
Year 7 Science Revision
Assessment
•
Cairine Henderson
•
Science
•
5th - 7th Grade
•
25 plays
•
Medium
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
81 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
Producers are ...
plants
able to do photosynthesis
also called autotrophs
all of these are true
2.
Multiple Choice
Arrows in a food web represent...
eating
sunlight
energy
matter
3.
Multiple Choice
All of these are types of consumers except...
omnivores
carnivores
decomposers
herbivores
4.
Multiple Choice
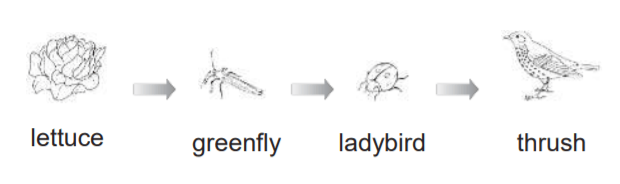
Who is the producer?
lettuce
greenfly
ladybird
thrush
5.
Multiple Choice
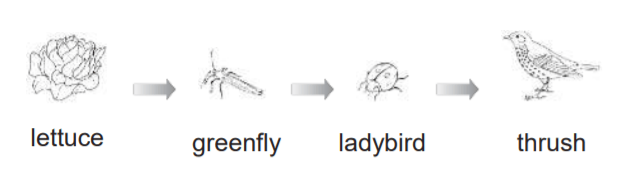
Who is the herbivore?
lettuce
greenfly
ladybird
thrush
6.
Multiple Choice
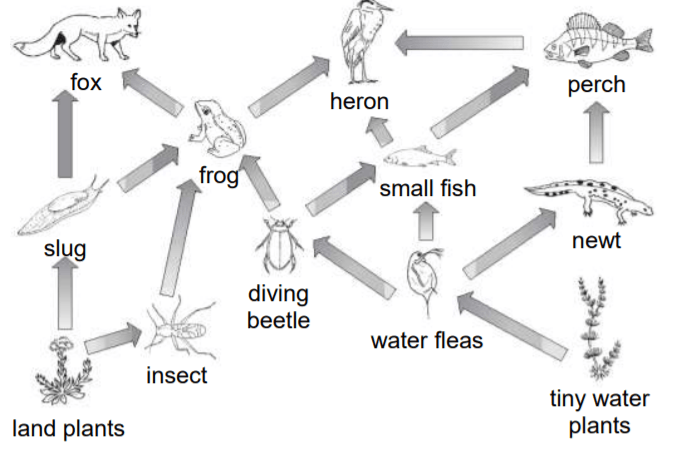
This is a food chain
This is a food web
This is an energy pyramid
7.
Multiple Choice
The original source of energy for a food web is...
plants
sun
producers
decomposers
8.
Multiple Choice
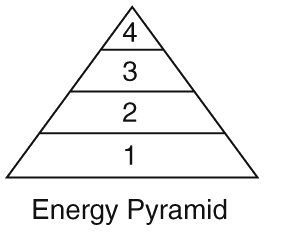
Level 1 on the pyramid
Producers
Primary Consumer
Secondary Consumer
Tertiary Consumer
9.
Multiple Choice

Level 2 on the pyramid
Producers
Primary Consumer
Secondary Consumer
Tertiary Consumer
10.
Multiple Choice

Level 3 on the pyramid
Producers
Primary Consumer
Secondary Consumer
Tertiary Consumer
11.
Multiple Choice

Level 4 on the pyramid
Producers
Primary Consumer
Secondary Consumer
Tertiary Consumer
12.
Multiple Choice
Decomposers get energy from...
the sun
eating plants
eating animals
dead things and waste
13.
Multiple Choice
worm
bacteria
mushroom
hawk
14.
Multiple Choice
fungus
mouse
plants
frogs
15.
Multiple Choice
composer
decomposer
producer
16.
Multiple Choice
consumers
decomposers
producers
17.
Multiple Choice

