G9 IGCSE Force & Motion Quiz
Assessment
•
•
Science, Physics
•
9th - 11th Grade
•
305 plays
•
Hard
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
50 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
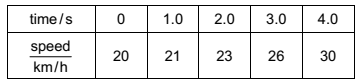
A train begins a journey from a station and travels 60 km in a time of 20 minutes.
What is the average speed of the train?
3.0 m/ s
5.0 m/ s
50 m/ s
60 m/ s
2.
Multiple Choice
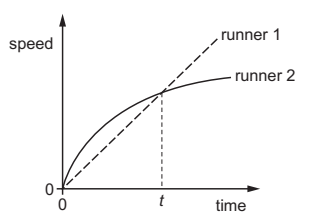
Two runners take part in a race.
The graph shows how the speed of each runner changes with time.
What does the graph show about the runners at time t ?
Both runners are moving at the same speed.
Runner 1 has zero acceleration.
Runner 1 is overtaking runner 2.
Runner 2 is slowing down.
3.
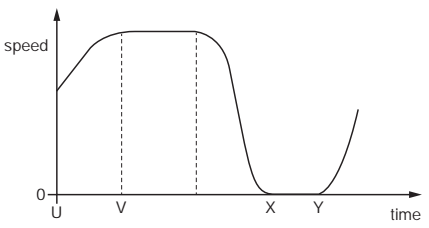
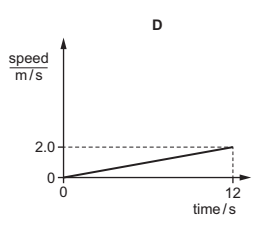
Multiple Choice
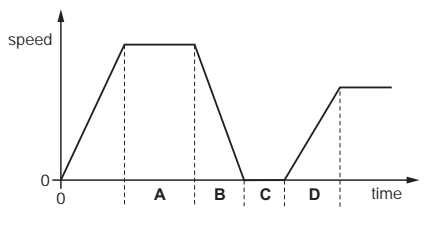
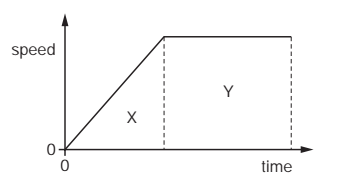
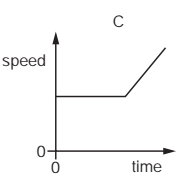
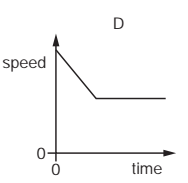
The graph shows how the speed of a van changes with time for part of its journey.
In which labelled section is the van decelerating?
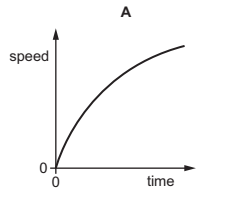
A
B
C
D
4.
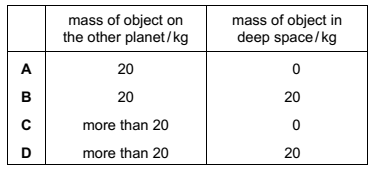
Multiple Choice
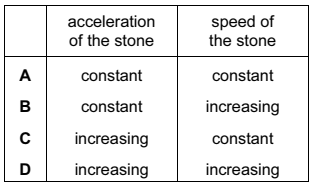
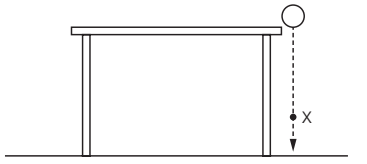
A large stone is dropped from a bridge into a river. Air resistance can be ignored.
Which row describes the acceleration and the speed of the stone as it falls?
