
Introduction to Cells
Assessment
•
Sauce A
•
Science
•
7th Grade
•
38 plays
•
Hard
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
75 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
Who was the first scientist to observe cells?
Schleiden
Leeuwenhoek
Robert Hooke
Virchow
2.
Multiple Choice
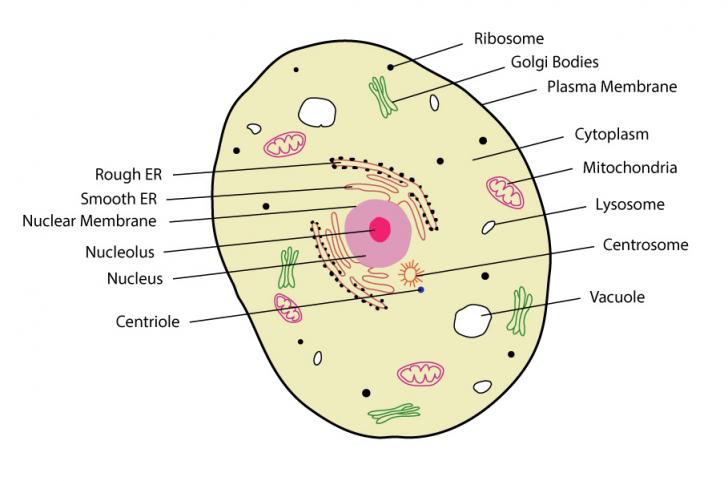
What is the significance of mitochondria as shown?
Controls which substances go into and out of the cell.
Helps take in food and convert it to energy the cell can use.
Clear gel-like fluid that moves the organelles.
Directs the cell's activities.
3.
Multiple Choice
What are two types of prokaryotes?
Eubacteria and archaebacteria.
Vaculoes and lysosomes.
Amoebas and flagellum.
Chloroplasts and proteins.
4.
Multiple Choice
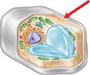
Which cell structure is the arrow pointing to?
Mitochondria
Cell Membrane
Cell Wall
Endoplasmic Reticulum
5.
Multiple Choice
What is the function of the nucleolus inside a cell's nucleus?
It is a structure where ribosomes are made.
A network of membranes that produces many substances.
A clear, gel-like fluid that fills the nucleus.
A green pigment that makes plants green.
6.
Multiple Choice
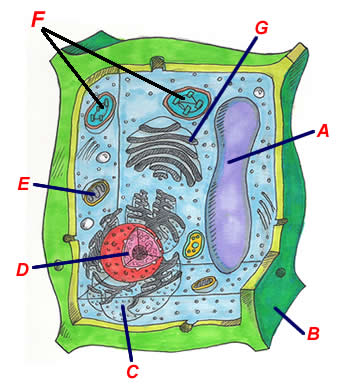
Which statement best classifies and describes the function of structure A?
It is a large central vacuole where it stores food, water, and wastes.
It is the nucleus where it contains the cell's DNA.
It is the ER where it produces many substances for the plant cell.
It is the golgi complex where it distributes materials to other organelles in the cell.
7.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following correctly defines what phospholipids are?
A web of proteins in the cytoplasm.
Lipids that contain phosphorus and are hydrophilic.
A membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell's DNA.
A lipid in which sugars are broken down to produce ATP.
8.
Multiple Choice
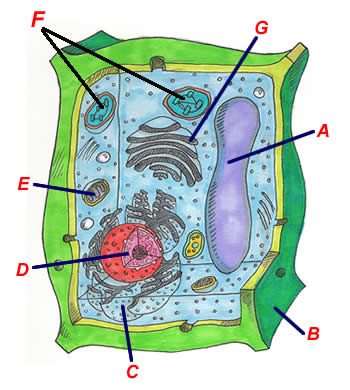
The diagram shows the typical structure of a plant cell. Which structure provides support and shape to the cell?
Structure B - Cell wall
Structure A- Large central vacuole
Structure C- Nucleus
Structure G- Golgi apparatus
9.
Multiple Choice
The ability to distinguish details on an object is called
Zooming
Graphics
Magnification
Resolution
10.
Multiple Choice
Thin strands of material that fills the nucleus and contains information for directing a cell's function is called
DNA
Nuclear envelope
Chromatin
Chromosomes
11.
Multiple Choice
Active in synthesis, modification, sorting and secretion of cell's products. Groups lipids and proteins together and distributes them in vesicles. Which comparison best contributes?
Golgi complex- Post Office
Golgi complex- City Limits
Mitochondria- Steel Mill
Nucleus- Post Office
12.
Multiple Choice

Where is there a low concentration of perfume?
In the bottle
On the hand
On the top
In the room
13.
Multiple Choice
What happens during osmosis?
Water molecules move from lower to higher concentration through the cytoplasm.
Water molecules move from a higher to lower concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
Water molecules are engulfed and vesicles are formed.
Water molecules does not remain homeostasis.
14.
Multiple Choice
What substance is the cell wall made mostly of?
Genetic material
Cellulose
Proteins
Amino acids
15.
Multiple Choice
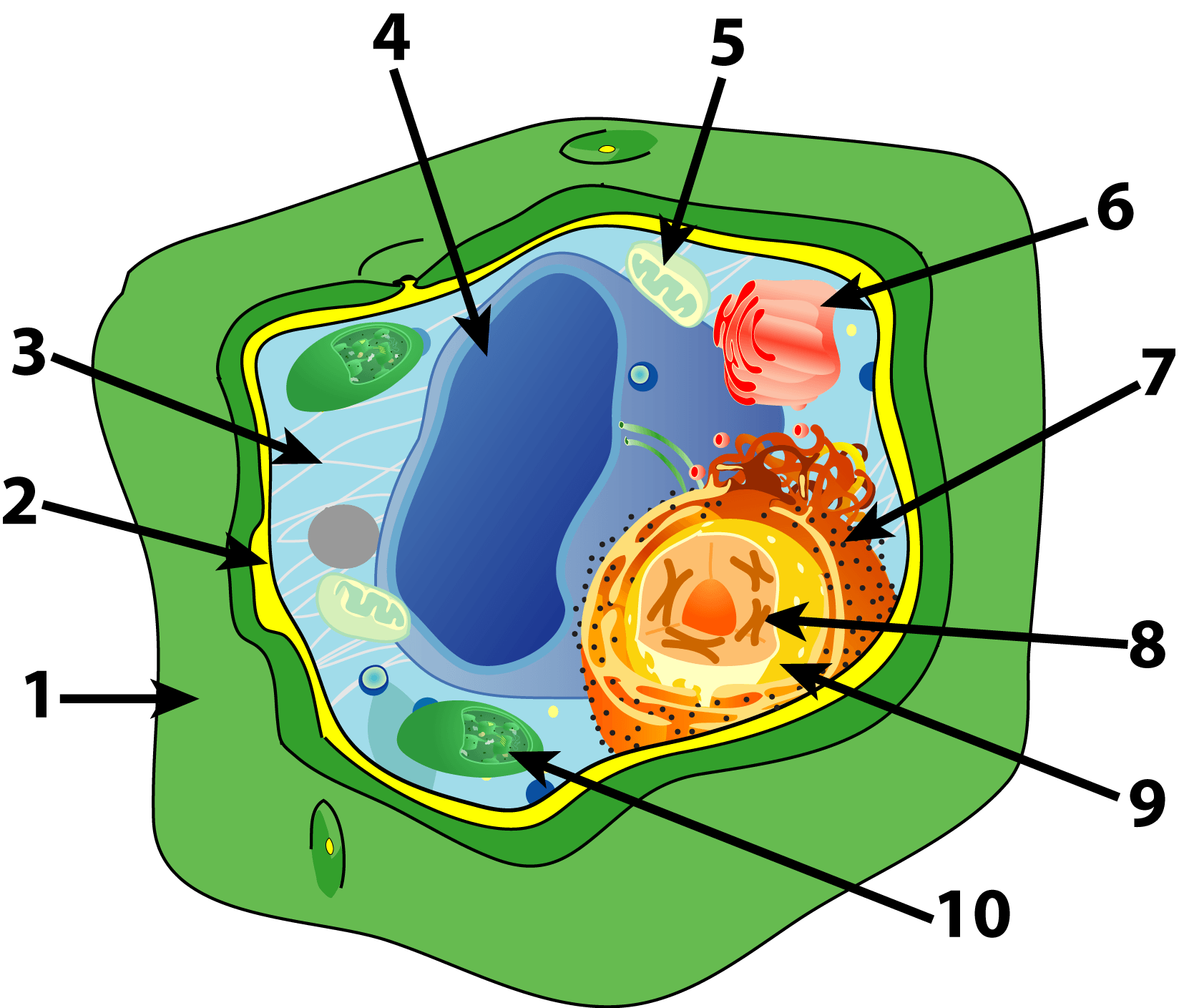
The image shows a plant cell. Which labeled parts can also be present in an animal cell? Choose the best one.
1 and 9
1 and 10
4 and 10
2 and 9
16.
Multiple Choice
Small cell structures in cells that carry out functions is a(n)
Ribosome
Centriole
Organelle
Cytoplasm
17.
Multiple Choice
The production of proteins occurs in the ribosomes of a cell using information regulated by genetic material. Which cell structure most likely controls the synthesis of proteins?
DNA or the nucleus
Mitochondria
Vesicles
ER or endoplasmic reticulum
18.
Multiple Choice
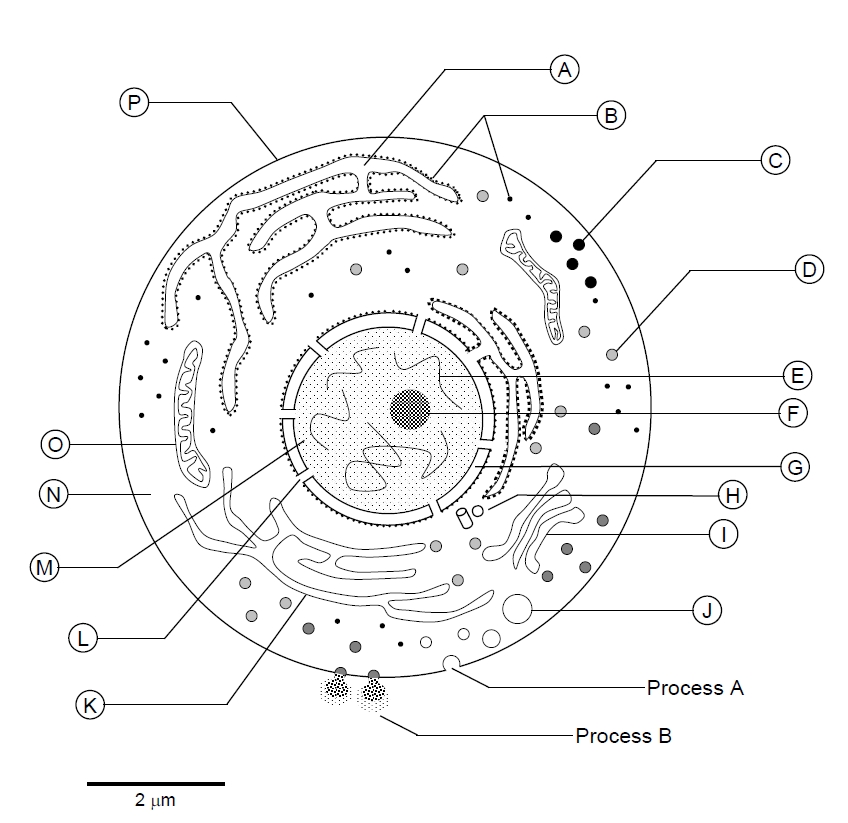
The diagram shows the structures of an animal cell. Look at letter M and E. What does both of these structures contain that is responsible for storing hereditary information that can be passed to parent to offspring?
Proteins and carbohydrates
Amino acids and chromosomes
Cellulose and nucleic acids
DNA and chromosomes
19.
Multiple Choice
Single-cell organisms that do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles are called
Prokaryotes
Eukaryotes
Cells
20.
Multiple Choice
A student listed some characteristics of a structure presented in an animal cell:
• It completely surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell.
• It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
• It separates the contents from the external environment.
Which cell structure is being described?
Cell wall
Ribosomes
Vacuole
Cell membrane
21.
Multiple Choice
A student list some characteristics of chloroplasts:
1. They contain chlorophyll.
2. They help in transport of materials in and out of the cell.
3. They are the control center of the cell.
4. They are the site ahere photosynthesis takes place.
What characteristics did the student list incorrectly?
3 and 4
3 and 1
2 and 3
1 and 4
22.
Multiple Choice
Oxygen is moving into an animal cell. Which term best describes this process?
Diffusion
Osmosis
Active transport
Endocytosis
23.
Multiple Choice
Which cell structure is involved in the process of osmosis?
Golgi body
Nucleus
Cell membrane
Cell wall
24.
Multiple Choice
A cell is placed in a salt solution that has the same concentration as the inside of the cell. What will happen to the cell?
The cell will contract
The cell will expand
The cell wall will remain the same size
The cell will burst
25.
Multiple Choice
Plant cells are capable of making their own food by photosynthesis. What specialized organelle do they have for capturing energy from sunlight?
Chloroplasts
Centriole
Mitochondria
Vacuole
26.
Multiple Choice
Which cell structure helps cell division to happen in animal cells?
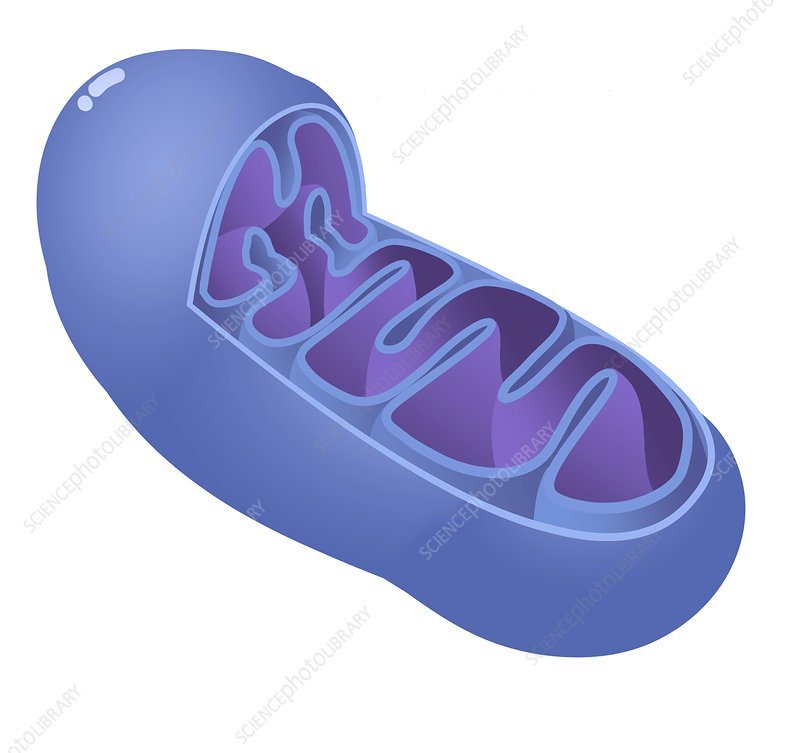
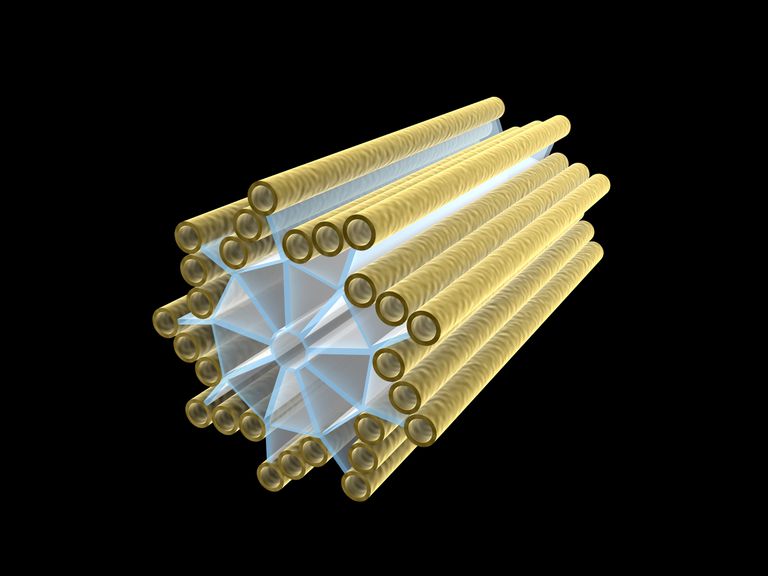
27.
Multiple Choice
How do materials pass into and out of the nucleus?
In the process of endocytosis
By flowing through the cytoplasm
From the ER to the golgi body
Through pores in the nuclear envelope
28.
Multiple Choice
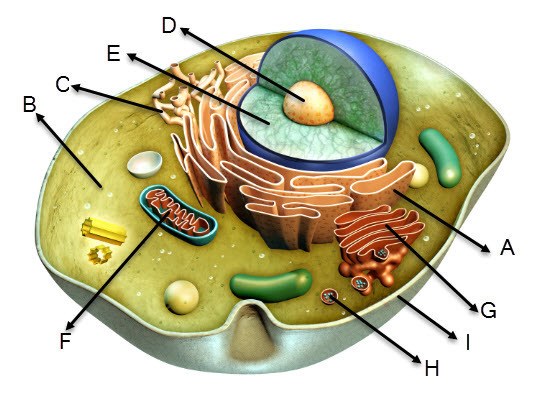
Cells contain structures that perform specific functions. Examine the diagram of the cell. Which structure is the golgi apparatus?
A
G
B
F
29.
Multiple Choice
Small grain shaped organelles that produces proteins are called
Lipids
Ribosomes
Lysosomes
Carbohydrates
30.
Multiple Choice
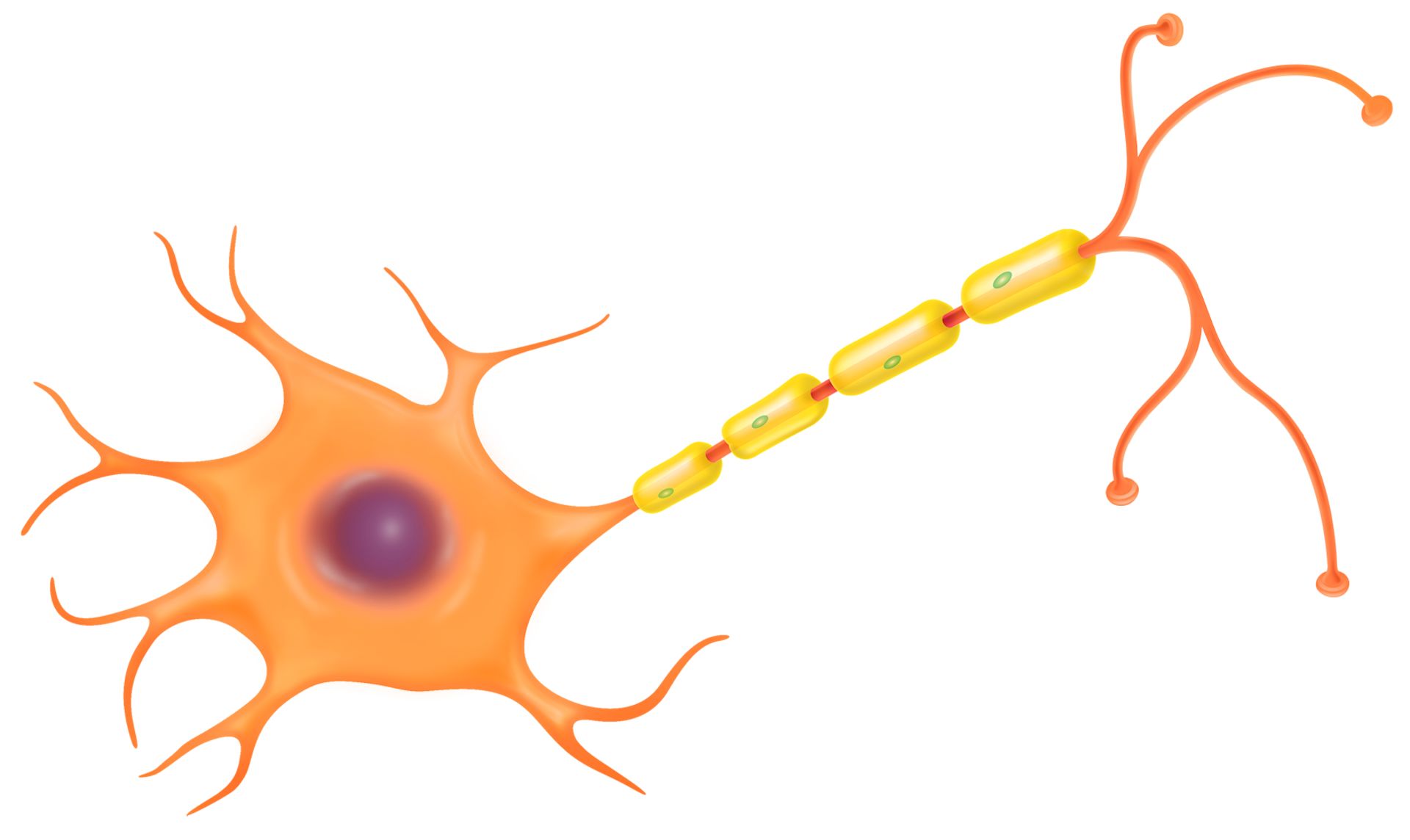
A nerve cell below uses energy to pump sodium out of the cytoplasm into a sodium rich environment. What type of cellular transport is being described?
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
Active transport
31.
Multiple Choice
Carlos was studying the cell membrane by using an egg as a model of the cell. He soaked the egg in vinegar for 2 days, then changed the liquid to salt water and soaked it for 2 more days. The egg's size increase then decrease. Which factor explains why the egg's size changed during the experiment?
The egg was selectively permeable, and liquids diffuse in and out of the egg.
The egg grew, causing it to increase, and then started to decay, causing it to shrivel.
The vinegar contaminated the egg, and the salt water reversed the effect.
Eggs need refrigeration and swell or shrink depending on the temperature of liquids.
32.
Multiple Choice
What is the cell membrane built a double layer of?
Transport proteins
Carbohydrate chains
Lipid molecules
Protein channels
33.
Multiple Choice
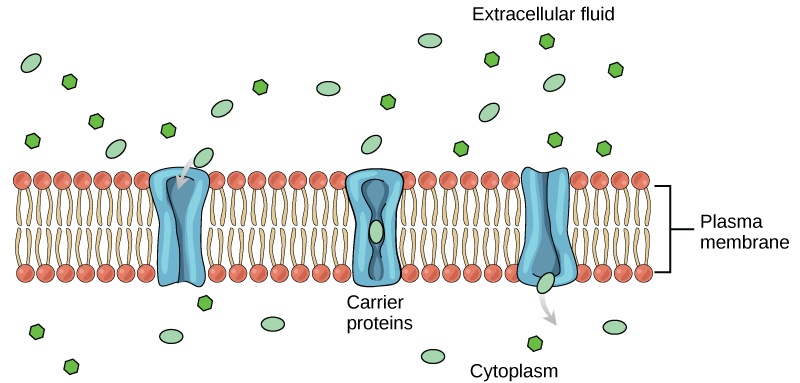
The diagram illustrates a cell membrane regulating passage of essential nutrients. Which property of the cell membrane is most closely associated with its ability to promote this process?
The cell membrane is able to obtain any substance.
The cell membrane is nonselectively permeable.
The cell membrane is selectively permeable.
The cell membrane is selectively nonpermeable.
34.
Multiple Choice
An instrument that makes small objects look larger is called a(n)
Microscope
Telescope
Electroscope
Hubblescope
35.
Multiple Choice
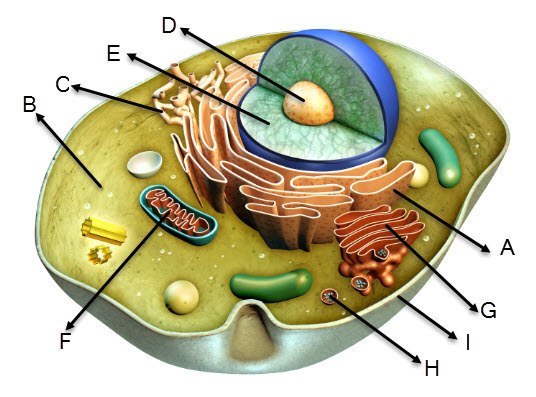
Examine the cell diagram. Which description is alinged with structure E?
It is the nucleus that contains genetic information for the cell.
It is the vacuole that stores water and other substances.
It is the mitochondrion that releases energy once food is broken down.
It is the cytoplasm that moves the organelles.
36.
Multiple Choice
A scientist observes that a young plant cell contains cytoplasm. However, as the cell matures, it expands by storing water. Which cell structure helps the plant maintain its shape through the process of cell growth?
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Lysosome
Cell wall
37.
Multiple Choice
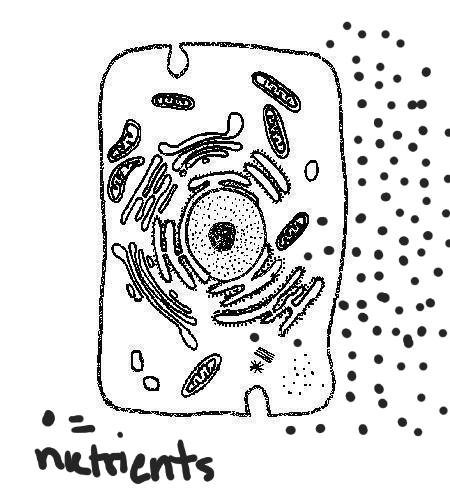

