
AP Microeconomics Market Structure Review
Assessment
•
Bryan Burns
•
Social Studies
•
11th Grade - University
•
48 plays
•
Medium
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
58 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
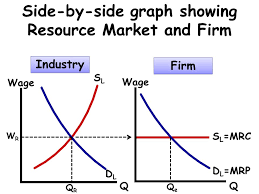
oligopsony
monopoly
monopsony
perfectly competitive factor market and firm
2.
Multiple Choice
What does marginal mean in the language of economics?
Additional
Less
Satisfaction
I can't believe it's not Butter.
3.
Multiple Choice
What does utility mean in the language of economics?
Additional
Less
Satisfaction
I can't believe it's not Butter.
4.
Multiple Choice
If every consumers needs are being met perfectly and every good that is being made is being sold, what type of efficiency is being achieved?
Productive Efficiency
Allocative Efficiency
5.
Multiple Choice
When there is only one seller of a good or service, they are said to have a?
Monopoly
Oligarchy
Monopolistic Competition
Perfect Competition
6.
Multiple Choice
When there are only a few sellers of a type of produce, like Smart phones, there is said to be an?
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic Competition
Perfect Competition
7.
Multiple Choice
When there is lots of competition in a market because the barriers to entry are low and there are many substitutes that exist, this is called?
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Monopolistic Competition
Perfect Competition
8.
Multiple Choice
monopoly
oligipoly
perfect competition
monopolistic competition
9.
Multiple Choice
perfect competition
monopolistic competition
monopoly
oligopoly
10.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about an imperfectly competitive firm’s marginal revenue (MR) curve if it has a linear and downward-sloping demand curve?
MR decreases at an increasing rate.
MR increases at first, then decreases.
MR is constant.
MR decreases and is less than demand.
MR is greater than demand.
11.
Multiple Choice
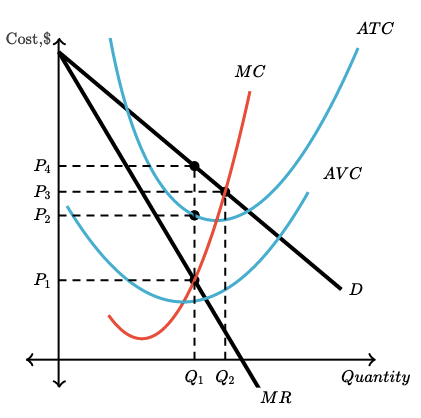
For the graph shown here, what quantity will this firm produce and what price will it charge?
Q2 ; P2
Q2 ; P3
Q1 ; P1
Q1 ; P2
Q1 ; P4
12.
Multiple Choice
P=Increase; Q=Increase
P=Increase; Q=Decrease
P=Decrease; Q=Decrease
P=No Change; Q=Increase
13.
Multiple Choice
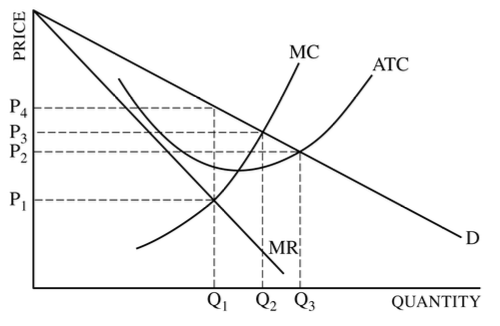
Q1 & P1
Q2 & P3
Q1 & P4
Q3 & P2
14.
Multiple Choice

