Unit 3 PE Acute physiological responses to exercise
Assessment
•
Stuart McGregor
•
Physical Ed
•
12th Grade
•
61 plays
•
Medium
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
18 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
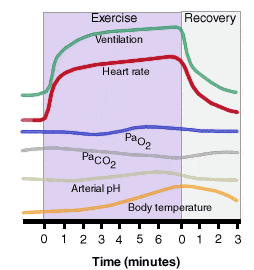
HEART RATE is what? Acute physiological response to exercise?
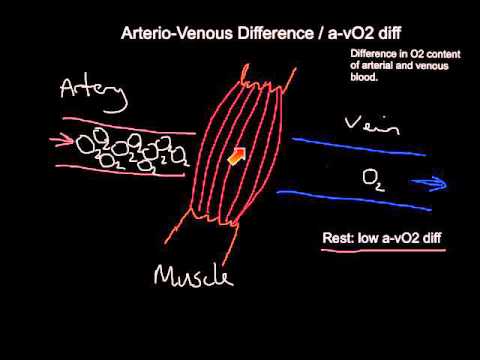
During exercise, blood flow is redirected away from the spleen, kidneys, guts and inactive muscles so that working muscles receive a greater % of Q.
The number of times the heart beats in one minute. Increases to a maximum of 220 - age.
The blood returning to the heart via the inferior and superior vena cava. Increases.
2.
Multiple Choice
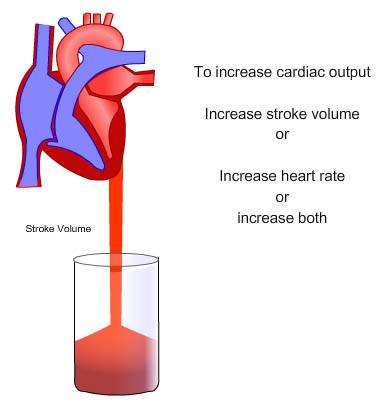
STROKE VOLUME is what? Acute physiological response to exercise?
The amount of blood ejected by the left ventricle per beat. Increases.
The amount of blood pumped out of the heart in one minute. Increases.
The number of times the heart beats in one minute. Increases.
The blood returning to the heart via the inferior and superior vena cava. Decreases.
3.
Multiple Choice
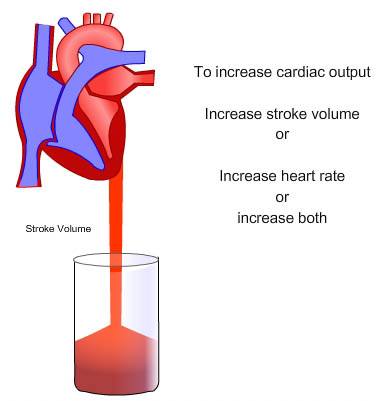
CARDIAC OUTPUT is what? Acute physiological response to exercise?
The number of times the heart beats in one minute. Increases.
The amount of blood ejected by the left ventricle per beat. Increases.
The amount of blood pumped out of the heart in one minute. Increases.
Pressure in the arteries following contraction of ventricles as blood is pumped out of the heart. Increases.
4.
Multiple Choice
SYSTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE is what? Acute physiological response to exercise?
During aerobic exercise, blood volume decreases. Plasma volume decreases rapidly in the first 5 minutes of exercise then stabilises.
Pressure in the arteries when the heart relaxes and ventricles fill with blood. Stays the same.
Pressure in the arteries following contraction of ventricles as blood is pumped out of the heart. Increases.
The number of times the heart beats in one minute. Increases.
5.
Multiple Choice
DIASTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE IS...
Pressure in the arteries following contraction of ventricles as blood is pumped out of the heart. Increases.
The blood returning to the heart via the inferior and superior vena cava. Increases.
Pressure in the arteries when the heart relaxes and ventricles fill with blood. Slight increase or may stay the same.
6.
Multiple Choice
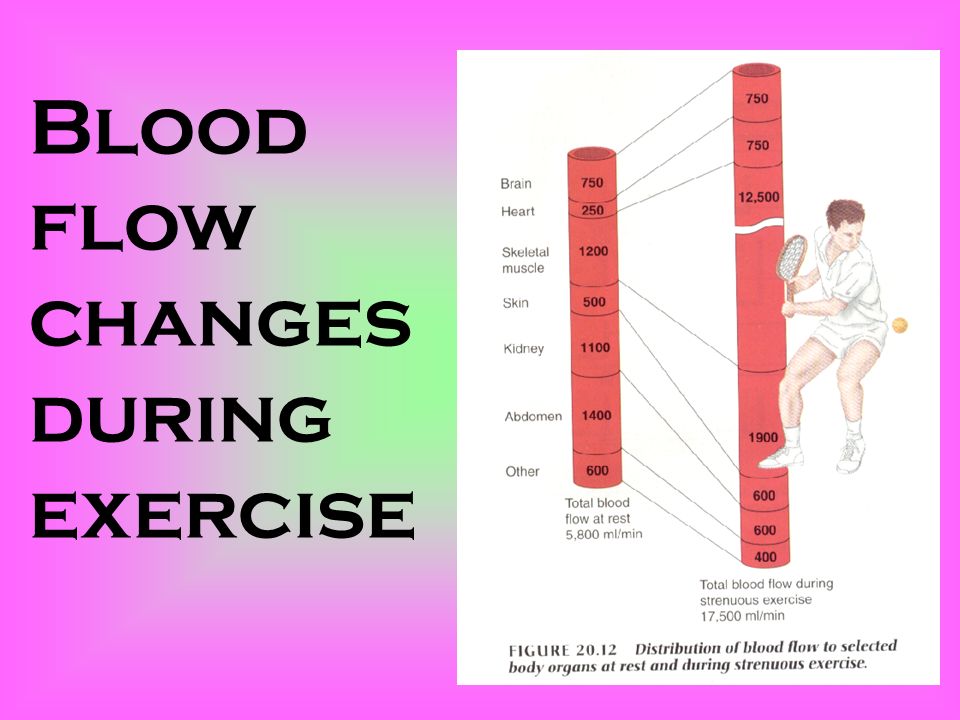
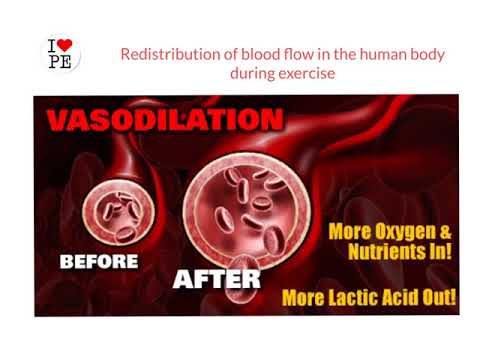
REDISTRIBUTION OF BLOOD FLOW is what? Acute physiological response to exercise?
During exercise, blood flow is redirected away from the spleen, kidneys, guts and inactive muscles so that working muscles receive a greater % of Q.
Pressure in the arteries following contraction of ventricles as blood is pumped out of the heart. Increases.
During aerobic exercise, blood volume decreases. Plasma volume decreases rapidly in the first 5 minutes of exercise then stabilises.

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Cardiovascular System
•
11th Grade

Acute Responses to Exercise
•
12th Grade

Heart Rate
•
6th - 8th Grade

The Cardiorespiratory System
•
11th Grade

Cardiovascular Anatomy
•
University

Physical Activity Test
•
9th - 12th Grade

Cardiovascular System
•
8th - 12th Grade

Acute Responses To Exercise
•
10th Grade