The diagram shows a cell membrane surrounded by nutrients. Which process best describes a way the cell can obtain these nutrients without requiring energy?
Osmosis
Diffusion
Active transport
Exocytosis
38.
Multiple Choice
What is the total magnification of a compound microscope with a 10x eyepiece and a 40x objective?
400x
4x
40x
50x
39.
Multiple Choice
What is the function of the flagellum in bacterial cells?
It produces enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions in cells.
Helps get rid of hazardous wastes that could harm the bacterial cell.
It helps the bacterium move.
It allows photosynthesis to happen.
40.
Multiple Choice
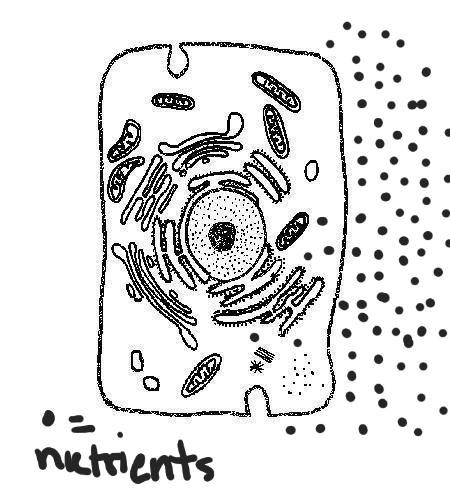

The diagram shows a cell surrounded by nutrients. Which statement most accurately describes the movement of nutrients by diffusion?
The nutrients will dissolve and then regrow.
The nutrients will move through the cell membrane to the higher concentration.
The nutrients will remain in equilibrium.
The nutrients will move the cell membrane to the lower concentration.
41.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are examples of unicellular eukaryotic organisms?
Amoebas and yeasts
Mushrooms and leaf cells
Red blood cells and humans
Algae and bacteria
42.
Multiple Choice
Which substances uses energy to pick up specific molecules and carry them across the cell membrane?
Protein channels
Carbohydrate chains
Transport proteins
Phospholipids
43.
Multiple Choice