Q1 & P1
Q2 & P3
Q1 & P2
Q3 & P2
15.
Multiple Choice
earn a higher profit
increase consumer surplus
decrease deadweight loss
make its demand more elastic
16.
Multiple Choice
P=Higher; Q=Same
P=Lower; Q=Same
P=Lower; Q=Higher
P=Higher; Q=Lower
17.
Multiple Choice
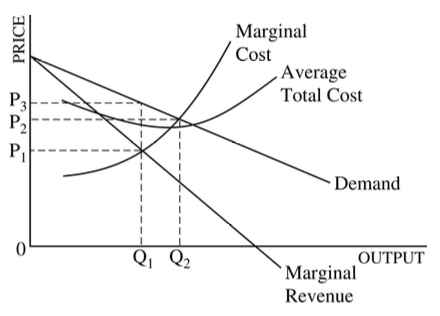
Q1, price at P3, and earn an economic profit
Q1, price at P1, and suffer a loss
Q2, price at P2, and earn an economic profit
Q2, price at P2, and earn only a normal profit
18.
Multiple Choice
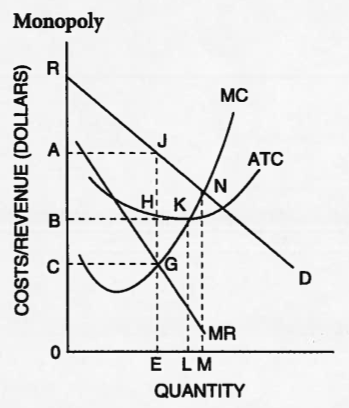
A
B
C
R
19.
Multiple Choice

0CGE
0AJE
AJHB
BAJN
20.
Multiple Choice

BKL0
CGE0
AJE0
BHE0
21.
Multiple Choice

0CGE
0AJE
AJHB
BAJH
22.
Multiple Choice

ABHJ
AJGC
ARJ
ARJE
23.
Multiple Choice
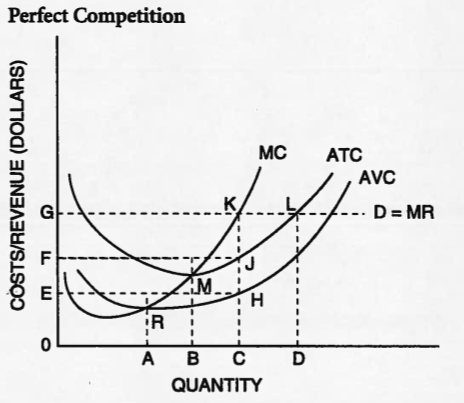
A
B
C
D
24.
Multiple Choice

