Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: DNA Replication
Assessment
•
Amanda Mandrell
•
Biology
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
413 plays
•
Medium
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
23 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
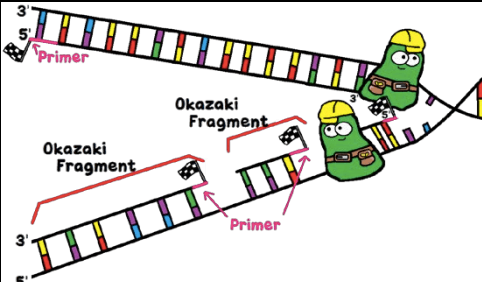
To understand DNA replication, we need to understand the “why.” Why does DNA need to replicate before cells divide?
So that each cell has a full copy of DNA
So that each cell has half a copy of DNA
So that each cell has a no copies of DNA
So that each cell has a different copies of DNA
2.
Multiple Choice
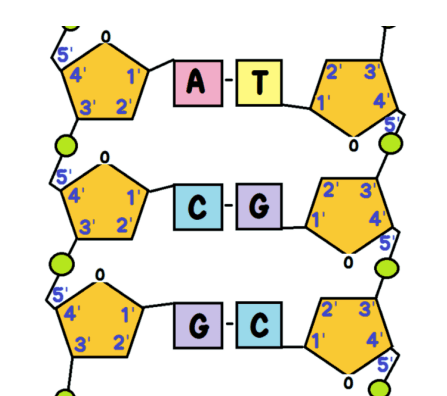
use the image to answer the questions
How many Deoxyribose (sugar).
Total number in image?
6
3
1
2
3.
Multiple Choice

use the image to answer the questions
How many Hydrogen bonds?
Total number in image?
6
3
1
2
4.
Multiple Choice

use the image to answer the questions
How many adenine?
Total number in image?
6
3
1
2
5.
Multiple Choice

use the image to answer the questions
How many thymine?
Total number in image?
6
3
1
2
6.
Multiple Choice

use the image to answer the questions
How many cytosine?
Total number in image?
6
3
1
2

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Replication Check In
•
9th - 11th Grade

Nucleic Acids
•
8th - 10th Grade

Introduction to Ecology & Levels of the Environment
•
6th - 8th Grade

Central Dogma
•
10th - 12th Grade

Nucleic Acids
•
9th Grade

Replication and Transcription
•
9th Grade

Meiosis Introduction
•
10th Grade

Nucleic Acids
•
9th - 12th Grade