
Principles of Programming Languages
Assessment
•
Shrikant Tiwari
•
Computers
•
University
•
4K plays
•
Hard
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
100 questions
Show answers
1.
Fill in the Blank
............. is the systemic operations to the development operations, maintenance and retirement of software.
2.
Multiple Select
There are two types of languages used within computer systems:
High Level
Low Level
Mid Level
Level 42
3.
Multiple Select
A high level programming language is...
very efficient on the processor
easy for humans to read
interpreted or compiled
multiple instructions per statement
assembled
4.
Multiple Select
A low level programming language is...
very efficient on the processor
easy for humans to read
interpreted or compiled
multiple instructions per statement
assembled
5.
Multiple Choice
High-level languages are faster to write than in assembly or machine language but they are harder to read and understand.
True
False
6.
Multiple Choice
The process of developing a sequence of instructions to enable a computer to accomplish a particular task.
Iterative Algorithm
Assembly Languages
Computer Programming
7.
Multiple Choice
formula which gives instructions for the computer to perform a specific task
Bit Depth
Vector Graphic
Bit-Mapped Graphic
Algorithm
8.
Multiple Choice
graphic representation of the step-by-step instructions of how the computer processes data
Linear Algorithm
flow chart
Iterative Algorithm
Software Development
9.
Multiple Choice
process of computer programming, documenting, testing and big fixing through successive phases in an orderly way
Linear Algorithm
flow chart
Iterative Algorithm
Software Development
10.
Multiple Choice
Flow Charts help programmers pay attention to the logic of solution to the problem.
True
False
11.
Multiple Choice

Which generation?
Machine Code - Low
Assembly Code - Low
High Level
12.
Multiple Choice
Computers must translate everything into binary
True
False
13.
Multiple Select
Assembly language is better than machine code because...
it is easier for humans to read
it is easier to remember the instructions
a person is less likely to make mistakes in assembly language
it is written using English-like keywords
14.
Multiple Choice
Debugging
Refixing
Error Checking
Problem Solving
15.
Multiple Choice
LOAD
STORE
ADD
SORT
16.
Multiple Choice
STOP
HALT
END
FINISH
17.
Multiple Choice
Assemblers, Compilers & Interpreters
Assemblers, Compilers & Converters
Assemblers, Scripters & Interpreters
Converters, Scripters & Interpreters
18.
Multiple Choice
The analysis phase ____________________
Determines what the program will do
Determines how the program will work
Determines whether or not the program works
Adds new features to the delivered program
19.
Multiple Choice
The operations and maintenance phase ____________________
Determines what the program will do
Determines how the program will work
Determines whether or not the program works
Adds new features to the delivered program
20.
Multiple Choice
The implementation phase ____________________
Determines whether or not the program is feasible
Determines which classes are needed and what they will do
Determines whether or not the program works
Implements the program code
21.
Multiple Choice
The design phase ____________________
Determines whether or not the program is feasible
Determines which classes are needed and what they will do
Determines whether or not the program works
Implements the program code
22.
Multiple Choice
SDLC means
Software Development life cycle
System development life cycle
Simple development learning cycle
Non of the above
23.
Multiple Choice
Software engineering involves
Using engineering tools and techniques in software development
Using scientific way to software development
Both A and B
Non of the above
24.
Multiple Choice
Risk Assessment is part of software engineering
True
False
Can't say
Non of the above
25.
Multiple Choice
ERD means
Entity relationships diagrams
Every real dialog
Engineering requirements diagrams
Non of the above
26.
Multiple Choice
The reason for software bugs and failures is due to
Software companies
Software Developers
Both Software companies and Developers
Software
27.
Multiple Choice
Someone who solves complex problems with mathematical and scientific application is Called
BCA students
Donald Trump
Engineer
Sportsmen
28.
Multiple Choice
What is software quality?
Satisfying client needs
Proving Best Lunch
Conducting Semester Exam
Reopening university And Colleges
29.
Multiple Choice
What do you understand by software?
New Movie
Set of sports items
Set of food items
Set of programs
30.
Multiple Choice
First step in Requirement Engineering
Gathering Requirement
Feasibility Study
Elicitation
requirement analysis
31.
Multiple Choice
Expand SRS
System Requirement Specification
System Requirement Software
Software Requirement Specification
Software Requesting Service
32.
Multiple Choice
Computer Works on which cycle?
Process,Output,Input
Output, Process Input
Input, Process,Output
None of the Above.
33.
Multiple Choice
CPU is .........................................of a computer.
Heart
Brain
BOth A & B
None of the Above
34.
Multiple Choice
How many types of computer generation ?
3
5
6
4
35.
Multiple Choice
What is the Brain of Computer?
UPS
CPU
SMPS
RAM
36.
Multiple Choice
Hardware and Software
Bits and Pieces
Inputs and Outputs
Plastic and Metal
37.
Fill in the Blank