producer
consumer
decomposer
autotroph
18.
Multiple Choice

an environment
an ecosystem
a food web
a food chain
19.
Multiple Choice
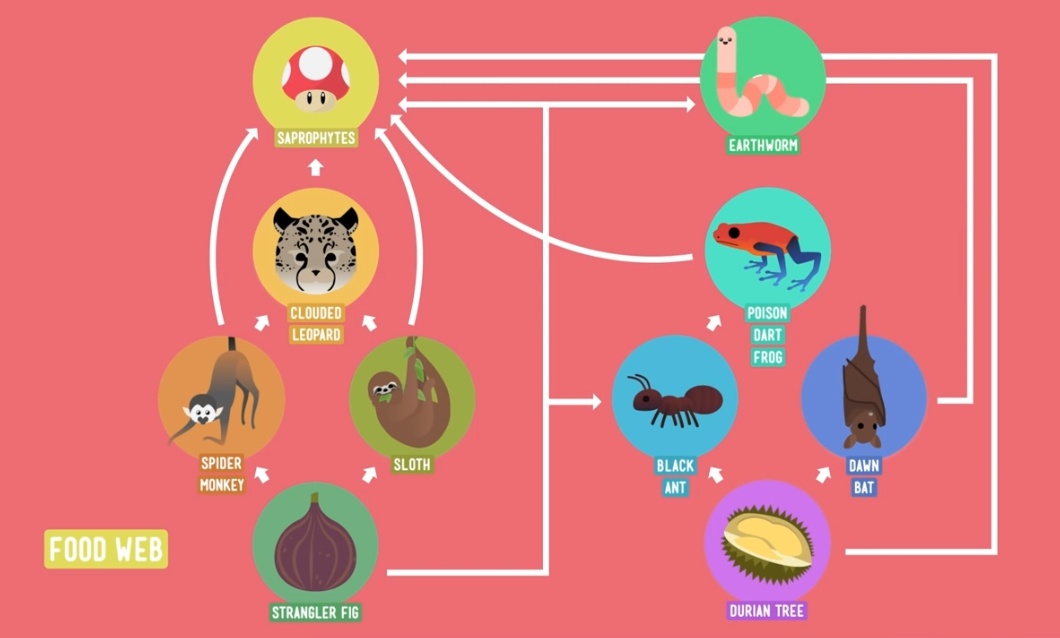
figs and spider monkeys
sloths and strangler figs
sloths and spider monkeys
ants and bats
20.
Multiple Choice
bats
insects
spider monkeys
strangler figs
21.
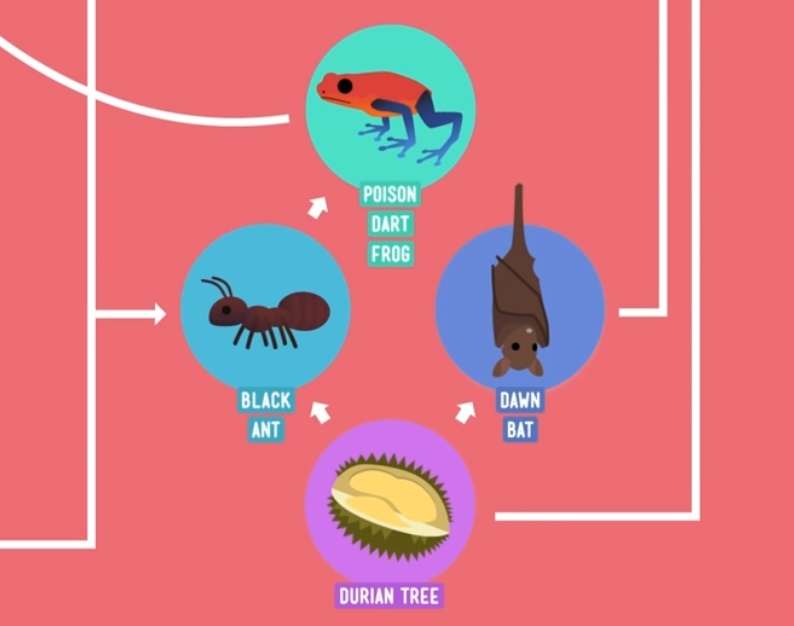
Multiple Choice
one species
two species
three species
several species
22.
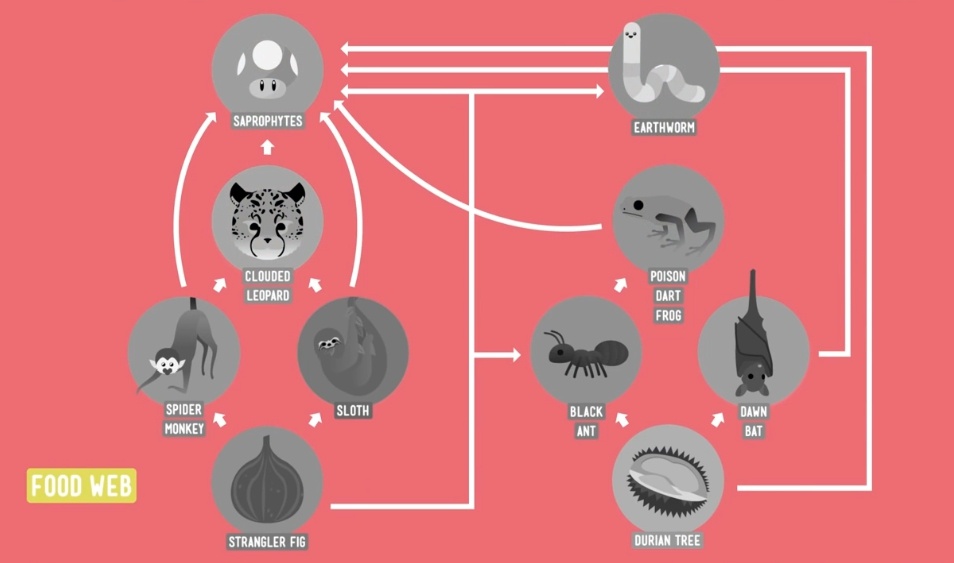
Multiple Choice

