Statistics and Probability
Assessment
•
Leonafe Pablo
•
Mathematics
•
11th Grade
•
1K plays
•
Hard
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
20 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
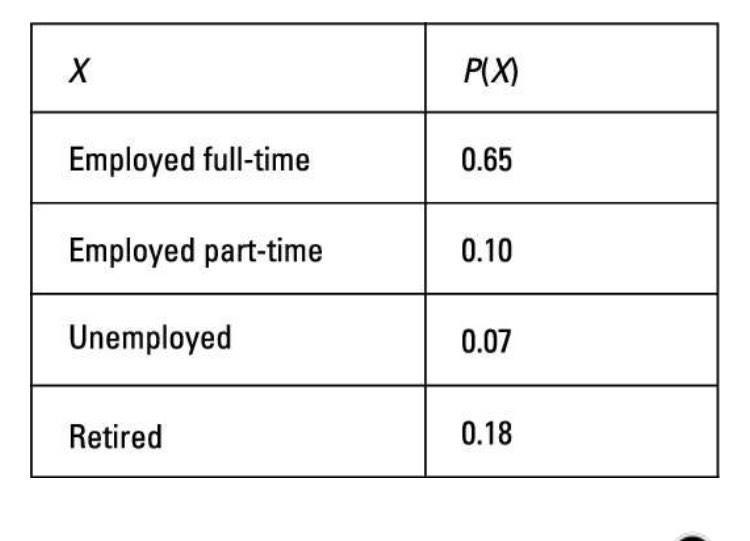
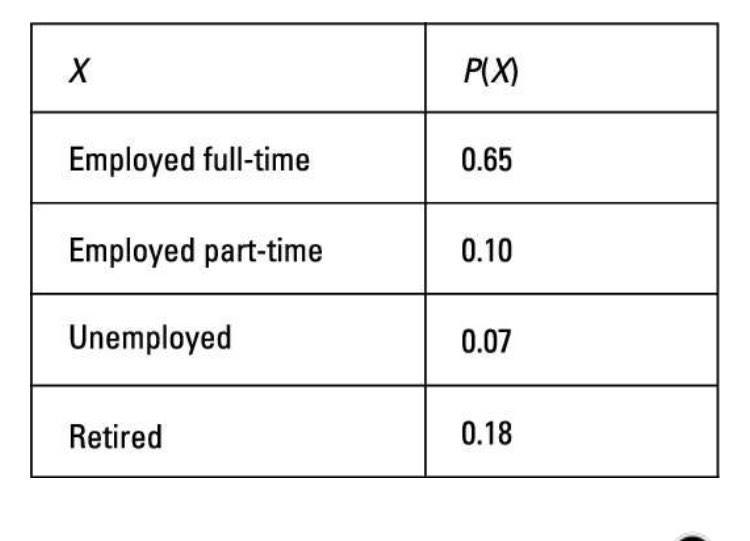
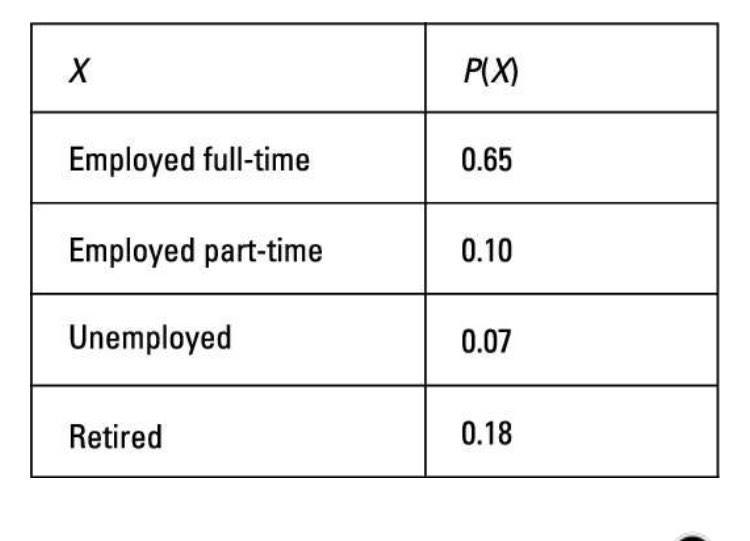
It is a numerical quantity that is assigned to the outcome of an experiment.
Statistics
Probability
Random Variable
Distribution
2.
Multiple Choice
It is the set of all possible outcomes in an experiment.
Random Variable
Sample Space
Mean
Data
3.
Multiple Choice
Two coins are tossed in an experiment. Which of the following list is the sample space?
S= {HH, HT, TH, TT}
S= {HH, TT}
S= { HT, TH, TT}
S= {HH, HT, TT}
4.
Multiple Choice
Supposed two coins are tossed consecutively and we are interested in the number of heads that will come out. Determine the values of the random variable H (number of heads).
0,2,3,4
0,1,2,3
0,1,2
0,1,2,3,4
5.
Fill in the Blank
Nico label an x- axis with points earned and the corresponding y - axis with the number of players. He plot one against the other and he obtain a bar graph called a what?
6.
Fill in the Blank
If you had no idea what the answer to this four option multiple choice was and took a wild guess, what is the probability that you are correct?

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Factoring
•
8th Grade

Introduction to Statistics
•
7th - 10th Grade

Statistics and Probability
•
11th Grade

Sampling Techniques
•
11th Grade

Two Step Word Problems
•
2nd Grade

Random Sampling
•
11th Grade

Factors
•
4th Grade

Probability
•
3rd Grade