whose person is this picture
38.
Multiple Select
please lisyen audio for question
printer
plotter
monitor
keyboard
39.
Multiple Choice

What is the name of this device?
Scanner
MICR
Bar code reader
Zip Code reader
40.
Multiple Choice
Programmers write programs to satisfy the needs of others called
Coders
End Users
Program Developers
41.
Multiple Choice
A phase in the Program Development Cycle that involves the consideration of what the end users want or need.
Understanding the Problem
Planning the Logic
Coding the Program
42.
Multiple Choice
A phase in the Program Development Cycle that involves the creation of Source Codes
Understanding the Problem
Planning the Logic
Coding the Program
43.
Multiple Choice
What part of an experiment contains the data tables and graphs?
Analysis
Conclusion
Hypothesis
Materials
44.
Multiple Choice
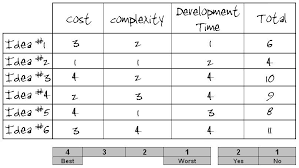
Using one of these will help your group decide on which model to build:
Design Brief
Design Evaluator
Decision Matrix
45.
Multiple Choice
If I find flaws in my solution I should....
Create a technical drawing instead
Be formal and perfect
go back and make modifications before moving forward
46.
Multiple Choice
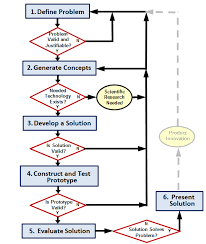
Why are there arrows going in all directions here?
To show that many ideas come from everyone
To show that the chart is incomplete
To show that you can go back to previous steps if needed
47.
Multiple Select
In software design three levels of design exist, which are-
External Design
Architectural Design
Detailed Design
Program Design
48.
Multiple Choice
Software can be described as Fit for Purpose if it:
Fulfils the requirements set out during the Analysis stage
Fulfils the requirements set out during the Design stage
Fulfils the requirements set out during the Implementation stage
Fulfils the requirements set out during the Testing stage
49.
Multiple Choice
A syntax error is caused by:
A large font size in your code
A typing error in your code
Using internal commentary in your code
Using indentation in your code
50.
Multiple Choice
Which system modelling tool best describes the hierarchy of subroutines and the sequence in which they are executed?
Dataflow diagram
System flowcharts
IPO diagrams
Structure charts
51.
Multiple Choice
What is shown on context diagrams?
The movement of data between processes.
The movement of data into and information out of a system.
The order in which processes occur in a system.
The nature of data structures used by processes within the system.
52.
Multiple Choice
What form of documentation/diagram is the most appropriate for showing the schedule and timelines for activity in a project?
Gantt chart
Storyboard
Data flow diagram
System flowchart
53.
Multiple Choice
The command STOP is used in a software language as a debugging tool to halt a program. The program cannot resume until the debugging command RUN is issued.
Program trace
Breakpoint
Stub
Value watching
54.
Multiple Choice
It should not use any specific programming language
True
False
55.
Multiple Choice
False/Fake
Unfinished
56.
Multiple Choice