one species
two species
three species
several species
23.
Multiple Choice
Air resistance
Gravity
Water resistance
Pressure
24.
Multiple Choice
Friction
Air resistance
Water resistance
Electrical resistance
25.
Multiple Choice
Einsteins
Newtons
Kg
Metres
26.
Multiple Choice
Downwards
Upwards
In all directions
Towards the centre of the Earth
27.
Multiple Choice
An influence, which cannot be measured, that causes something to move, stop moving or change direction.
An influence, which can be measured, that causes something to move, stop moving or change direction.
Something which has power.
An influence, which can be measured, that causes something to move.
28.
Multiple Choice
Friction
Air resistance
Water resistance
Wind
29.
Multiple Choice
Gravity
Air resistance
Friction
Water resistance
30.
Multiple Choice
A parachute
A ball falling through the sky
Brakes on a bike
A wind turbine
31.
Multiple Choice
...a smaller force to have a greater effect
....a bigger force to have a smaller effect
... a force to be stopped
...a force to be used in a useful way.
32.
Multiple Choice
Applied forces
Balanced forces
Unbalanced forces
33.
Multiple Choice
True
False
34.
Multiple Choice
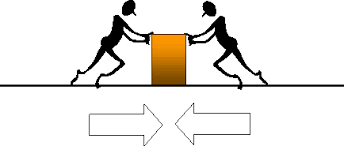
unbalanced
weak
balanced
Hulk Smash!
35.
Multiple Choice
larger
smaller
equal
cannot be determined
36.
Multiple Choice
Contact Force
Balanced Force
Unbalanced Force
Net Force
37.
Multiple Choice
gravity
friction
air
mass
38.
Multiple Choice
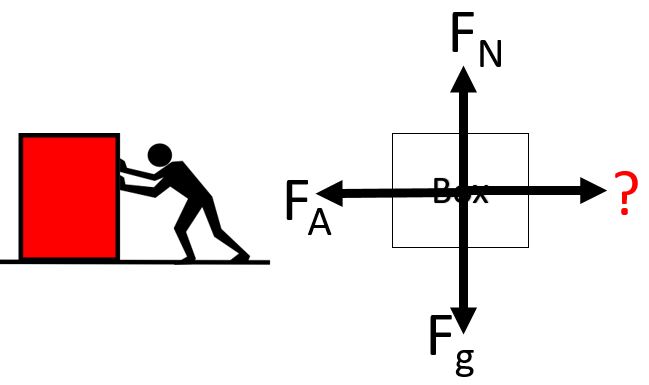
frictional force
weight force
thrust
buoyant force
39.
Multiple Choice
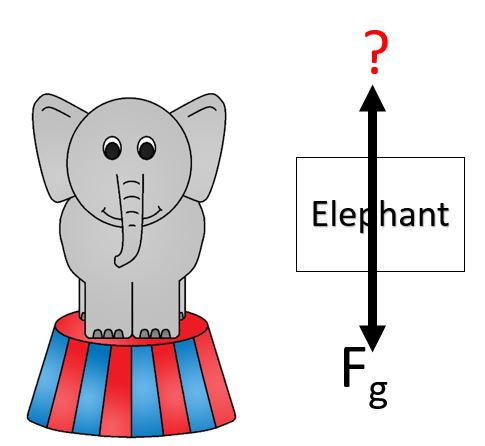
weight force
normal force
applied force
frictional force
40.
Multiple Choice
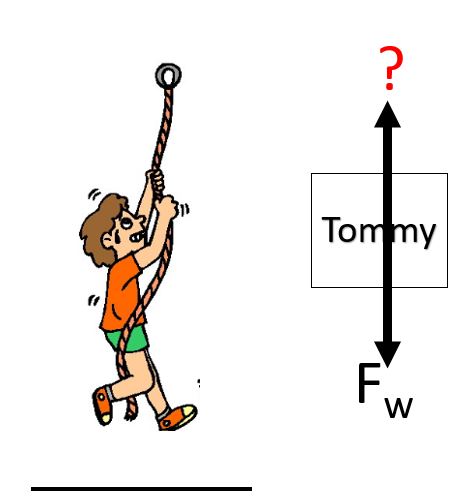
tension force
gravitational force
normal force
applied force
41.
Multiple Select
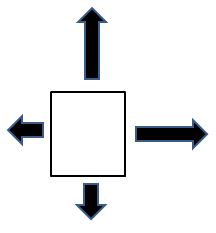
This object would be moving (pick all that are correct):
up
down
left
right
42.
Multiple Choice