K
M
L
R
25.
Multiple Choice

0GKC
FGKJ
0EHC
0FJC
26.
Multiple Choice
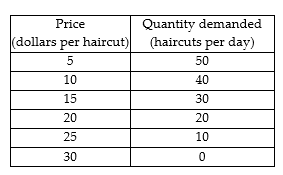
Christy's Haircuts, the sole supplier of haircuts in a small town, faces the demand schedule shown in the table above. What is Christy's marginal revenue from the 25th haircut?
zero
$5
$7
$5.50
27.
Multiple Choice
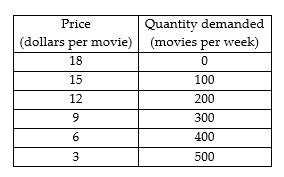
Roxie's Movie Theatre is the only one in town. The table above gives the demand schedule for movies. If Roxie's is a single-price monopoly and the marginal cost of a movie is $6, Roxie's will charge ________ a movie and will sell ________ movie tickets a week.
$15; 100
$12; 200
$6; 400
$9; 300
28.
Multiple Choice
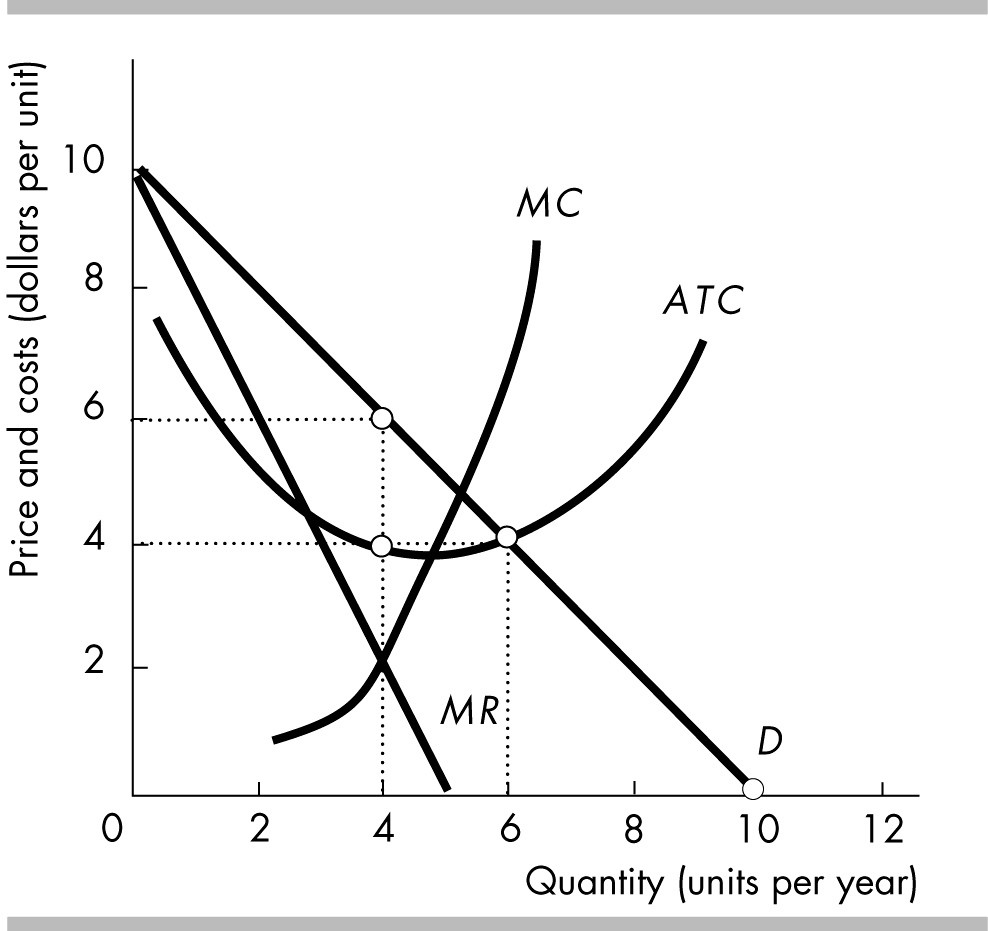
For the unregulated, single-price monopoly shown in the figure above, when its profit is maximized, output will be
4 units per year and the price will be $6.
4 units per year and the price will be $4.
6 units per year and the price will be $4.
None of the above answers is correct.
29.
Multiple Choice
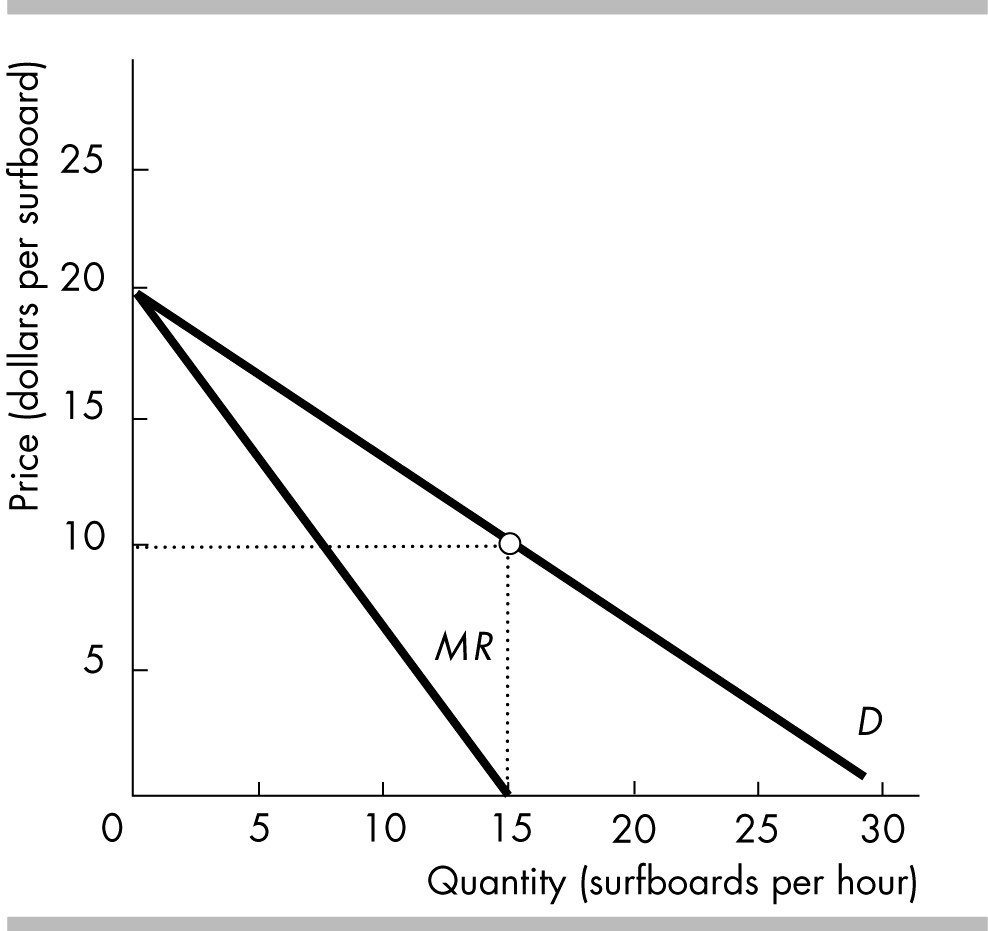
Sue's Surfboards is the sole renter of surfboards on Big Wave Island. Sues demand and marginal revenue curves are illustrated in the figure above. Sue's Surfboards currently rents 15 surfboards an hour. Sue's total revenue from the 15 surfboards is
$300
$220
$150
$100
30.
Multiple Choice
In long-run equilibrium, the marginal benefit exceeds the price charged by the firms.
In long-run equilibrium, the price is greater than the marginal cost.
In long-run equilibrium, average total costs are minimized.
In long-run equilibrium, the firm is earning economic profits.
31.
Multiple Choice
Monopoly
Monopolistic Competition
Perfect Competition
Oligopoly
32.
Multiple Choice
Price equals marginal cost and average total cost.
Price equals average total cost but is greater than marginal cost.
Price equals marginal cost and is greater than average total cost.