What symbol is shown here
Process
Decision
Terminator
Input/Output
57.
Multiple Choice
An Arrow
A Line
A Square
A Diamond
58.
Multiple Choice
If
To provide a response if a statement is not met
To provide a response if a statement is met
A loop with a condition set at the start
Used in a question as part of the decision process
59.
Multiple Choice
Else
To provide a response if a statement is not met
To provide a response if a statement is met
A loop with a condition set at the start
Used in a question as part of the decision process
60.
Multiple Choice
Then
To provide a response if a statement is not met
To provide a response if a statement is met
A loop with a condition set at the start
Used in a question as part of the decision process
61.
Multiple Choice
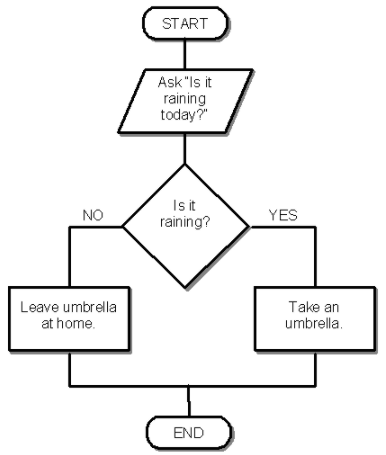
Yes
Leave umbrella at home
Take an umbrella
62.
Multiple Choice
For
Used to create a counting loop
To display a response on screen to the user
A loop with a condition set at the start
Requires an entry from the user in response to a question
63.
Multiple Choice
Used to create a counting loop
To display a response on screen to the user
A loop with a condition set at the start
Requires an entry from the user in response to a question
64.
Multiple Choice
While
To provide a response if a statement is not met
To provide a response if a statement is met
A loop with a condition set at the start
Used in a question as part of the decision process
65.
Multiple Choice
top to the bottom
left to the right
right to the left
bottom to the top
66.
Multiple Choice
A decision tree uses _________ to calculate likely outcomes.
stakeholder information
facts and statistics
estimates and probabilities
shareholder data
67.
Multiple Choice
BENEFITS OF USING DECISION TREES include:
Uses quantitative data only – ignores qualitative aspects of decisions
It is based on assumptions and estimates
Choices are set out in a logical way
Assignment of probabilities and expected values prone to bias
68.
Multiple Choice
DRAWBACKS OF USING DECISION TREES include:
Probabilities are just estimates – always prone to error
Choices are set out in a logical way
Potential options & choices are considered at the same time
Use of probabilities enables the “risk” of the options to be addressed
69.
Multiple Choice
When a sub-node splits into further sub-nodes, then it is called
Decision Node
Splitting
Pruning
Terminal Node
70.
Multiple Choice

make a plan!
make a decision
evaluate choices
determine need or want
71.
Multiple Choice