The down-arrow in this diagram is most-likely:
gravity
normal
a push or pull
friction
43.
Multiple Choice

The up-arrow in this diagram is most-likely:
gravity
normal
a push or pull
friction
44.
Multiple Choice

If this object were moving right, the left-arrow in this diagram is most-likely:
gravity
normal
a push or pull
friction
45.
Multiple Choice
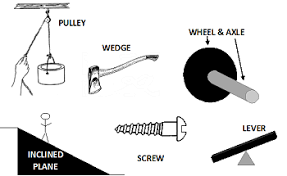
Wheels, levers, pulleys, ramps, screws, and wedges are forms of _______________________.
potential energy
simple machines
chemical changes
dark matter
46.
Multiple Choice
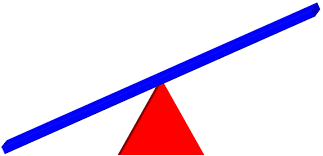
The pivot point of a lever is called the _________.
load
bar
effort
fulcrum
47.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a lever?
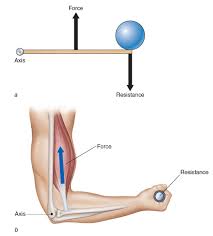



48.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of a ramp? (inclined plane)



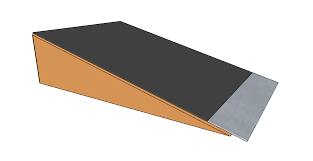
49.
Multiple Choice

A prosthetic arm is an example of a _________.
ramp
screw
pulley
lever
50.
Multiple Choice

