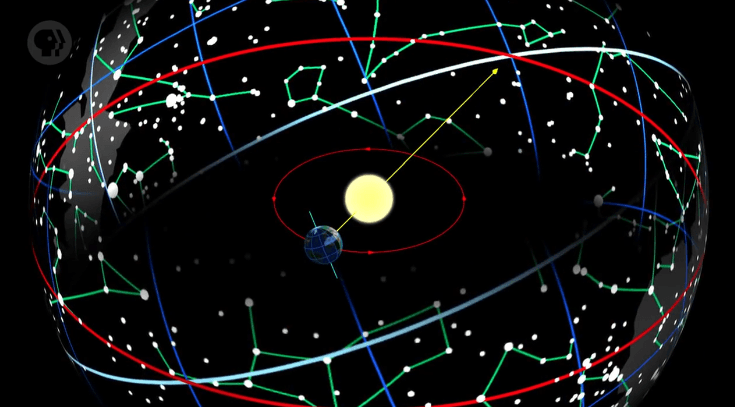
circular
ellipses
parabolas
hyperbolas
60.
Multiple Choice
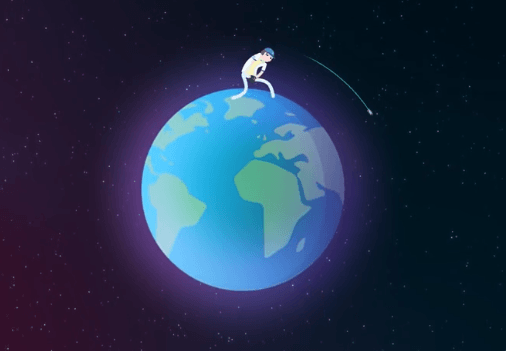
In order to break free of a planet's gravity, an object must be moving at _____ .
escape velocity
getaway acceleration
a break-away pace
a liberation altitude
61.
Multiple Choice
about 11 kilometers per second
about 110 kilometers per second
about 11 kilometers per hour
about 110 kilometers per hour
62.
Multiple Choice
about 0.9% as strong
about 9% as strong
about 49% as strong
about 90% as strong
63.
Multiple Choice
microgravity
microweight
microdensity
micromass
64.
Multiple Choice

microgravity
weight
density
pressure
65.
Multiple Choice

in orbit
in constant motion
in uniform motion
massless
66.
Multiple Choice
Velocity has a direction
Speed uses Distance /Time
Velocity doesn't include time
Velocity doesn't include distance
67.
Multiple Choice
how far you go
how much distance is covered over a period of time
how fast you accelerate
the change in the location of a object
68.
Multiple Choice
How is revolution related to an orbit?
Revolution is the same as rotation.
It revolves around an object.
An orbit is the path that an object takes during a revolution.

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

The Sun
•
8th Grade

Solar System
•
9th Grade

Solar System
•
4th - 6th Grade

Solar System
•
6th - 8th Grade

Tools for Space Exploration
•
4th Grade

Space Technology
•
8th Grade

Sun, Earth, and Moon
•
5th Grade

Gravity in Space and Objects in the Solar System
•
8th Grade