gather information
make a decision
plan how to reach your goal
evaluate your choices
72.
Multiple Choice
Decision trees are only useful if the choices at each decision point are binary
Both decision trees and tables can have redundancy, if not carefully designed
Both decision trees and tables are good for modelling complex logic
73.
Fill in the Blank
................ can be used to specify complex decision logic in a high level software specification?
74.
Multiple Select
The 2 types of Software are:
Operating System
System
Business
Application
75.
Multiple Select
Types of application software:
Business
Operating System
Robotics
Educational
Computer Games and Environment
76.
Multiple Choice
Easier for us to understand
Easier to debug
Programs require less file space
77.
Multiple Choice
No technical skill is required
Needs to be translated before it can be executed
Difficult for humans to debug
78.
Multiple Choice
Are closer to human language. Like oracle, VB, VC++, SQL etc. Most of them are used to access database, they allow the programmer to define “what” is required without telling the computer and “How” to implement it.
Machine
Assembly
High Level
4GL
79.
Fill in the Blank
Programming Methods- the use for programming __________ it depends upon the size and the complexity of the program. When a program beyond a particular size and complexity, a traditional methodology may fail to give efficient results and in the case one has to either use a new method which will satisfy the need.
80.
Multiple Choice
The programmers may use them in other parts of the programs knowing that only their abstract properties without concern for the details of their implementation
Simplicity, Clarity and Unity
Orthogonality
Naturalness for Application
Support for Abstraction
81.
Multiple Choice
A program may be tested by executing it with text input data and checking the output results against the specifications. For verification and troubleshoot the programs.
Ease of Program Verification
Programming Environment
Portability of Program
Cost
82.
Multiple Choice
Analyse or Defined the Problem – analyse problem, consists of reviewing program specifications, meeting with the analysts and users; and identifying program components.
TRUE
FALSE
83.
Fill in the Blank
A ..................... is an artificial language designed to express computations that can be performed by a machine, particularly computer.
84.
Multiple Select
Why study programming language?
To improve your understanding of the language you are using
To increase your vocabulary of useful programming constructs
To make is easier to learn a new language
To make it easier to design a new language
85.
Multiple Choice
Abstraction is:
adding to a problem
filtering out all irrelevant characteristics and unnecessary details
finding characteristics
looking for similarities
86.
Multiple Select
Select all that applies in Abstraction?
is a problem solving tool
removes unimportant information
adds important information
simplifies a situation
focuses on what is important
87.
Multiple Choice
Decomposition
Abstraction
Programming
Algorithmic Thinking
88.
Multiple Select
The widely used abstraction mechanisms in software design are-
Functional Abstraction
Data Abstraction
Control Abstraction
Procedure Abstraction
89.
Multiple Choice
Which one is not the benefit from using modularization ?
Ease of Understanding
Reusable of code
Increasing algorithm performance
Elimination of redundancy
90.
Multiple Choice
Which one of cohesion level that has the strongest internal strength of a module ?
Logical cohesion
Temporal cohesion
Sequential cohesion
Functional cohesion
91.
Multiple Choice
In which one of the following types of coupling, complete data structures are passed from one module to another?
Control Coupling
Stamp Coupling
External Coupling
Content Coupling
92.
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is the correct ordering of the coupling of modules from strongest (least desirable) to weakest (most desirable)?
content, common, control, stamp, data
common, content, control, stamp, data
content, data, common ,stamp, common
data, control, common, stamp, content
93.
Multiple Choice
Consider the sentence: A book has one or more pages. Which of the following best characterizes the relationship between the Book class and the Page class?
Inheritance
Specialization
Association
Composition
94.
Multiple Choice
What is Top Down Design?
start function at the top, break down into parts, definitions at the bottom
Put the steps at the top and put the explanation in layers at the bottom
Write a 10 page story about how to run the code and break it into chapters to help you organize.
95.
Multiple Choice
Stepwise refinement is:
Identifying the main steps needed in your program
Breaking down each step until it becomes easy to code
96.
Multiple Choice
Which of these is not a reason for breaking problems down into modules
Reusability
Easier to test and debug
Allows only one programmer to work on a solution
Individual modules are easier to maintain.
97.
Multiple Choice
A graphical representation of the modular structure of a solution is a
Structure chart
Modular diagram
Top down design
Identfier table
98.
Multiple Choice
What is a software design strategy?
A graphical or textual description of the software
A fundamental idea that can be applied to designing a system.
A systematic approach for producing a design.
An overall plan and direction for developing a design.
99.
Multiple Choice
What is “white box” testing?
Unit testing
Integration testing
Testing with knowledge of the system internals
Testing without knowledge of the software internals
100.
Multiple Choice
What is “black box” testing?
System testing
Integration testing
Testing with knowledge of the system internals
Testing without knowledge of the software internals

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Parts of a Computer
•
1st Grade

Parts of Computer
•
KG - 2nd Grade

Principles of Programming Languages
•
University

Computer Memory
•
University

Computer Basics
•
University

Computer Mouse
•
1st Grade

Hardware and Software
•
3rd Grade

Computer Networks
•
8th Grade