A crane uses ___________ to lift heavy loads.
ramps
pulleys
axles
wedges
51.
Multiple Choice

Renewable Energy Resource
Nonrenewable Energy Resource
52.
Multiple Choice

Renewable Energy Resource
Nonrenewable Energy Resource
53.
Multiple Choice

Renewable
Nonrenewable
54.
Multiple Choice

Renewable
Nonrenewable
55.
Multiple Choice
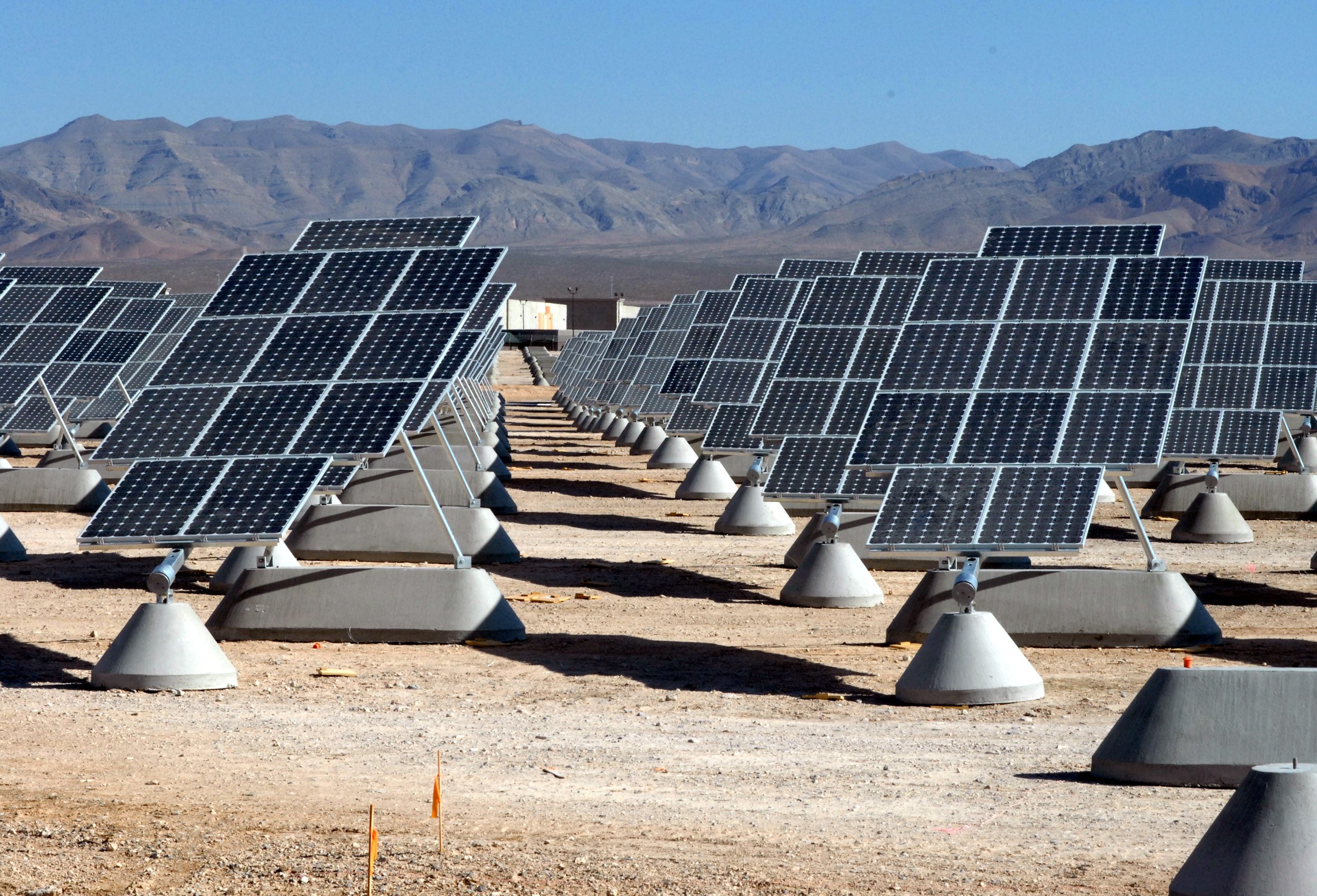