The firm earns positive economic profits by producing at minimum average cost.
33.
Multiple Choice
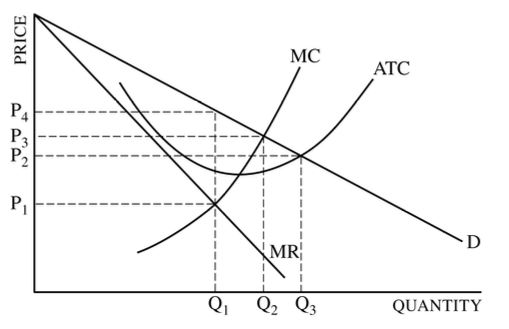
making a profit in the short-run
incurring a loss in the short-run
making a profit in the long-run
breaking even in the long-run
34.
Multiple Choice
MC = marginal cost, and ATC = average total cost. In monopolistic competition, which of the following most accurately describes the long-run equilibrium conditions for a firm?
P>ATC, MR=MC, and P>MC
P=ATC, MR=MC, and P=MC
P=ATC, MR=MC, and P>MC
P=ATC, MR>MC, and P>MC
35.
Multiple Choice
shift the demand curve for its product to the left
make its product more similar to its competitors’
reduce the industry’ s barriers to entry
make the demand for its product less price elastic
36.
Multiple Choice
Perfect Competition
Monopolistic Competition
Oligopoly
37.
Multiple Choice
Define collusion
When two cars collide on the road
a secret agreement between two competing firms to sell their similar products at the same price
38.
Multiple Choice
monopoly
oligopoly
perfect competition
monopolistic competition
39.
Multiple Choice
maintain existing prices.
raise their prices.
go out of business.
lower their prices.
40.
Multiple Choice
Game theory is used to explain
why firms price discriminate
how monopolies evolve into oligopolies
strategic behavior of firms in oligopoly
profit maximization in monopoly
price leadership of monopolistic competition
41.
Multiple Choice
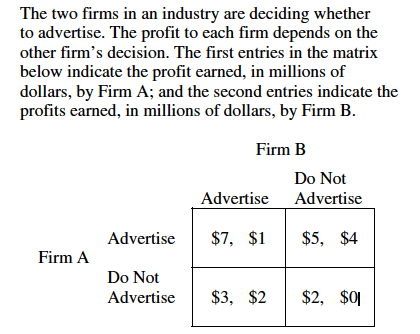
Based on the payoff matrix, which of the following is correct?
Firm A always gets a smaller share of the industry profits.
Firm A’s dominant strategy is to advertise.
Firm B’s dominant strategy is not to advertise.
The dominant strategy for both firms is not to advertise.
Neither firm has a dominant strategy.
42.
Multiple Choice
In the long run, new firms will enter a monopolistically competitive industry:
provided economies of scale are being realized.
even though losses are incurred in the short run.
until minimum average total cost is achieved.
until economic profits are zero.
43.
Multiple Choice
A monopolistically competitive firm maximizes profits or minimizes losses in the short run by
Setting price equal to marginal cost.
Producing at the output level where ATC is minimized.
Producing at the output level where MR equals MC.
Producing at the output level where MC equals ATC.
44.
Multiple Choice
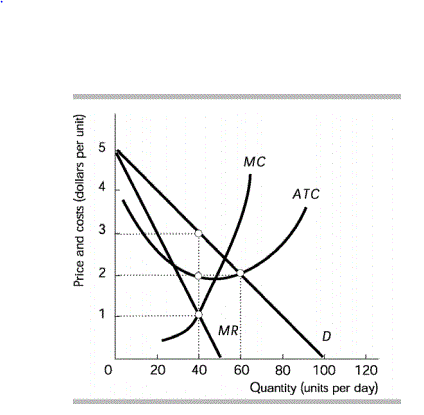
In the above figure, the monopolistically competitive will experience what change into the long run?
a right shift of it's demand curve.
a left shift of it's demand curve.
a right shift of it's supply curve.
a left shift of it's supply curve.
45.
Multiple Choice
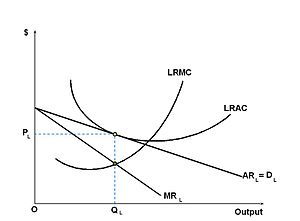
If this graph is for a monopolistically competitive firm, it best represents
short run economic loss.
short run extra-normal profit.
long run economic profit.
long run equilibrium at normal profit.
short run accounting loss.
46.
Multiple Choice
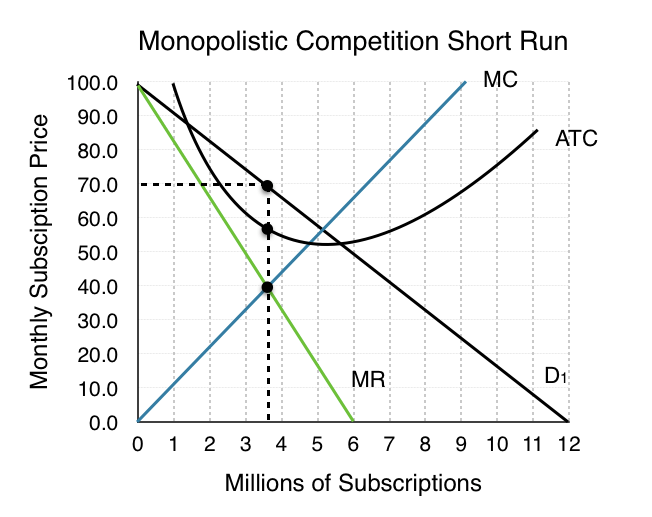
This firm will charge a price of _____ and make a per unit ___ of _____.
70; loss; 10.
60; normal profit; 0.
70; profit; 3.5.
60: profit; 10.
70; profit; 10.
47.
Multiple Choice
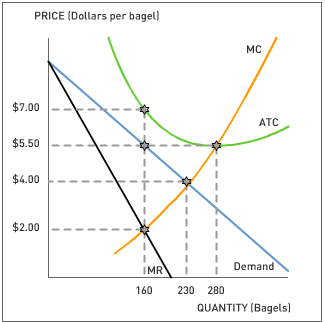
This firm will charge a price of _____ and make a per unit ___ of _____.
7; loss; 1.5.
7; normal profit; 0.
7; profit; 1.5.
5.5: loss; 1.5.
5.5; profit; 1.5.
48.
Multiple Choice
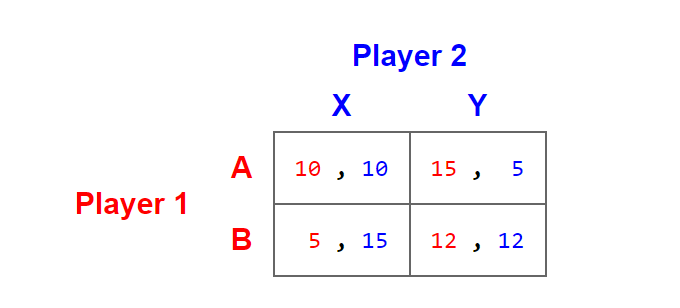
A,X
A,Y
B,X
B,Y
49.
Multiple Choice
The cartel model of oligopoly predicts that
all firms in the industry act in unison to set monopoly price
each producer acts independently of others
firms follow the low-price firm in the industry
differences in cost of production discourage individual firms from cheating