The diagram shows a model of a bacterial cell a student created. The student needs to add a card for each structure that explains its function. Which table shows the correct arrangement of the cards with the cell structures?
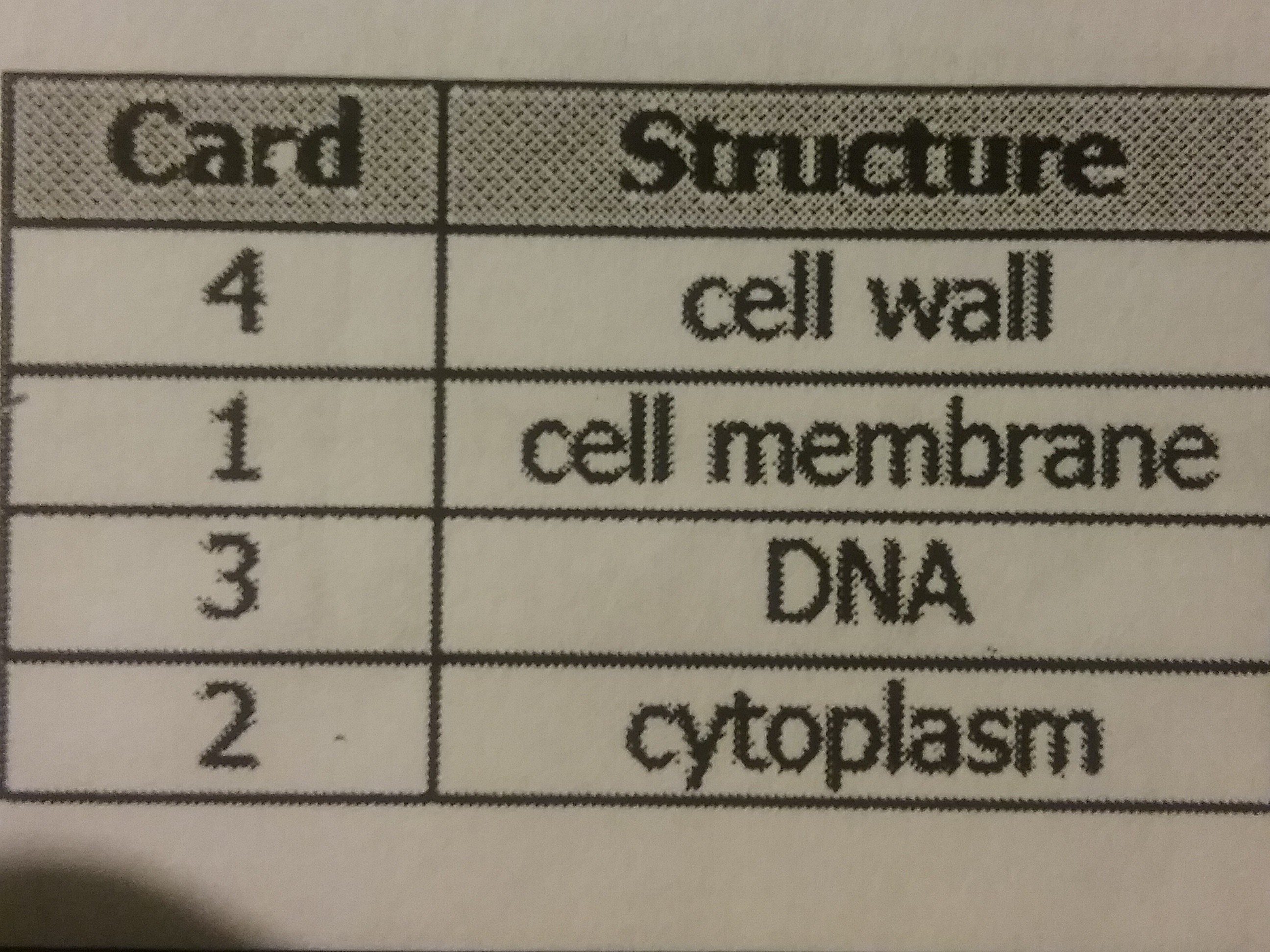
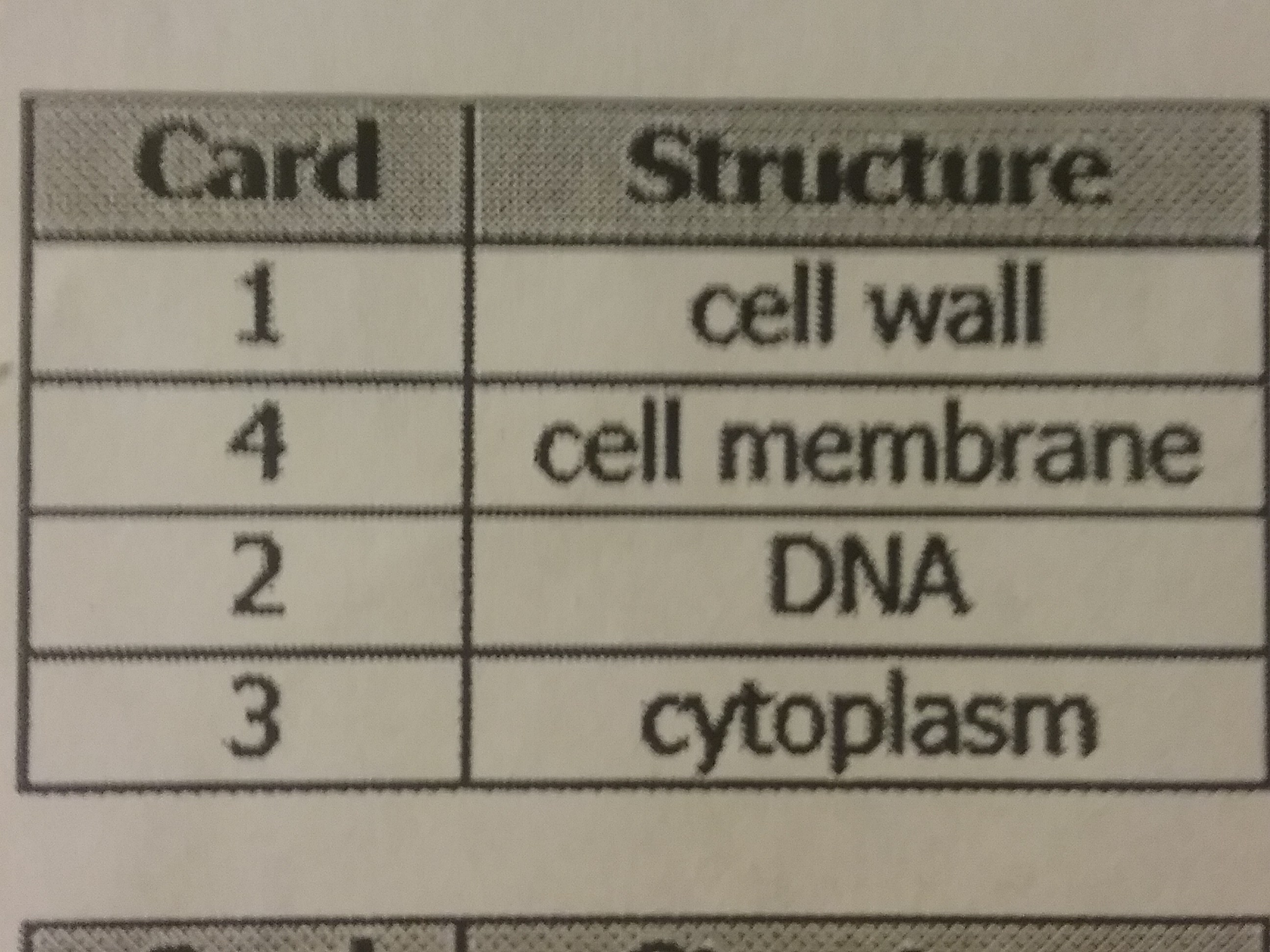
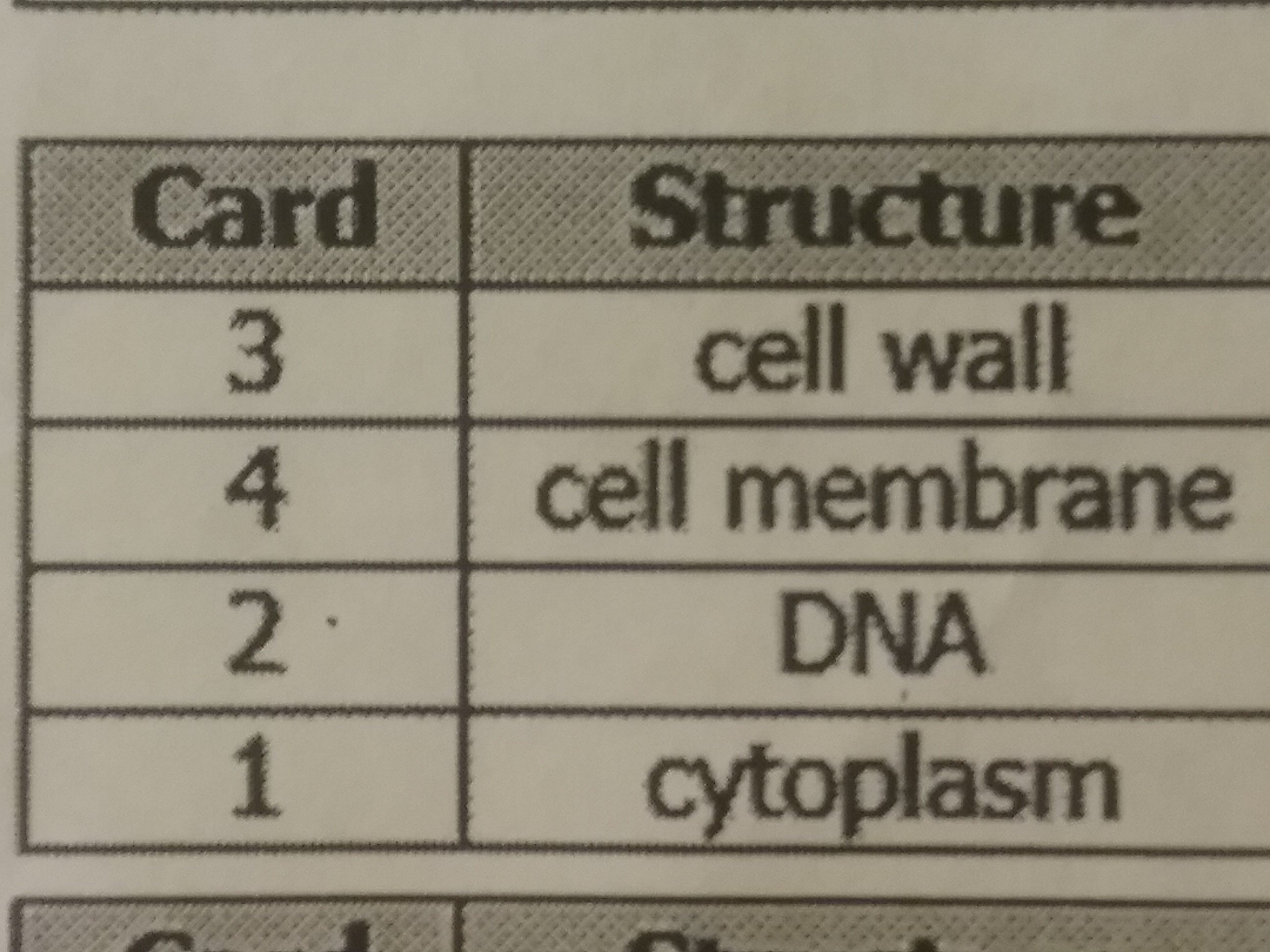
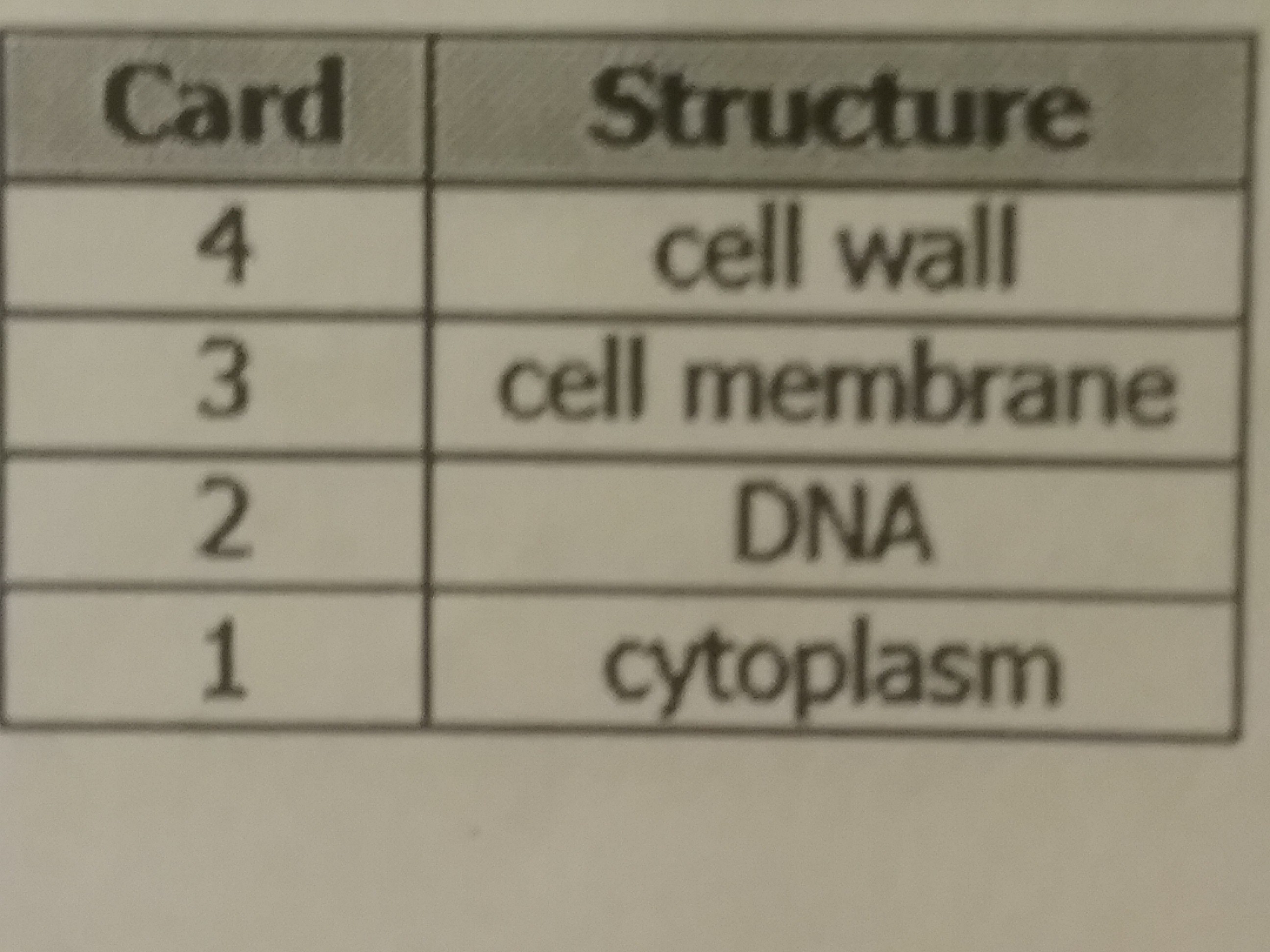
44.
Multiple Choice
A cell has difficulty storing food and wastes. This most likely indicates a problem with which organelle?
Lysosomes
The vacuole
The golgi complex
The cell wall
45.
Multiple Choice
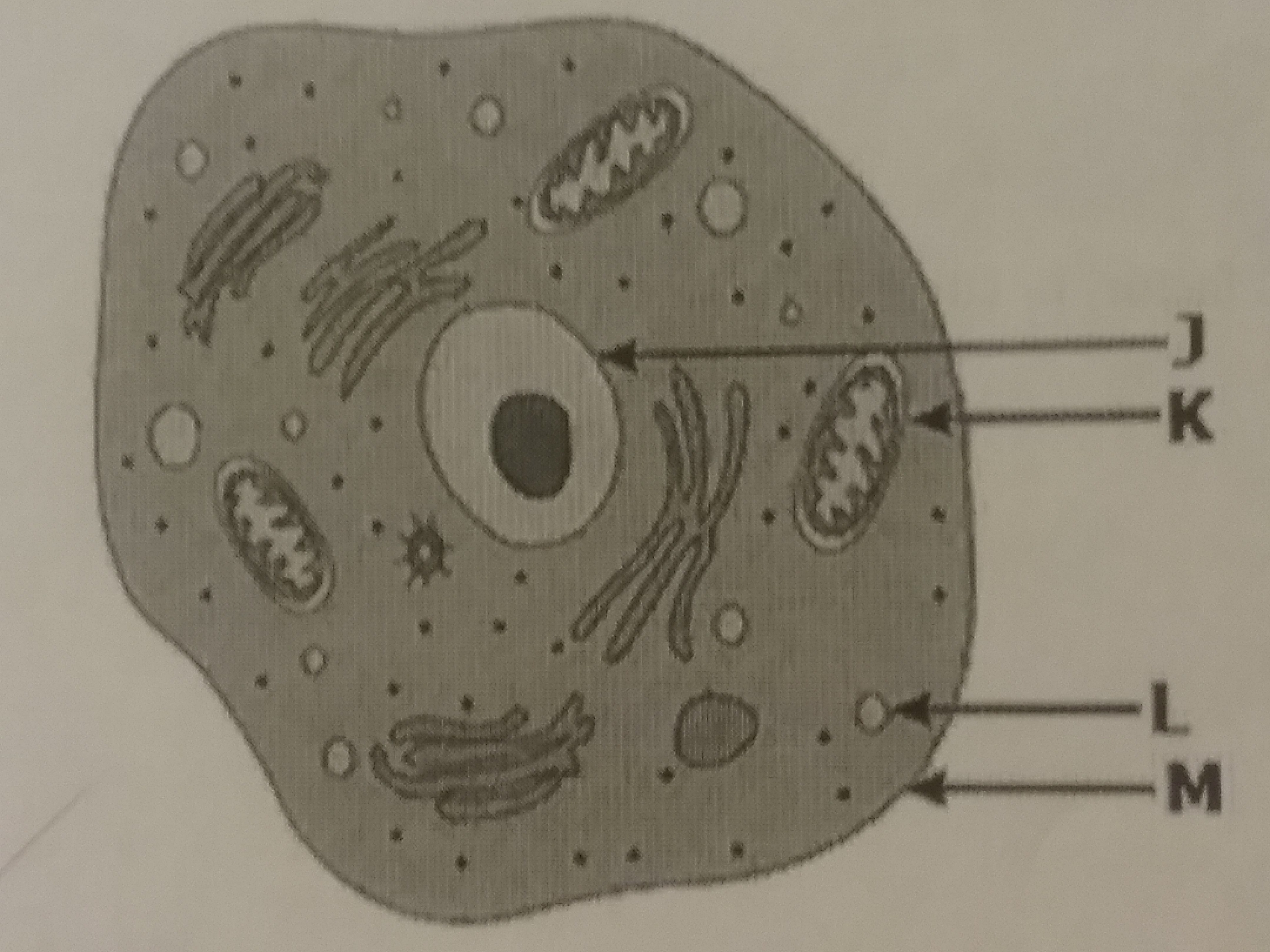
A student examines a cell with organelles J, K, L, and M labeled. Correctly identify the organelles.
J: Nucleus, K: Centriole, L: Lysosome, M: Cell wall
J: Nucleus, K: Lysosome, L: Vacuole, M: Cell wall
J: Nucleus, K: Vacuole, L: Mitochondria, M: Cell membrane
J: Nucelus, K: Mitochondria, L: Lysosome, M: Cell membrane
46.
Multiple Choice
What is the role of simple diffusion?
It helps the cell contract
It helps the movement of particles maintain in balance
It controls the movement of particles
It allows the cell to expand or contract
47.
Multiple Choice
What are proteins in cells?
Large organic molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur.
Helps speed up chemical reactions in cells and living things.
Energy-rich organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Very long organic compounds
48.
Multiple Choice
Which level of organization is the basic unit of structure and function in humans?
Tissues
Cells
Organs
Organ system
49.
Multiple Choice
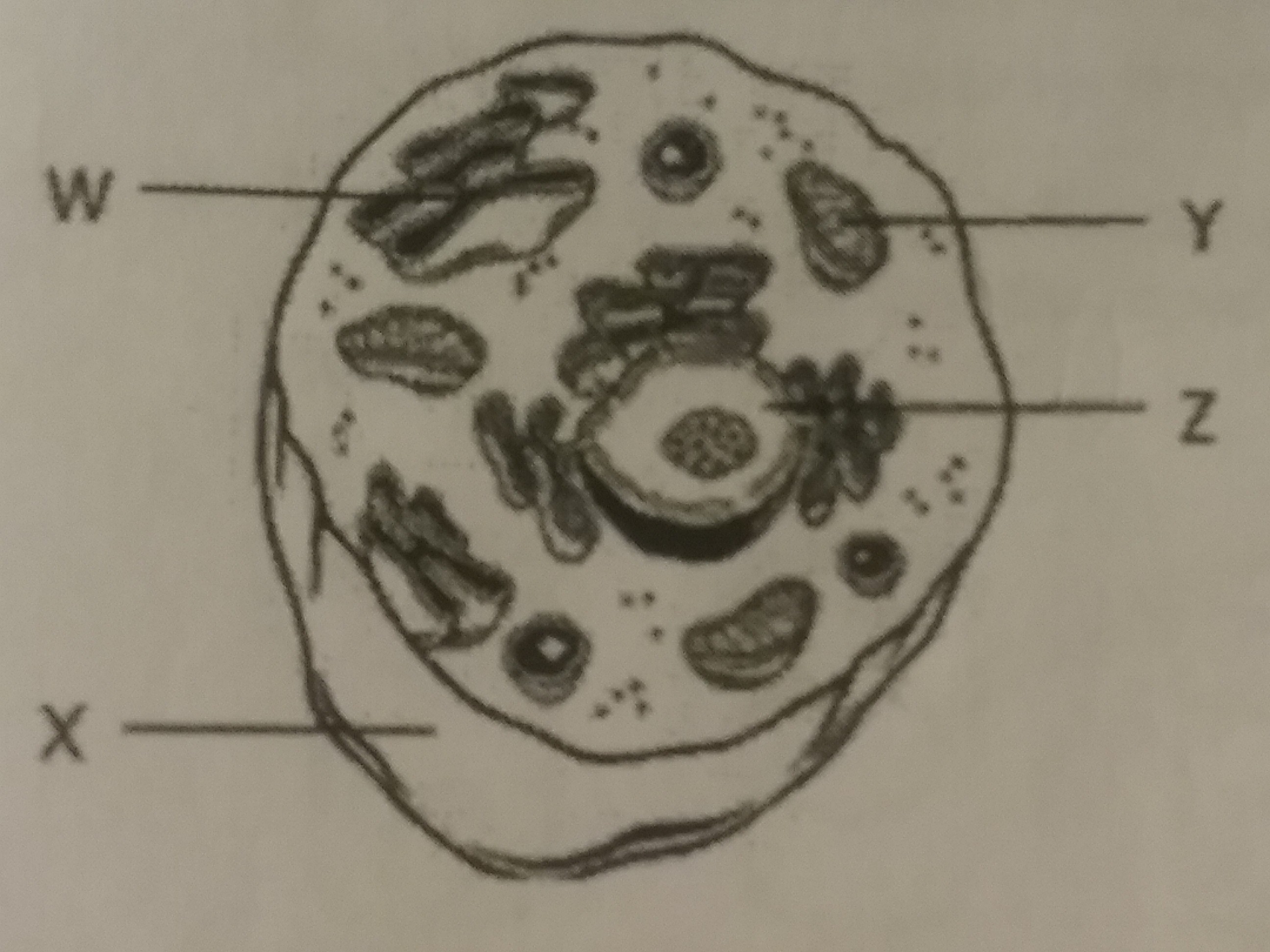