Renewable
Nonrenewable
56.
Multiple Choice
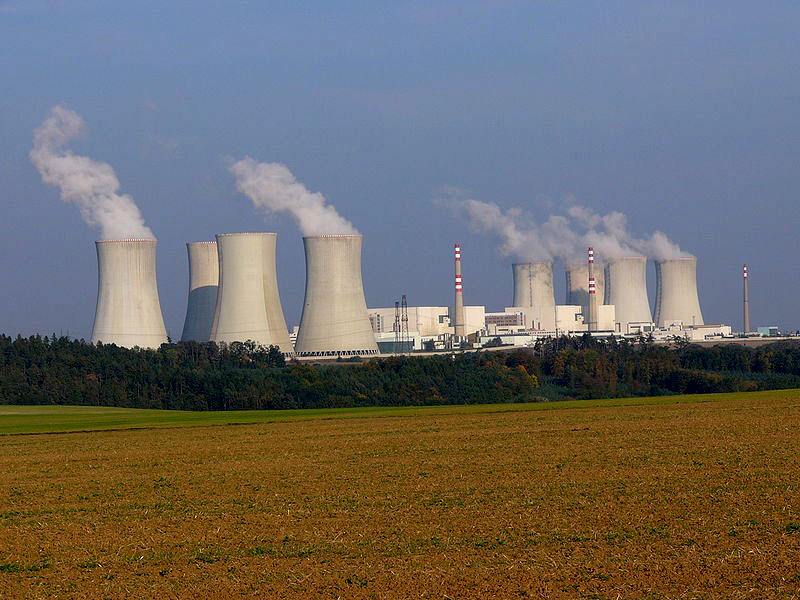

Renewable
Nonrenewable
57.
Multiple Choice
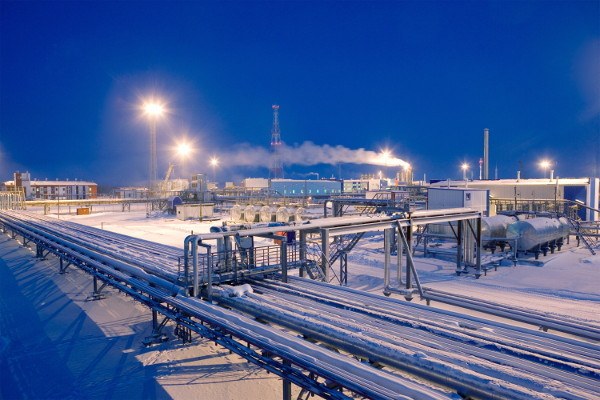

Renewable
Nonrenewable
58.
Multiple Choice
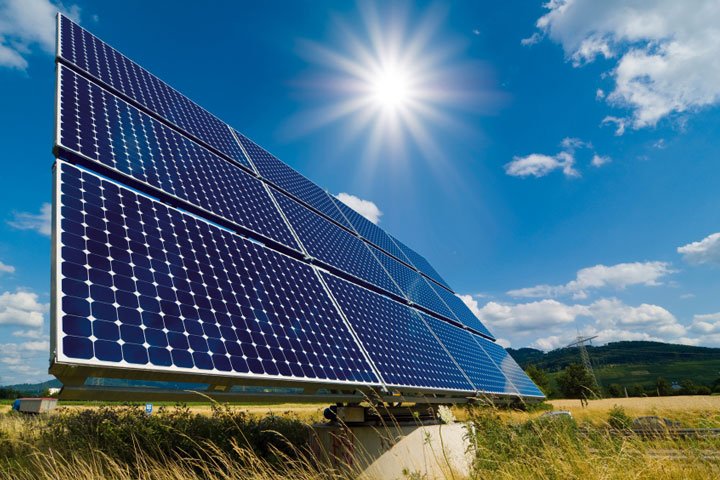

