Energy System Interplay 2
Assessment
•
Joel Octigan
•
Physical Ed
•
12th Grade
•
41 plays
•
Hard
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
39 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
Lactate Inflection Point can occur when an athlete
exercises at submaximal intensity.
fails to improve their lactate tolerance.
depletes their muscle and liver glycogen stores.
exceeds their VO2 maximum.
2.
Multiple Choice
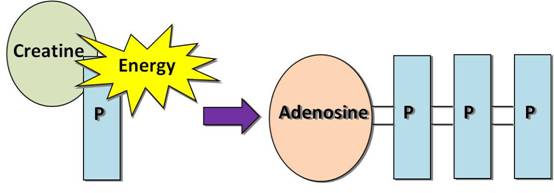
With regard to ATP production, the:
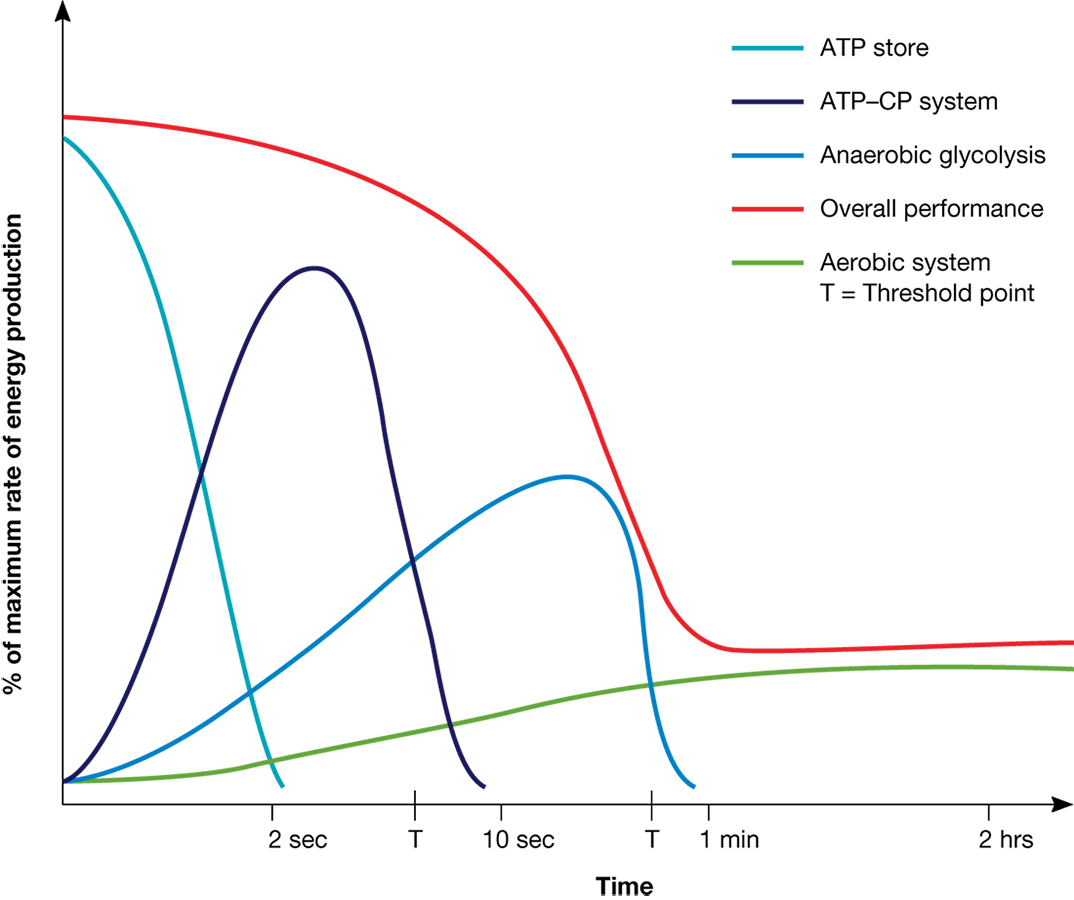
ATP-PC energy system has the highest yield and slowest rate.
Anaerobic Glycolysis energy system has the lowest yield and highest rate.
Aerobic Glycolysis has the highest yield and lowest rate.
Aerobic Lipolysis has the highest yield and lowest rate.
3.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a situation when anaerobic glycolysis would NOT be the dominant source of energy?
In a 400 metre race
In the red blood cells
When a marathon runner approaches the finish line
Anaerobic Glycolysis would be dominant in all of the situations above
4.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following correctly outlines a change that would occur at the commencement of exercise?
Decreased Lactic Acid
Increased Inorganic Phosphates (Pi)
Increased PC stores
None of the above
5.
Multiple Choice
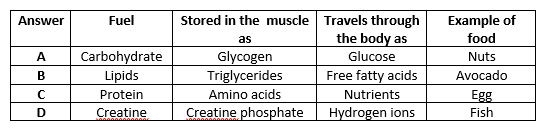
Which of the following fuels takes the longest to deplete?
Intramuscular ATP
Phosphocreatine (PC)
Glycogen
Water
6.
Multiple Choice
A Centre player for Netball spends 34% of the time working at maximal effort and 66% of the time resting (work to rest ration is 1:2). The Dominant Energy System during work time for the Centre Player is
The ATP-PC System
The Anaerobic Glycolysis System
The Aerobic Energy System
Both the ATP-PC System and the Anaerobic Glycolysis System

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Hockey
•
5th Grade

Exercise Physiology
•
11th Grade

Fruits in Chinese
•
6th - 9th Grade

Endurance
•
4th - 6th Grade

Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
•
9th - 12th Grade

Energy Systems
•
11th Grade

Energy Systems
•
11th Grade - University

Soft Tissue Injuries
•
12th Grade