Study the diagram. Which organelle regulates what enters and leaves the cell?
W: Golgi body
X: Cell membrane
Y: Mitochondrion
Z: Nucleus
50.
Multiple Choice
Cathy wrote the structures and functions of different cell organelles. Which structure is INCORRECTLY paired with its function.
Chloroplast: provides food
Mitochondrion: provides support
Nucleus: controls cell
Vacuole: stores water
51.
Multiple Choice
In which structure does photosynthesis take place in a green plant.
Nucleus
Mitochondrion
Lysosome
Chloroplasts
52.
Multiple Choice
Which statement correctly describes the differences between cell membranes and cell walls?
Cell membranes are only found in animal cells, while cell walls are found in both plant and animal cells.
The cell membranes of plant and animal cells are flexible and do not have a definite shape, while the cell walls of plant cells are rigid which gives plant cells a definite shape.
Cell membranes are the outermost covering in plant cells, while cell walls are in direct contact with the cytoplasm of animal cells.
The cell membranes of plant and animal cells are impermeable, which allows nothing to pass, while the cell walls of plant cells are permeable which allows small things to pass
53.
Multiple Choice
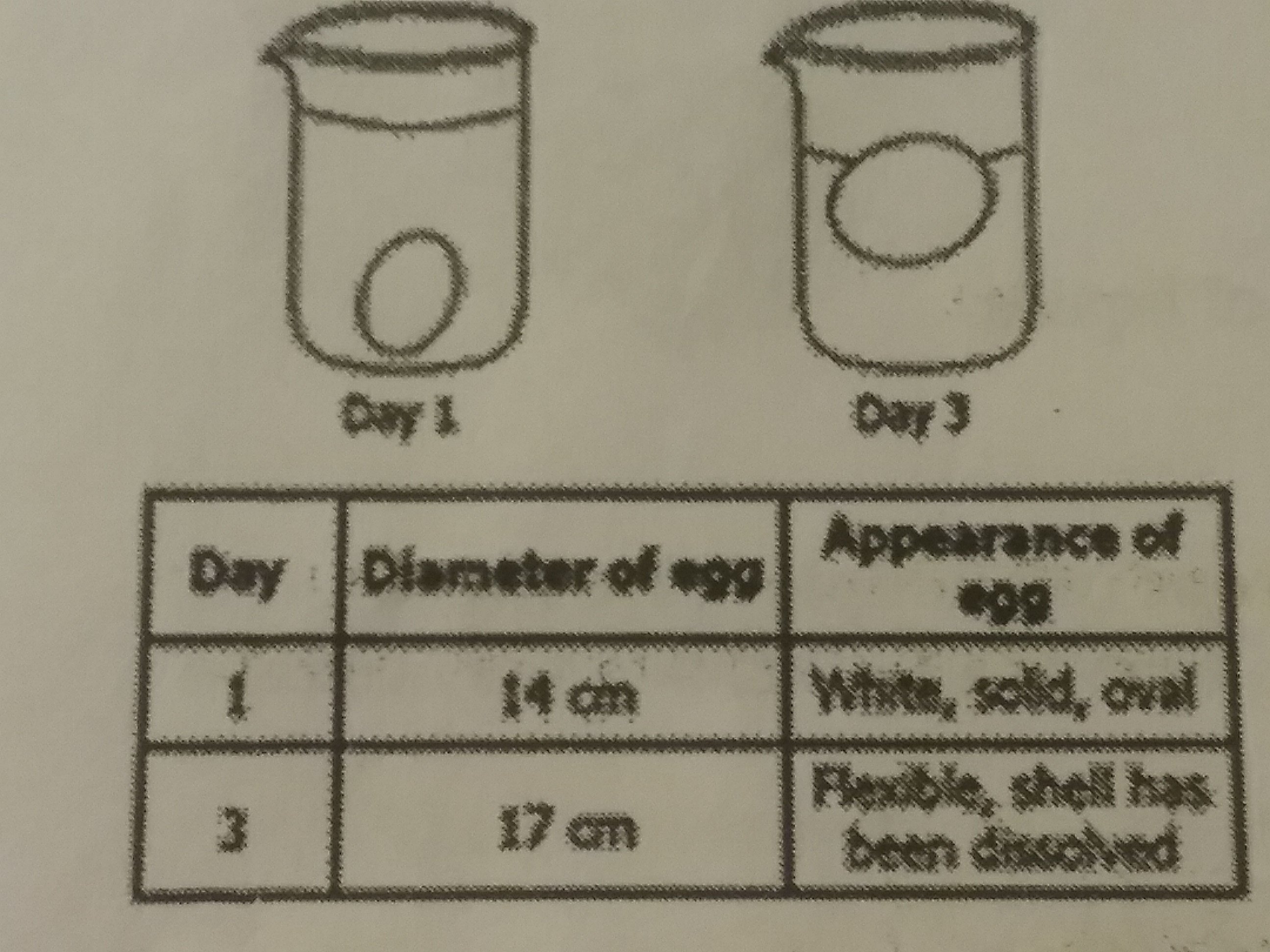
Carlos was studying the cell membrane by using an egg as a model of the cell. He soaked an egg in vinegar for 2 days and measured the circumference. His results are shown in the diagram and table. Which statement best explains why the egg's size increased?
The egg began to decompose, and bacteria caused the egg to swell.