the markup on marginal cost should be the same for all firms
50.
Multiple Choice
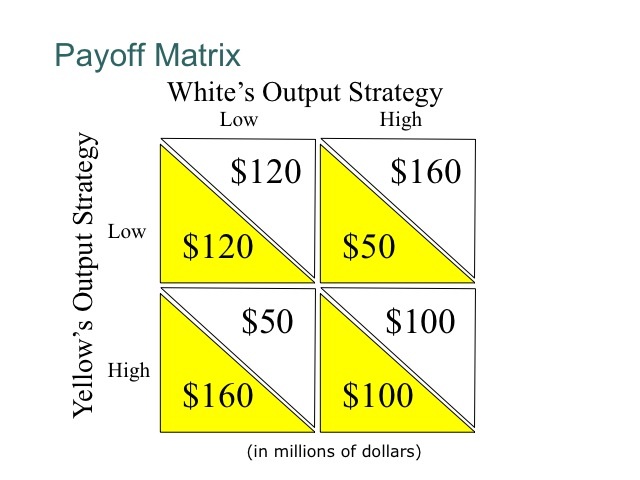
high
low
51.
Multiple Choice
What would facilitate collusion between firms in an oligopolistic industry
An increase in the number of firms
large fluctuations in demand
rapid changes in technology
a standardised product
52.
Multiple Choice
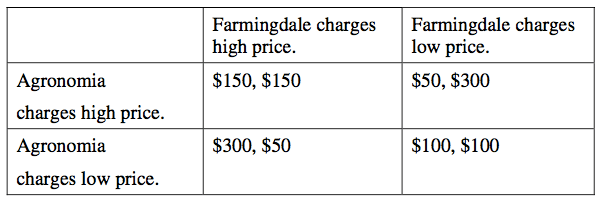
Agronomia = $50; Farmingdale = $100
Agronomia = $150; Farmingdale = $150
Agronomia = $300; Farmindale = $50
Agronomia = $100; Farmingdale = $100
53.
Multiple Choice
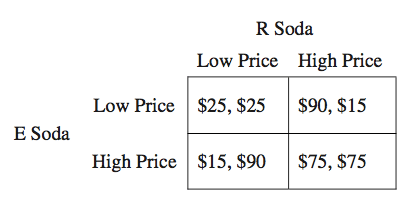
the soft-drink industry. The companies cannot cooperate. Each firm can follow a high-price strategy or a low-price strategy for pricing its product. In the payoff, the first entry in each cell shows the profits to E Soda and the second entry shows the profits to R Soda. It can be concluded that:
neither E Soda nor R Soda has a dominant strategy
E Soda has a dominant strategy but R Soda does not
Both firms will choose the high-price strategy
Both firms will choose the low-price strategy
54.
Multiple Choice
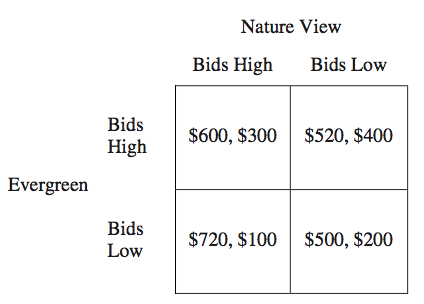
a landscaping contract. The payoff matrix shows what each firm’s total weekly profits from all its operations will be for each combination of bids. The first entry in each cell shows Evergreen’s profit, and the second entry in each cell shows Nature View’s profit. A Nash equilibrium results under which of the following conditions?
When both firms bid low
When Evergreen bids high and Nature View bids low
When both firms bid high and when both firms bid low
When Evergreen bids low, no matter what Nature View’s bid is
55.
Multiple Choice
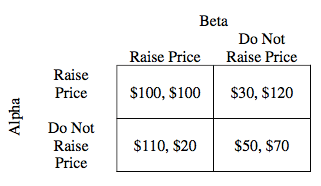
Alpha: Do Not Raise; Beta: Do Not Raise
Alpha: Do Not Raise; Beta: Raise
Alpha: No Dominant Strategy; Beta: Raise
Alpha: Raise; Beta: Do Not Raise
56.
Multiple Choice

