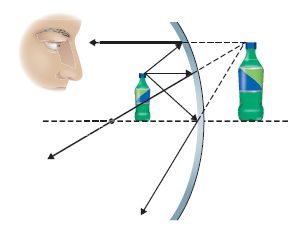
Curved Mirror Ray Diagrams
Assessment
•
Lori Bouchard
•
Physics
•
10th - 11th Grade
•
174 plays
•
Medium
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
20 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Select
An image behind the mirror is...
virtual
real
inverted
upright
2.
Multiple Select
An image that points below the principal axis is (choose 2)...
virtual
real
upright
inverted
3.
Multiple Choice
If the object is beyond C (2F)...
image is real, smaller and inverted
image is real, smaller and upright
image is virtual, smaller and inverted
image is real, bigger and upright
4.
Multiple Choice
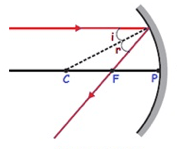
This ray diagram is for which mirror?
concave
convex
plane
window
5.
Multiple Choice
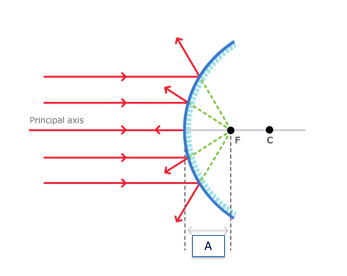
In the image, all the rays meet at F, What is F
focal length
focal point
center of curvature
reflection
6.
Multiple Select
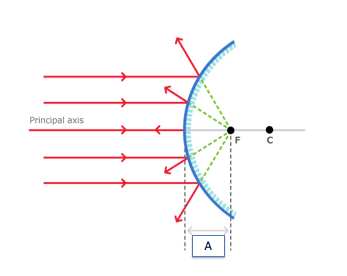
This image is showing a convex mirror because the image is (choose 2 answers)
real light rays meet behind the mirror
real light rays don't meet
the focal point is in front of the mirror
the focal point is behind the mirror

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Mirror Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

Reflection of Light
•
7th - 10th Grade

Sources of Light
•
10th Grade

Light and Shadow
•
2nd - 4th Grade

Light
•
11th Grade

Light and Color
•
6th - 8th Grade

Ray Diagrams
•
10th Grade

Ray Diagrams
•
9th - 12th Grade