A chemical reaction with the vinegar formed gases inside the egg.
The vinegar caused the surface of the egg to relax, resulting in expansion and swelling.
The surface of the egg is selectively permeable and allows liquids to diffuse into the egg.
54.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following correctly explains what proteins are made out of after ribosomes has completed its synthesis of proteins?
Sugars, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates
Lipids called phospholipids
Hydrochloric acids and rubidium hydroxide
Organic compounds called amino acids
55.
Multiple Select
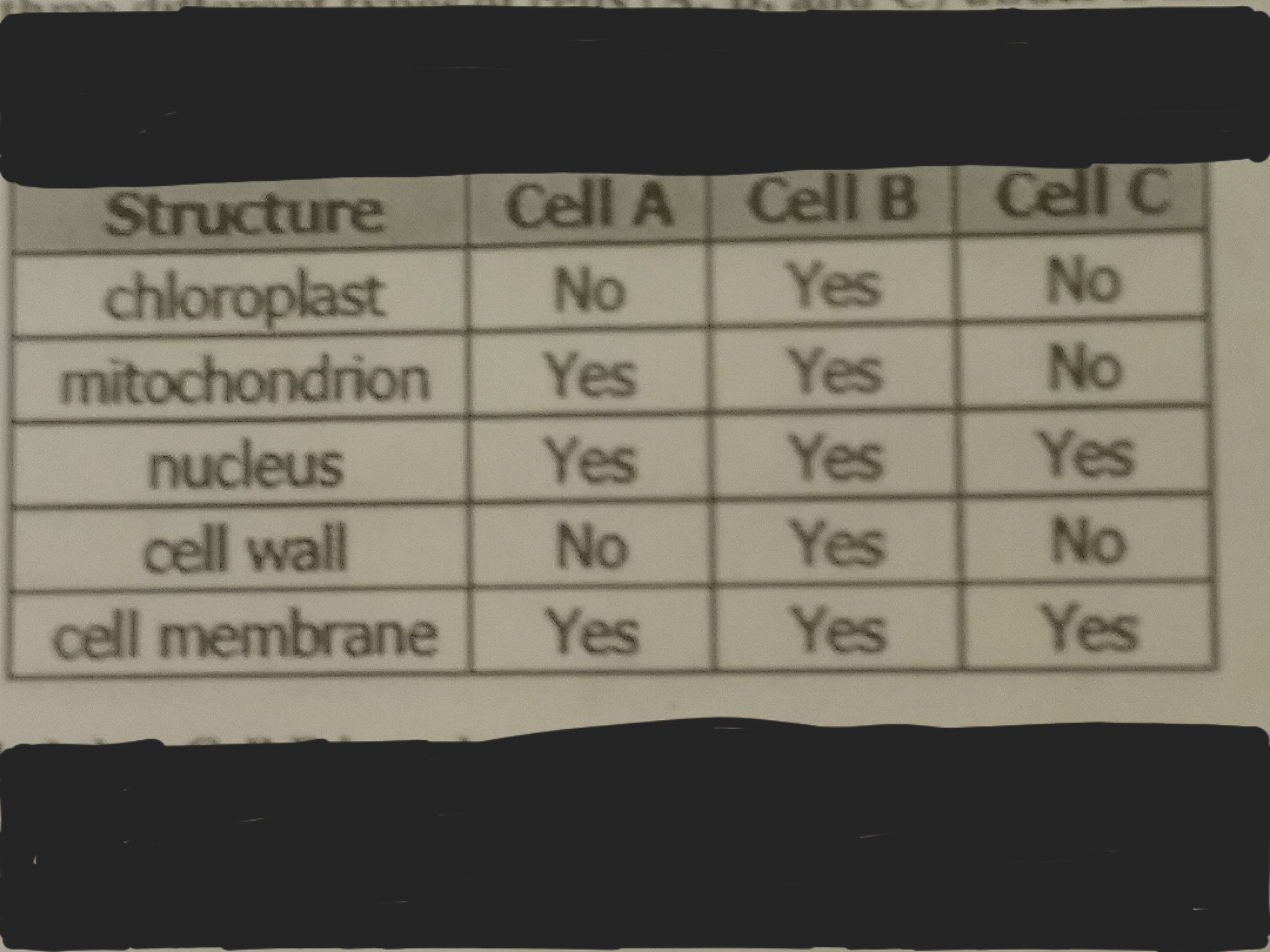
A student observed three different types of cells (A, B, and C) under a mircoscope. He made a list of the structures present and absent in the observed cells in the table shown. The student concluded that Cell B is a plant cell. Which structures observed in Cell B led the student to the conclusion? MARK ALL THAT APPLY.
It contains chloroplasts
It contains a cell membrane
It contains a cell wall
It contains a nucleus
56.
Multiple Choice
Which Venn diagram accurately depicts thr similarities and differences between plant and animal cells?
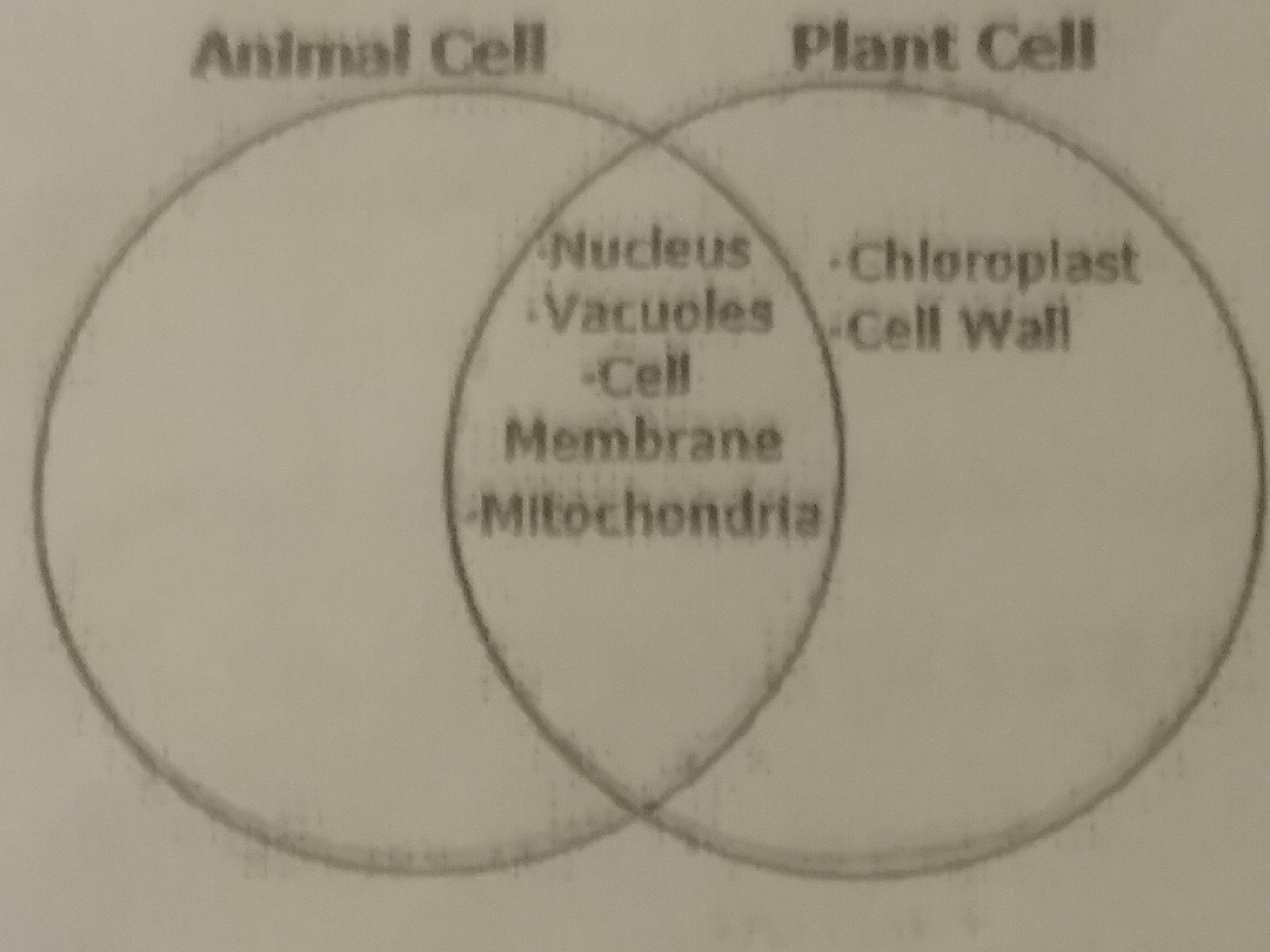
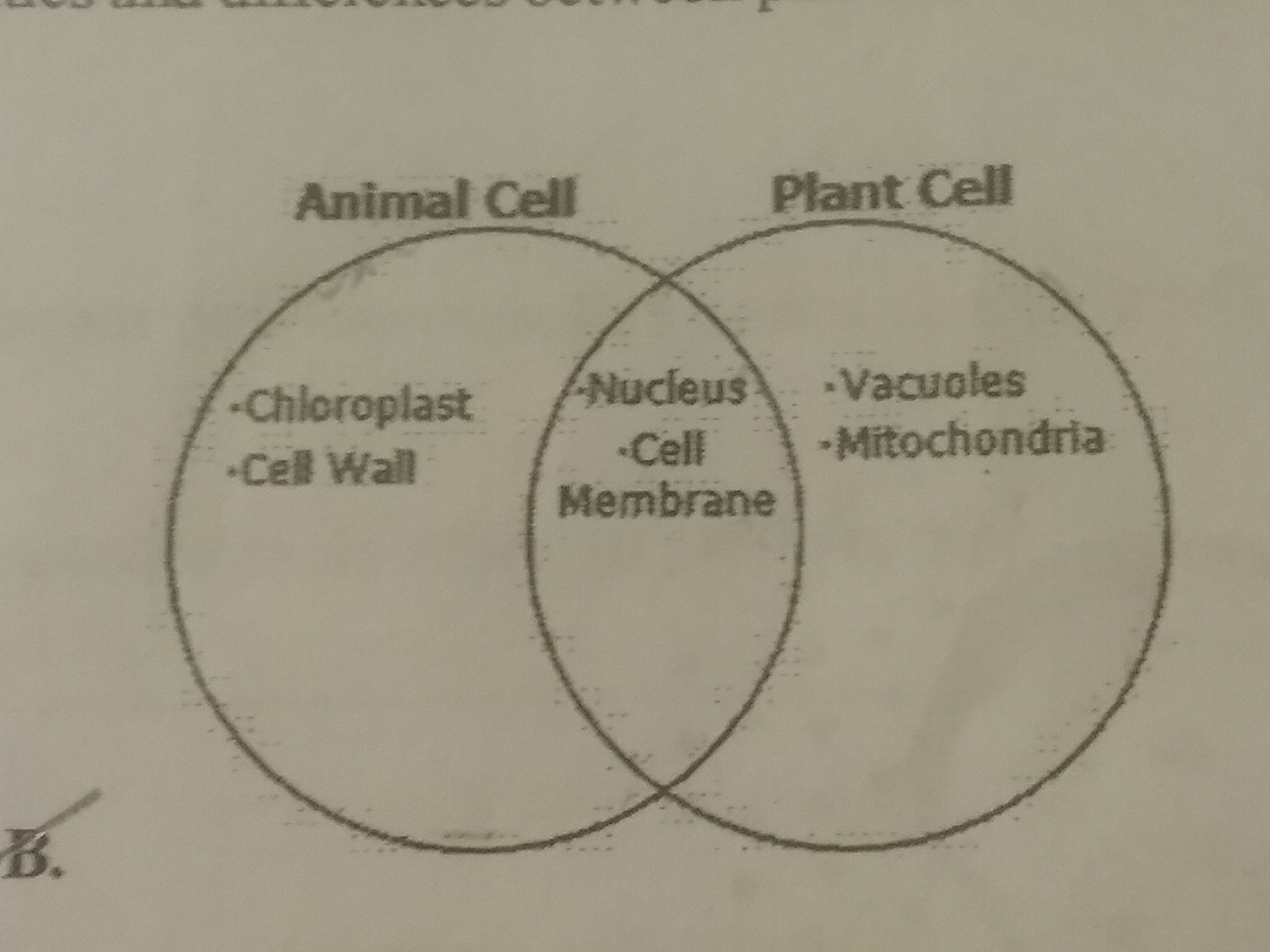
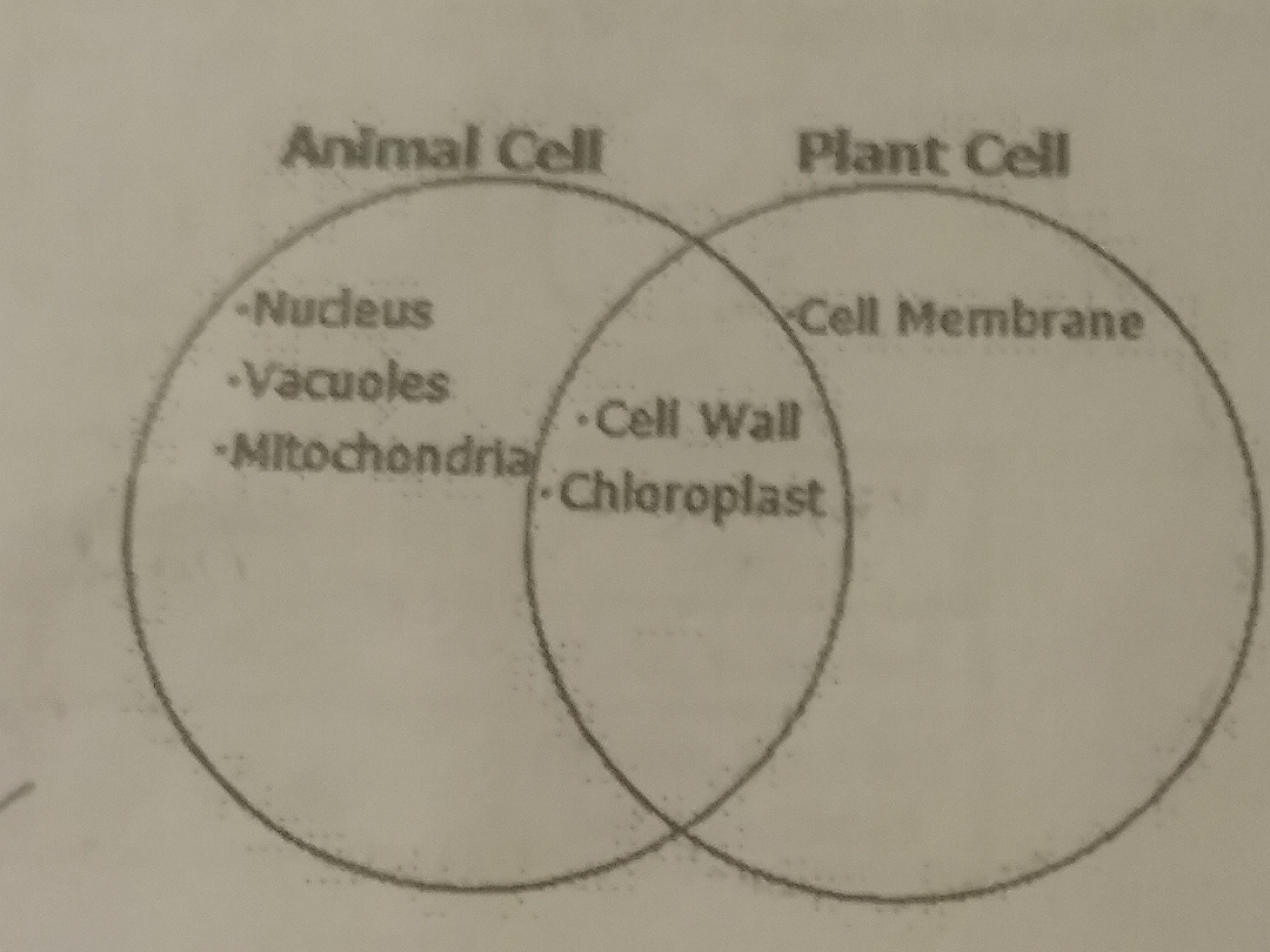
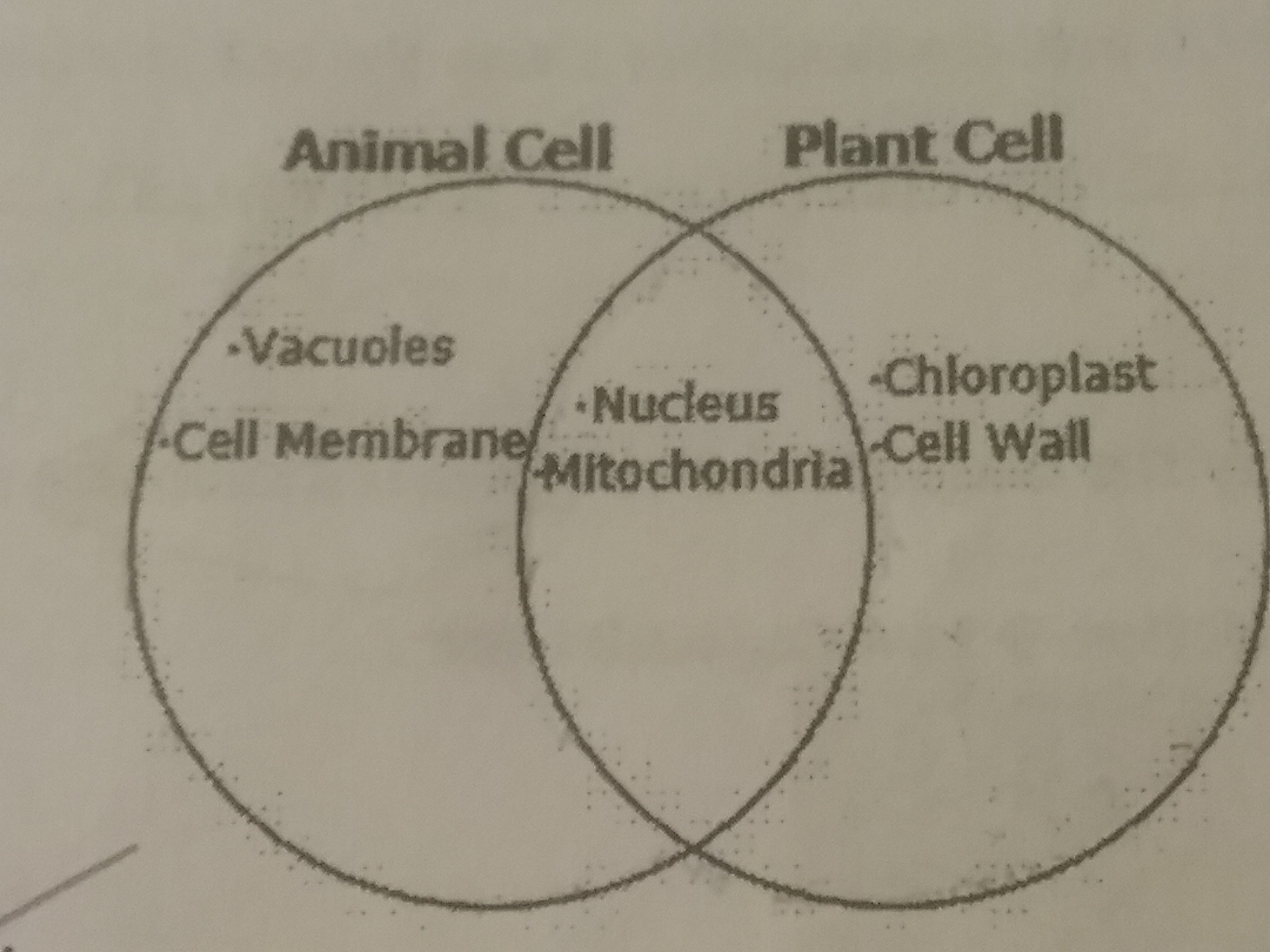
57.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly shows the levels of organization in a human from lowest to highest?
Cell to organ system to tissue to organ
Organ to tissue to organ system to cell
Cell to tissue to organ to organ system
Organ system to cell to organ to tissue
58.