A,X
A,Y
B,X
B,Y
57.
Multiple Choice
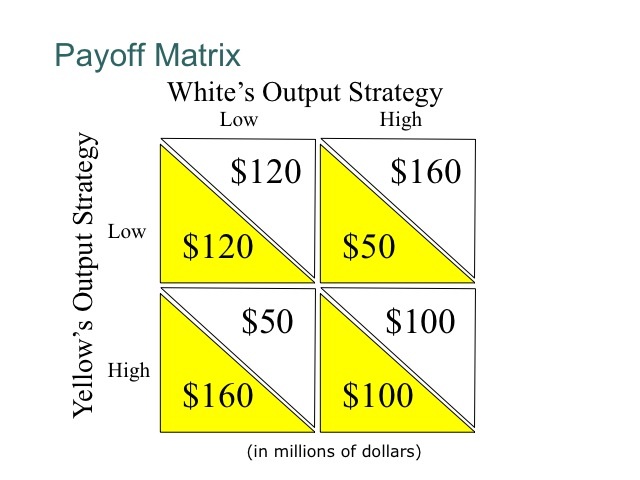
high
low
58.
Multiple Choice
Oligopoly, Monopoly, Perfect Competition, Monopolistic Competition
Perfect Competition, Oligopoly, Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition
Monopoly, Oligopoly, Monopolistic Competition, Perfect Competition
Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition, Perfect Competition, Oligopoly

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Market Structures
•
9th - 12th Grade

Supply and Demand
•
5th Grade

Economy
•
4th Grade

Demand
•
12th Grade

Demand & Law of Demand
•
9th - 12th Grade

Supply and Demand
•
2nd Grade

Macroeconomics
•
12th Grade

Monetary and Fiscal Policy
•
9th - 12th Grade