A
B
C
D
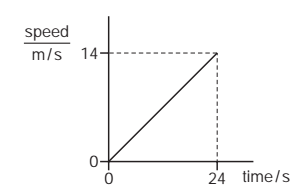
5.
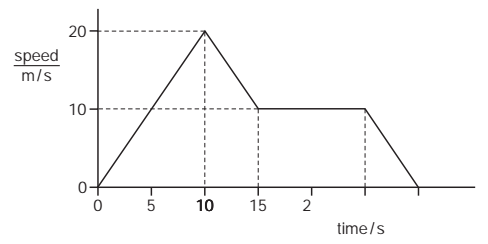
Multiple Choice
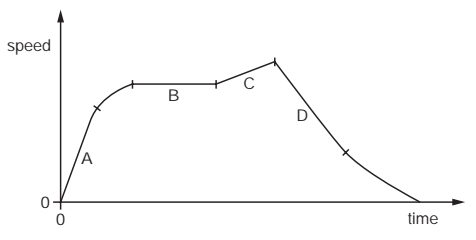
A car travels along a straight road.
The speed-time graph for this journey is shown.
During which labelled part of the journey is the resultant force on the car zero?
A
B
C
D
6.
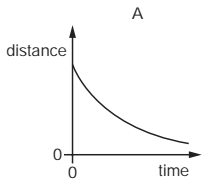
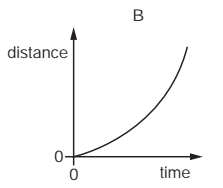
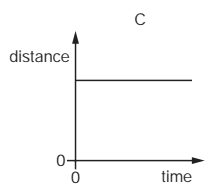
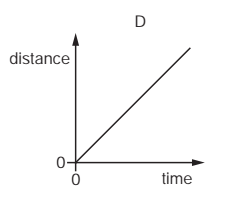
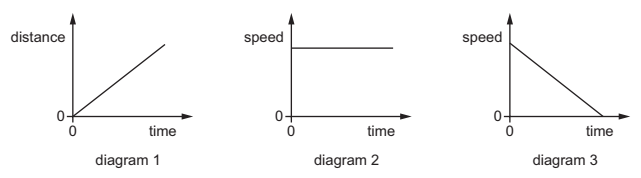
Multiple Choice
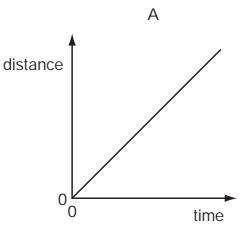
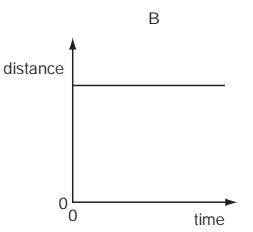
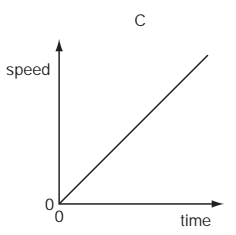
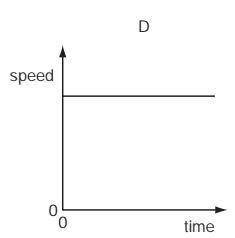
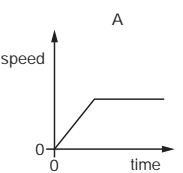
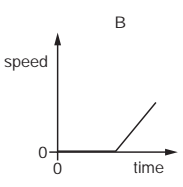
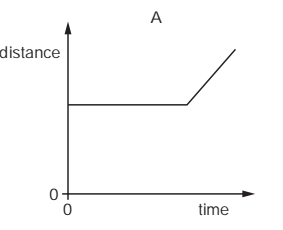
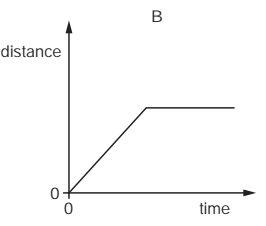
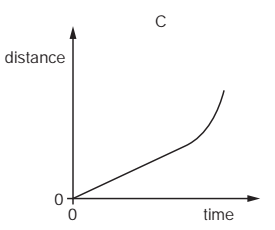
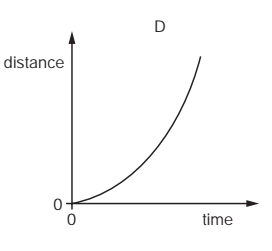
An object moves at a constant speed for some time, then begins to accelerate.
Which distance-time graph shows this motion?

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Calculating Speed
•
5th Grade

Calculating Speed
•
5th - 8th Grade

Acceleration
•
8th - 9th Grade

Speed, Velocity & Acceleration
•
6th - 8th Grade

Acids & Alkalis
•
6th Grade

Analyze Motion Graphs
•
6th Grade

Velocity or Acceleration?
•
8th Grade

Independent & Dependent Variables
•
4th Grade