Multiple Choice
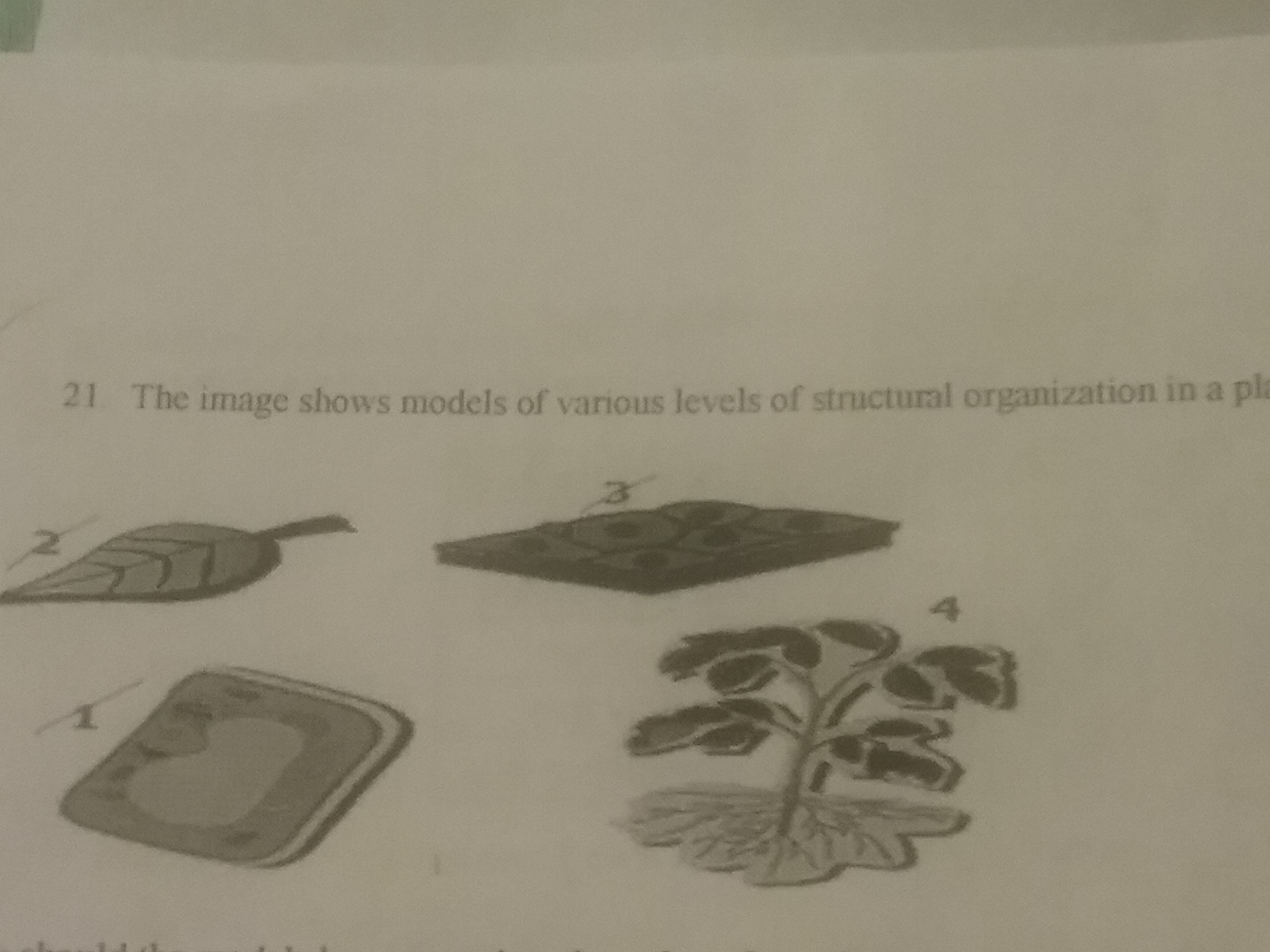
How should the models be arranged to show thrm from the most simple to the most complex?
1 -> 3 -> 4 -> 2
1 -> 4 -> 2 -> 3
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4
1 -> 3 -> 2 -> 4
59.
Multiple Choice
A small sac that moves and distributes materials within a cell and carry new proteins from the ER to the golgi apparatus is called a(n)
Vesicle
ER
Centriole
Vacuole
60.
Multiple Choice
Which model accurately represents the levels of organization within a plant?
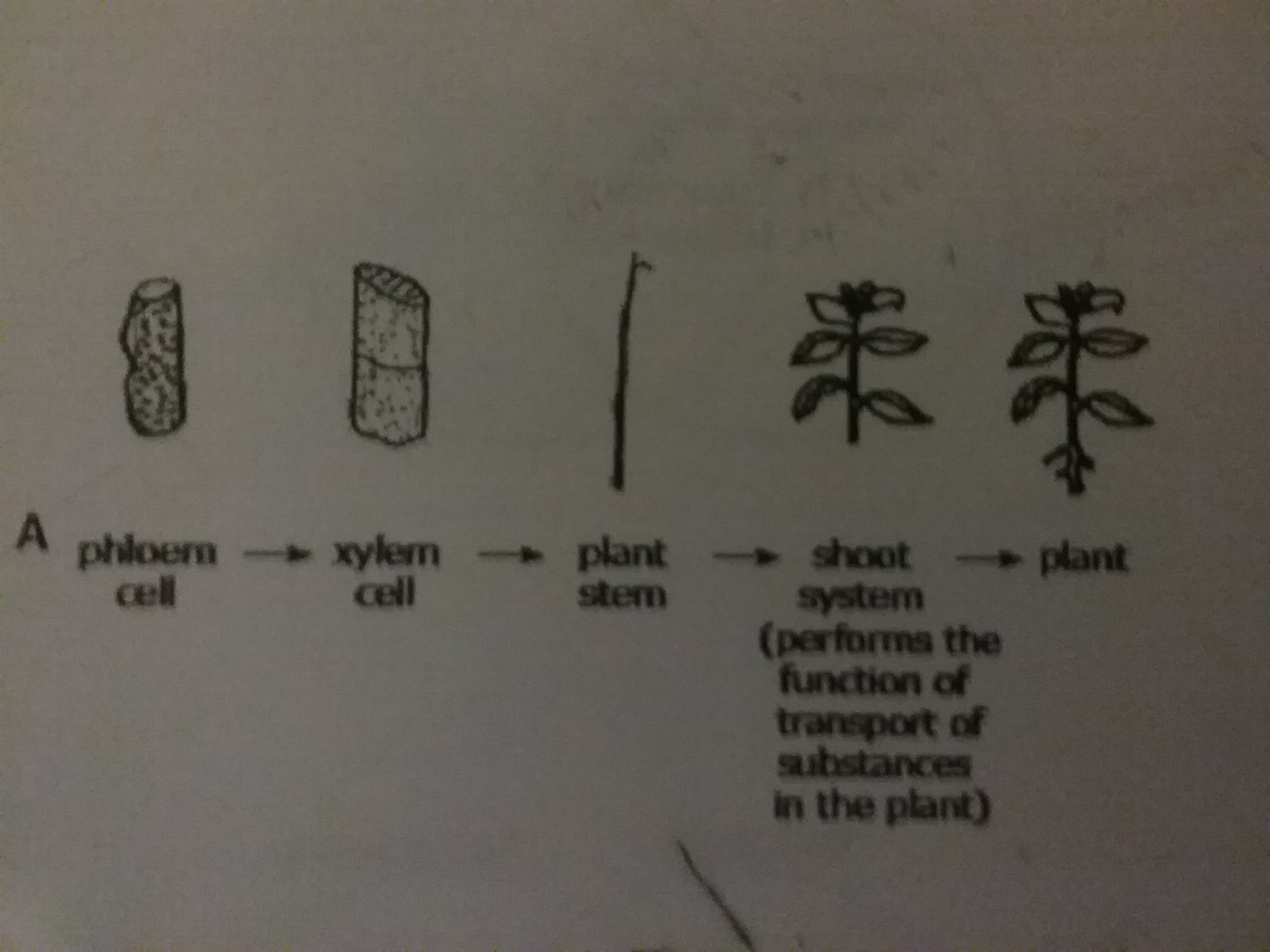
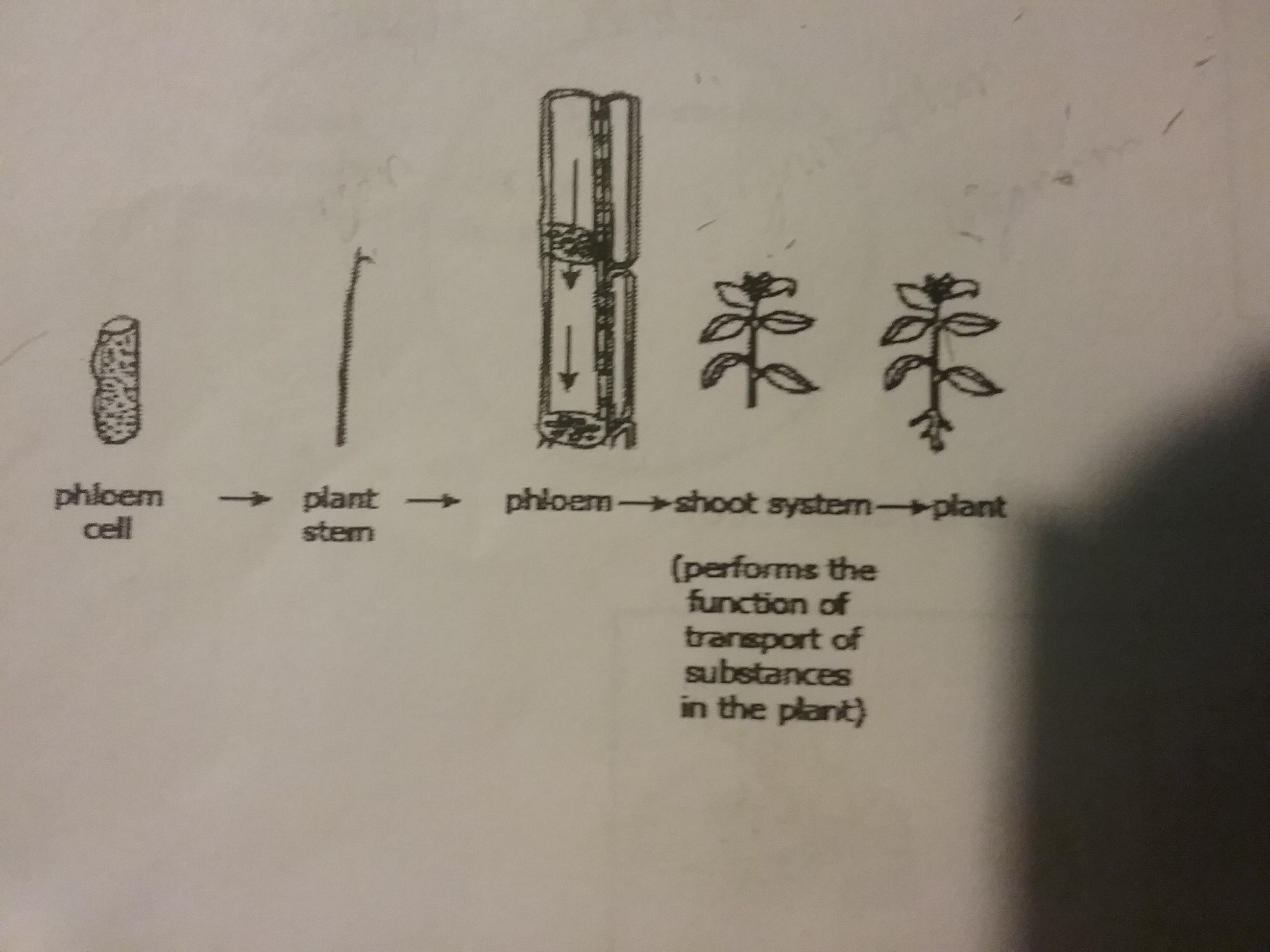
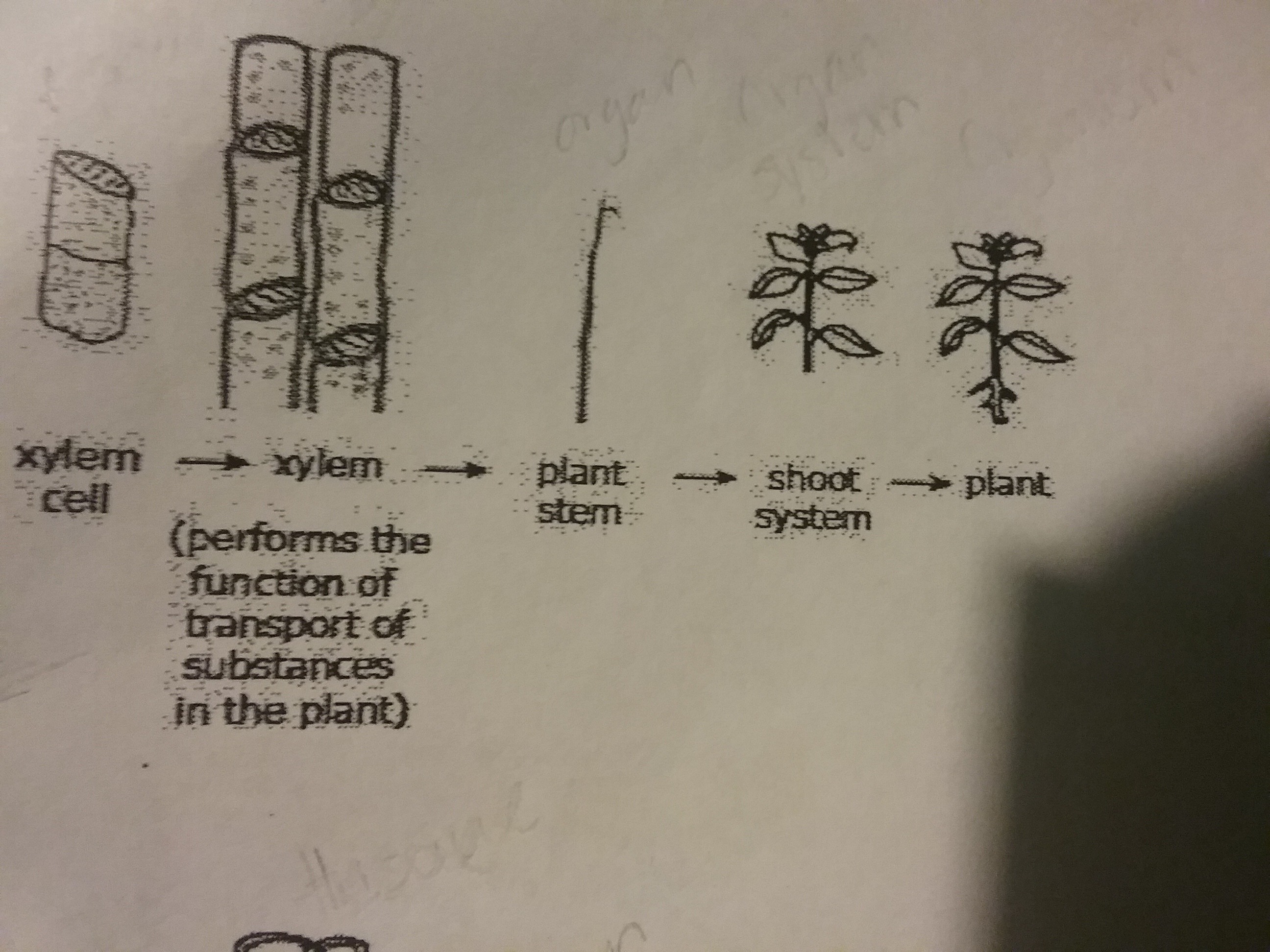
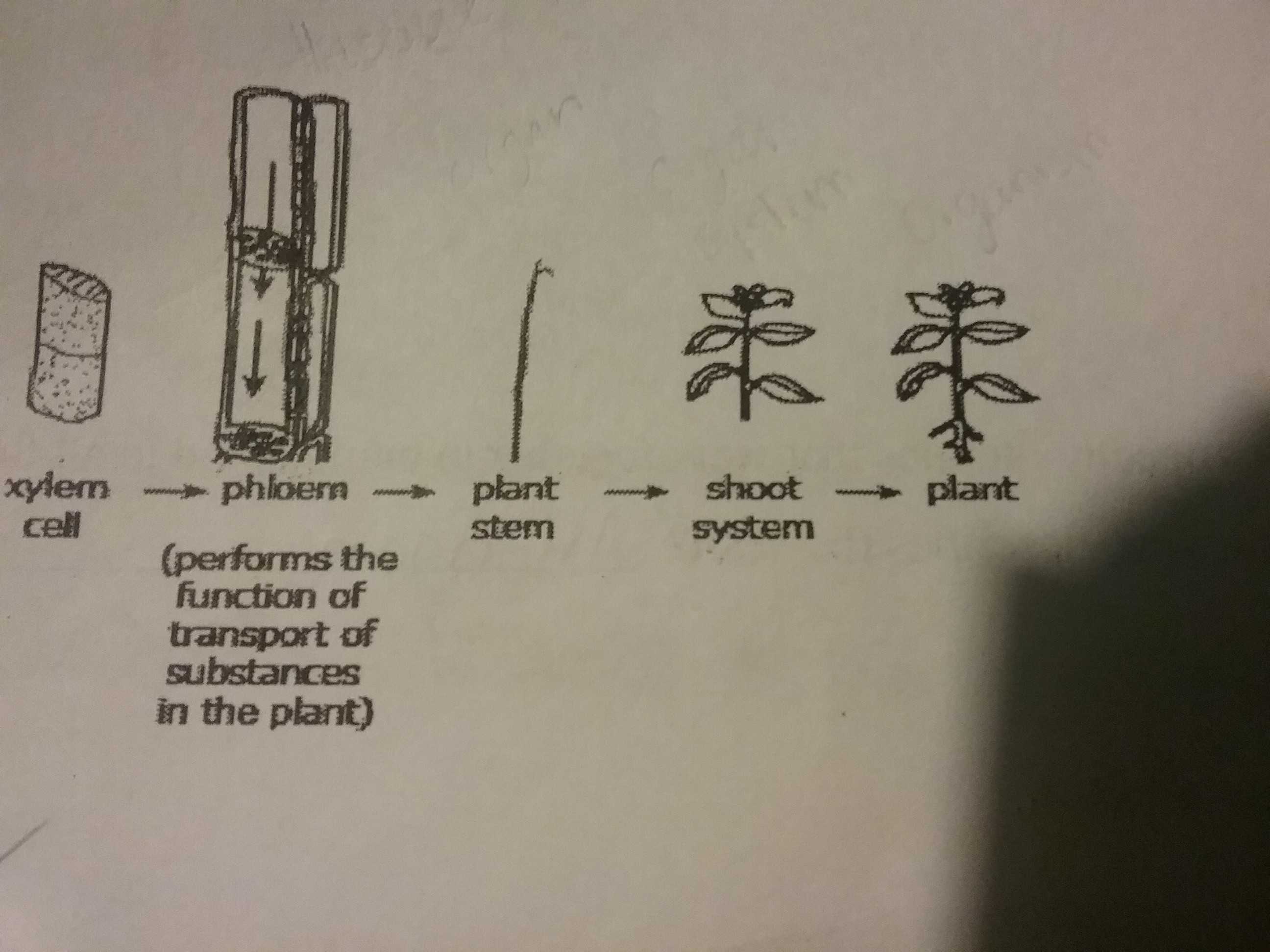
61.
Multiple Choice
The heart is made up of muscle tissues and connective tissues that work together to pump blood to all the parts of the body. Which level of organization best describes the heart?
A cell
A tissue
An organ system
An organ
62.
Multiple Choice
What special region in the nucleus are ribosomes made?
In the nucleolus
In the nuclear membrane
Outside of the rough ER
In the golgi apparatus
63.
Multiple Choice
The human body has many levels of organization. Which diagram shows the correct order of these levels?
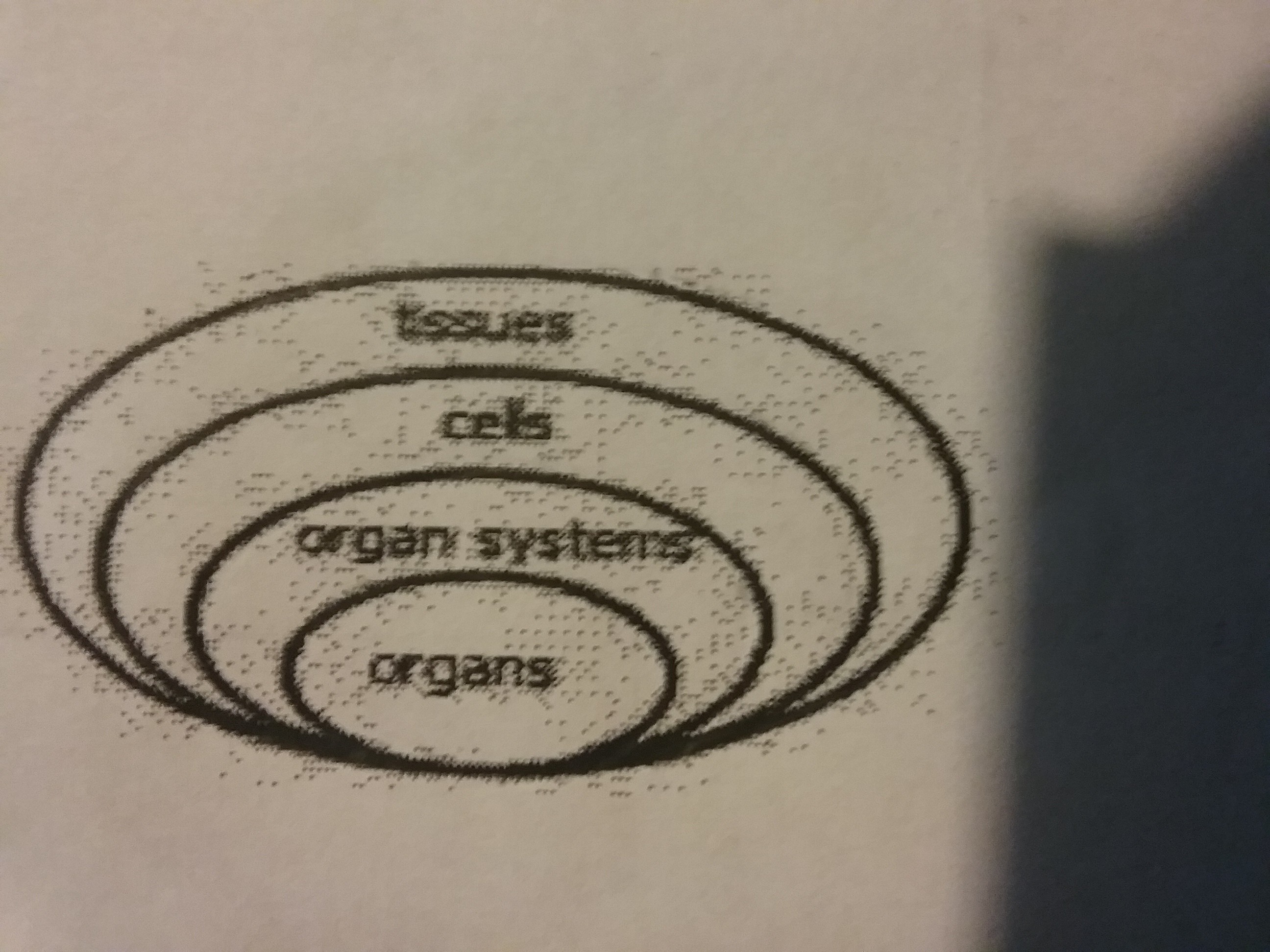
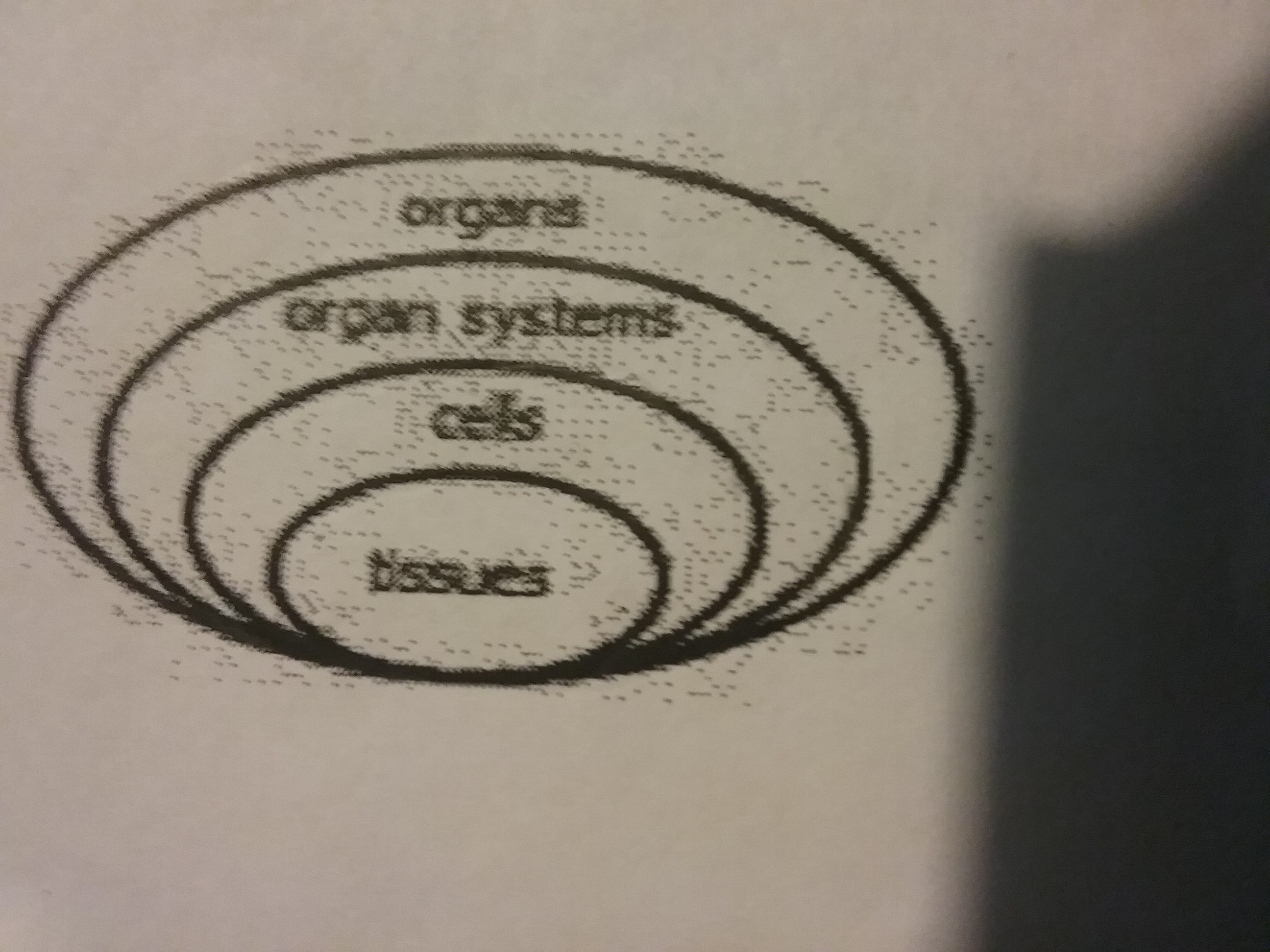
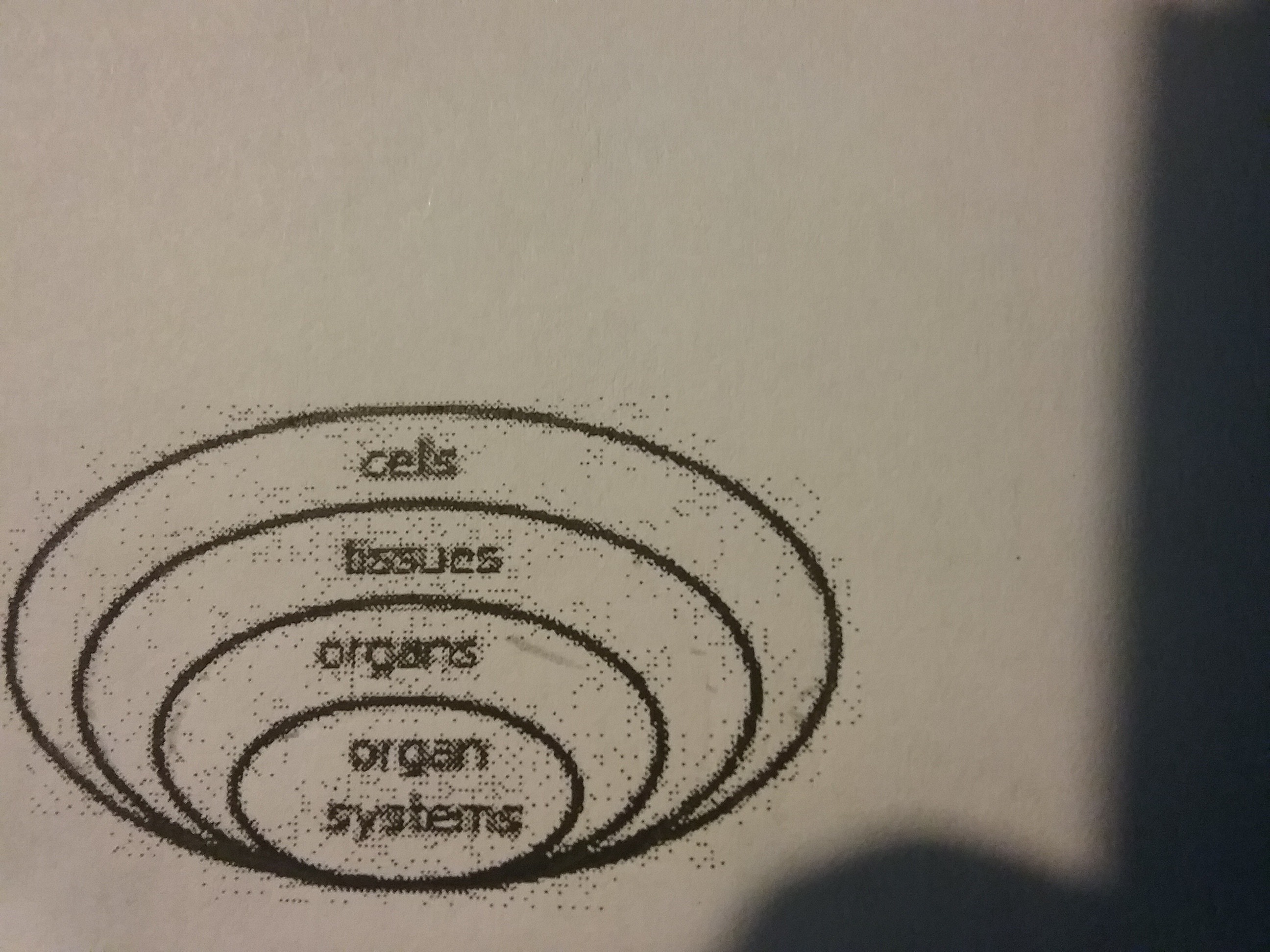
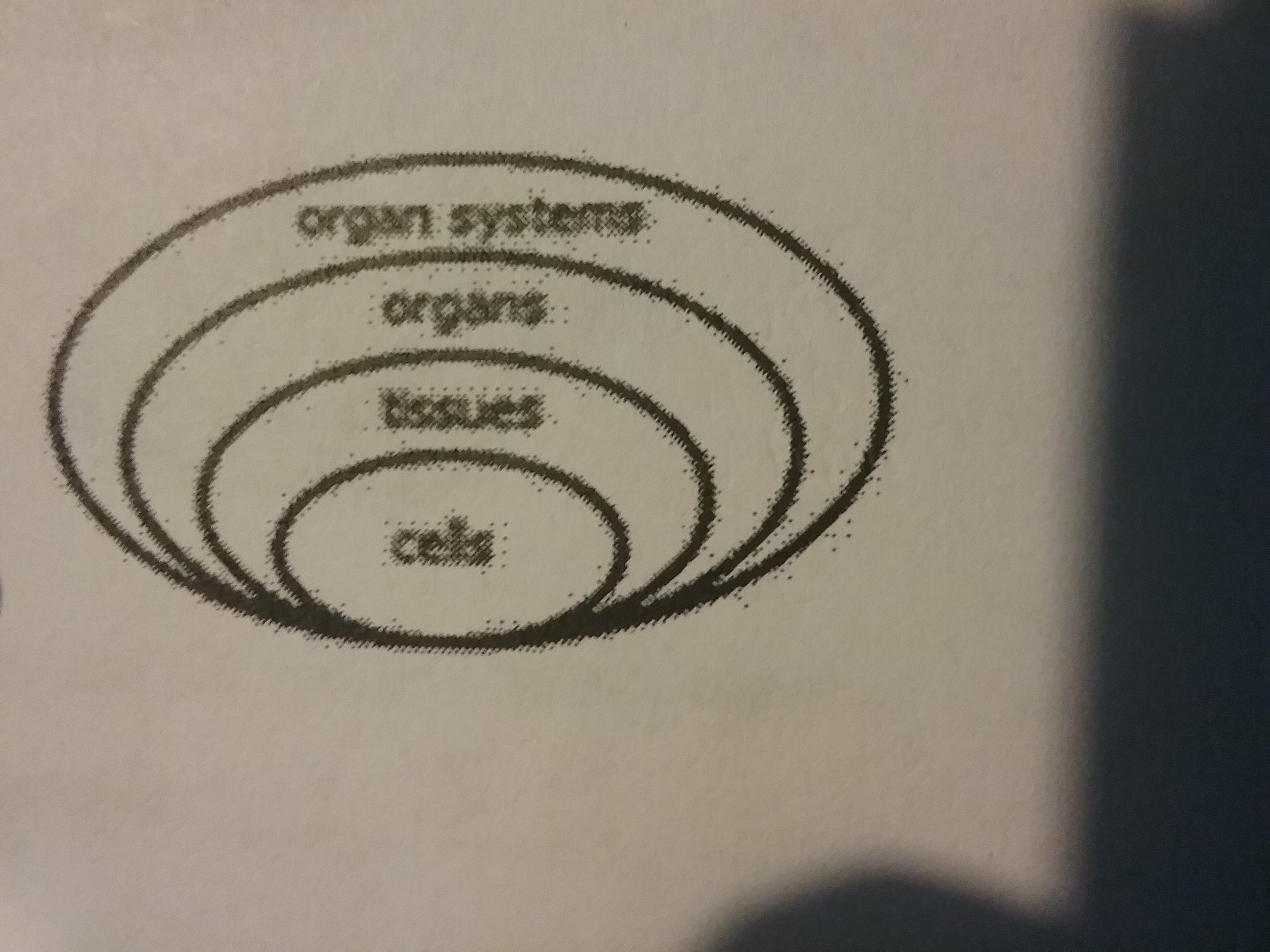
64.
Multiple Choice
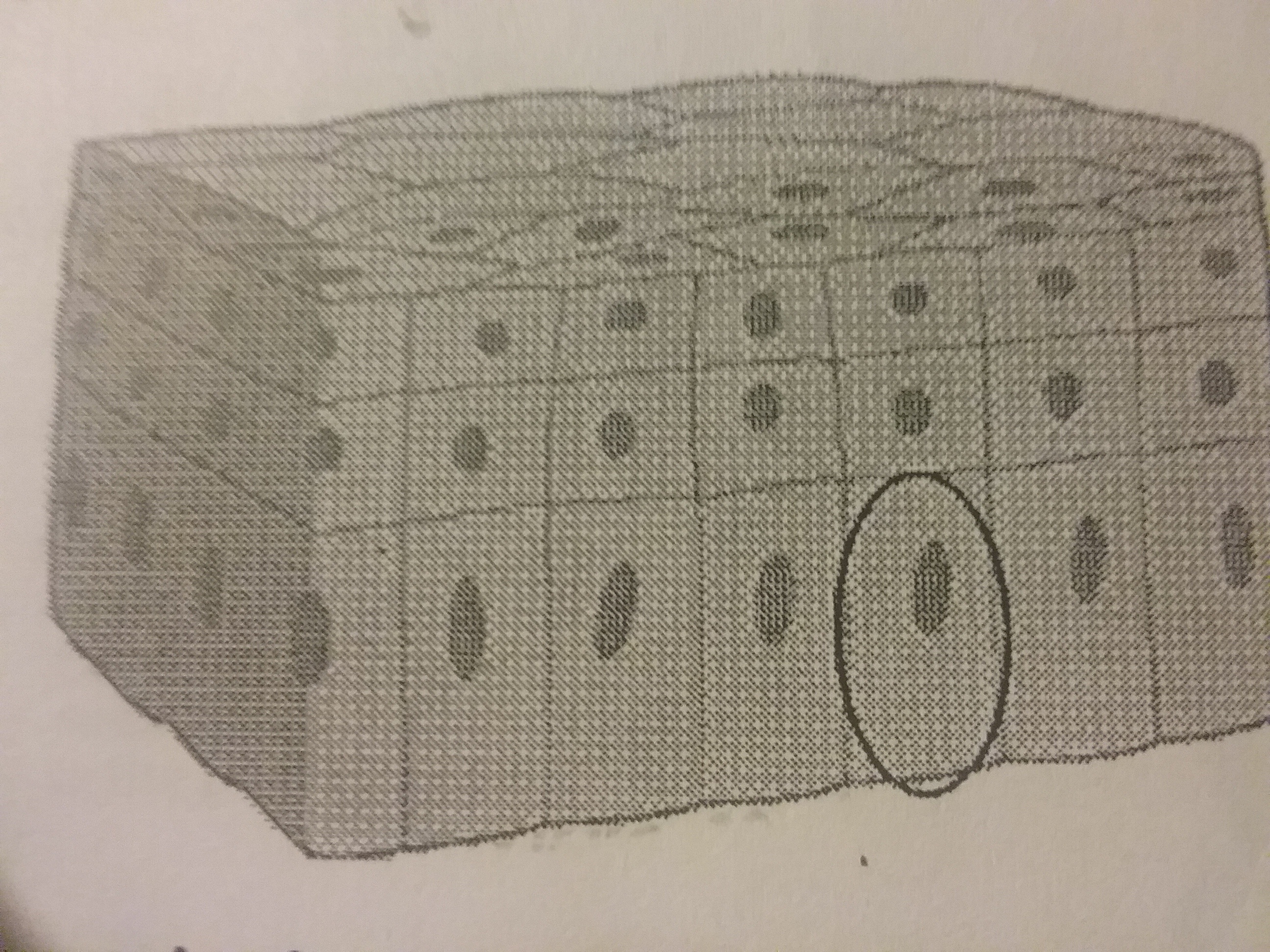
The diagram shows a cross section of a layer of skin. Which level of structural organization does the circled portion represent?
A cell
A tissue
A organ
A organ system
65.
Multiple Choice

Study the diagram showing water molecules and a cell membrane. Which cellular process is being represented?
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
Endocytosis
66.
Multiple Choice

Cell function is often compared to the operation of a factory or city. Jasmin put together this table comparing cell organelles to functions in a city. Jasmin's teacher told her she made one mistake. Which comparison should Jasmin change?
Vacuole- Recycling center
Golgi body- Electric current
Lysosome- Border
Ribosome- Construction sites
67.
Multiple Choice
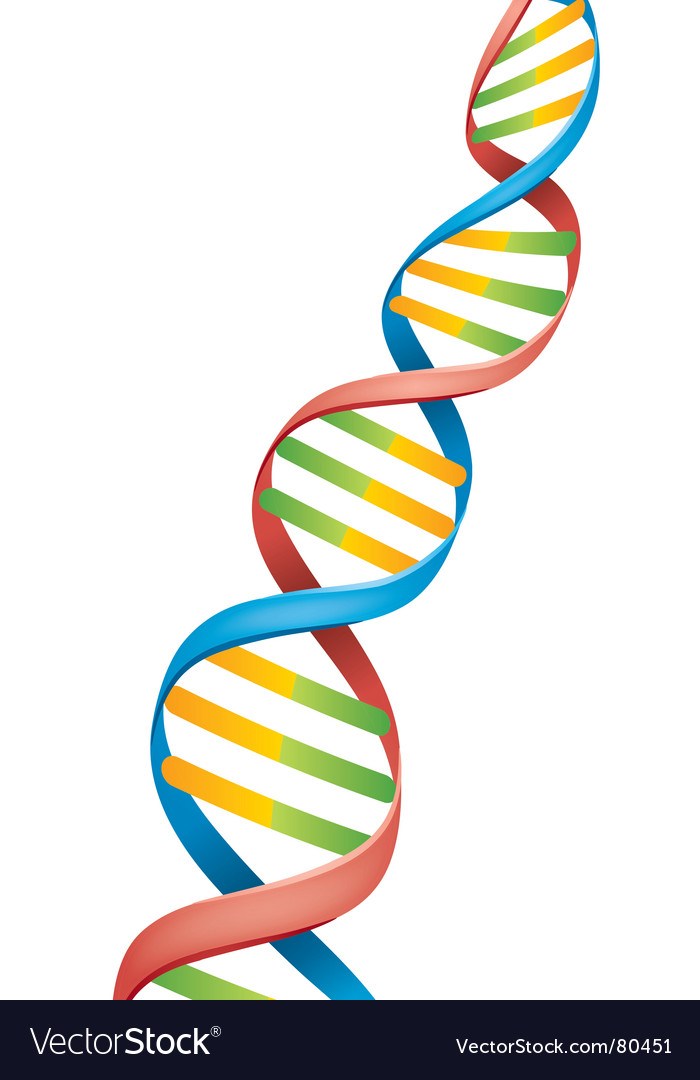

The image shown shows the double helix of DNA. Where is DNA mostly found in multicellular or unicellular eukaryotes?
In centriole
In the nucleus
In the vacuole
In the ER
68.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the difference between smooth ER and rough ER?
Smooth ER lacks ribosomes, while rough ER is covered in ribosomes.
Smooth ER allows photosynthesis to take place, while rough ER directs the synthesis of ribosomes
Smooth ER is covered in ribosomes, while rough ER lacks ribosomes.
Smooth ER is where cell divsion to take place, while rough ER allows photosynthesis to happen.
69.
Multiple Choice
How is a solar panel similar to chloroplasts?
They both use water and sugars to produce substances that can be useful for life.
They both take in food and convert it to energy.
They both take in energy from the sun and use it to produce things that are important for the environment.
70.
Multiple Choice
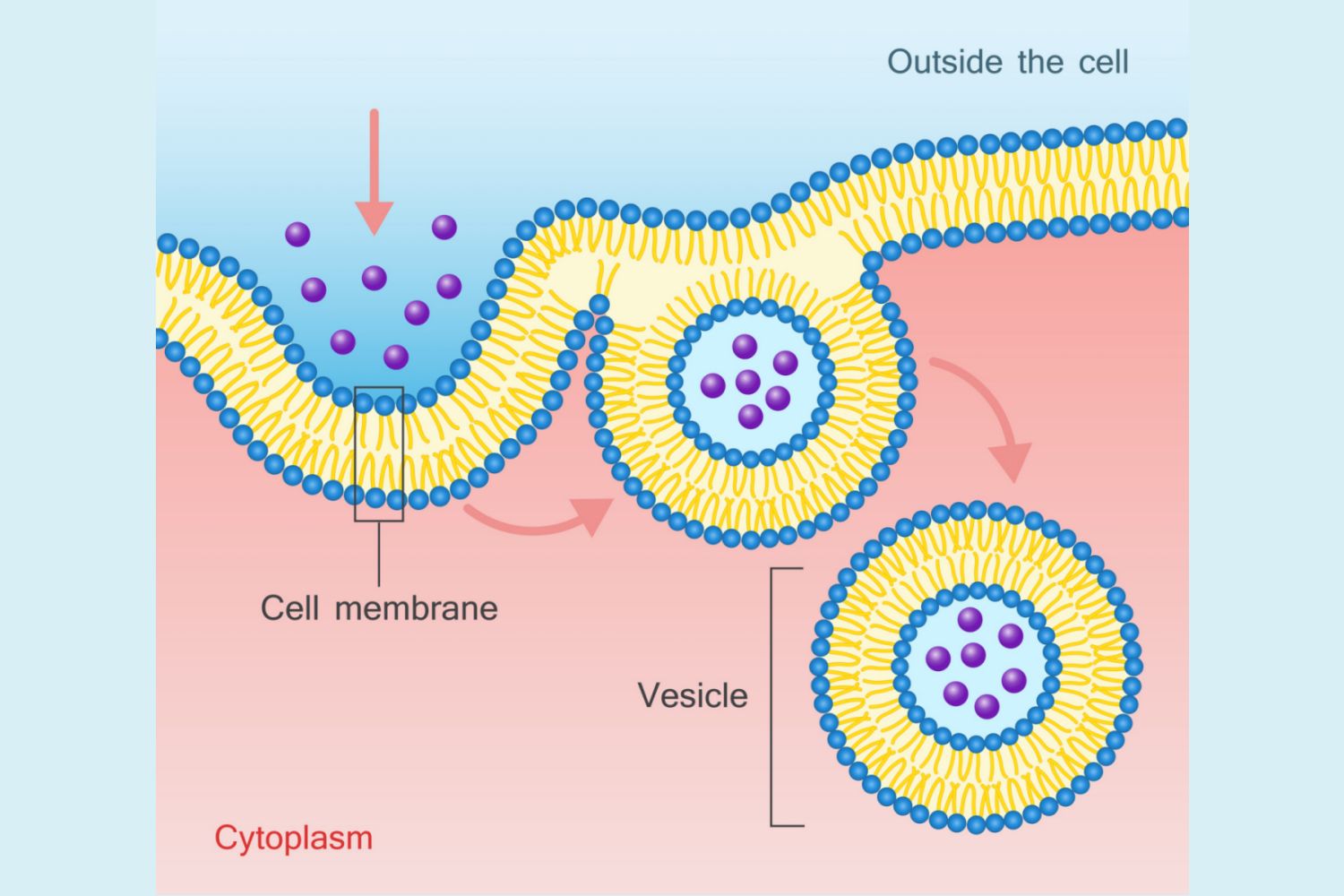
Look at the diagram. Which cellular process is being represented?
Exocytosis
Diffusion
Osmosis
Endocytosis
71.
Multiple Choice
During endocytosis, what is formed after a large particle is engulfed by the cell membrane?
Vescicle
A nucleus
A centriole
A ribosome
72.
Multiple Choice
What happens during exocytosis?
A vacuole or vesicle fuses with the cell membrane. The cell membrane then forms an opening and spill the contents.
The cell membrane changes shape and engulfs the particle. A vesicle is then formed.
Particles moves from higher concentration to lower concentration.
The cell membrane form channels where proteins and sugars can pass through easily.
73.
Multiple Choice
Why is diffusion and osmosis considered as passive transports?
They both move from lower concentration to higher concentration by using cellular energy.
They both move from higher concentration to lower concentration without the use of cellular energy.
They both use water and nutrients for them to move.
They boh use cellular energy since they move in a process called endocytosis.
74.
Multiple Choice
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
It stores food, water, and other materials needed by cells.
It converts food into energy the cell can use.
They are found mostly in animal cells that are responsible for digestion of wastes inside a cell.
It is a system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other materials are made; it is part of the internal delivery system of the cell.
75.
Multiple Choice
What are the three types of plant tissues?
Nerve tissue, epithelial tissue, and connective tissue
Transport tissue, protective tissue, and ground tissue
Stem tissue, leaf tissue, and root tissue
Fibrous tissue, taproot tissue, xylem tissue

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Cells and Cell Organelles
•
7th Grade

Plant and Animal Cells
•
5th - 6th Grade

Plant and Animal Cells
•
6th Grade

Cell Organelles
•
7th Grade

Plant and Animal Cells
•
5th Grade

Cell Structure and Function
•
7th - 8th Grade

Plant and Animal Cells
•
6th - 8th Grade

Cells Cells and more Cells
•
1st - 3rd Grade