Wind
Hydro
Nuclear
Solar
59.
Multiple Choice
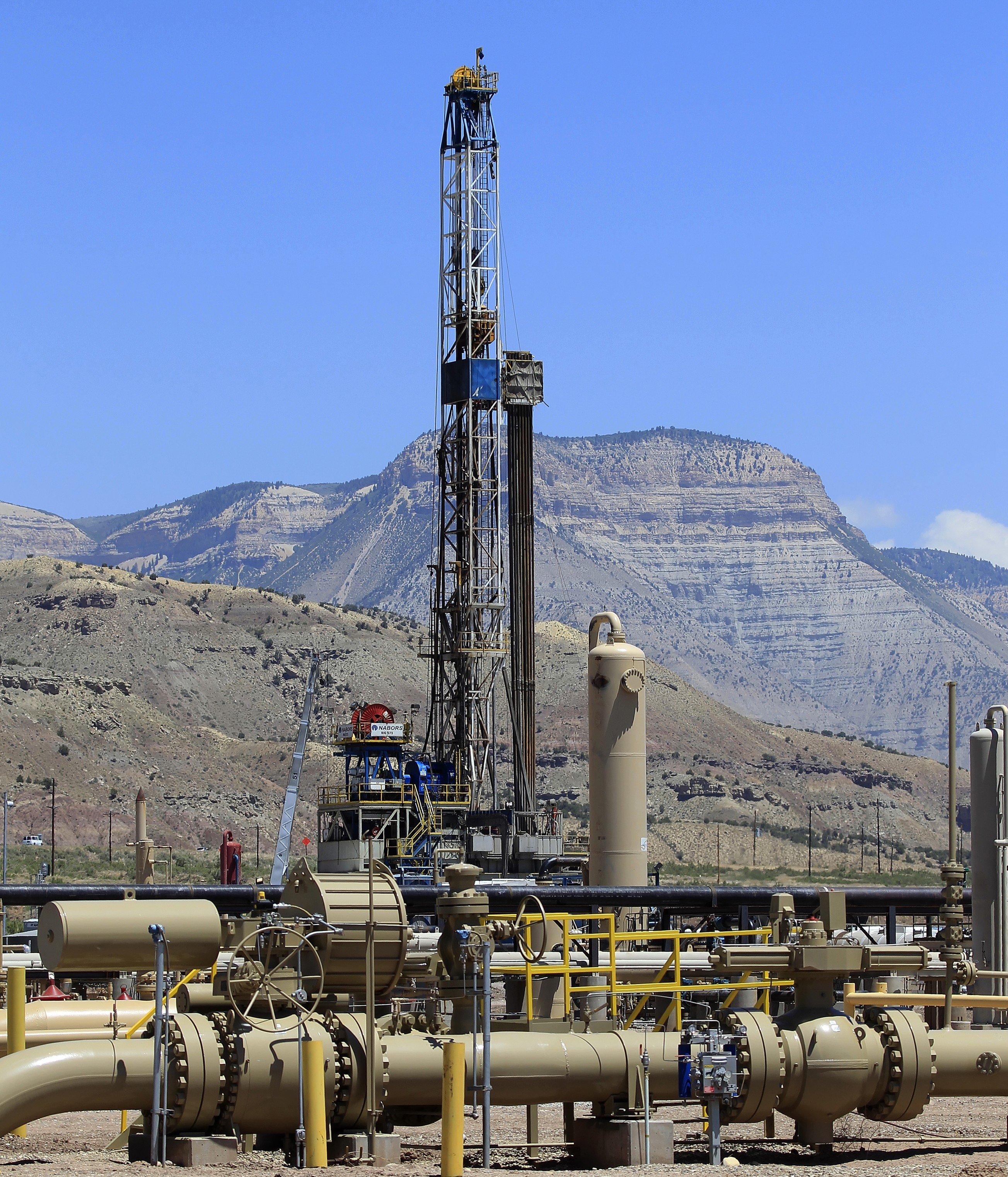

Geothermal
Natural Gas
Coal
Nuclear
60.
Multiple Choice
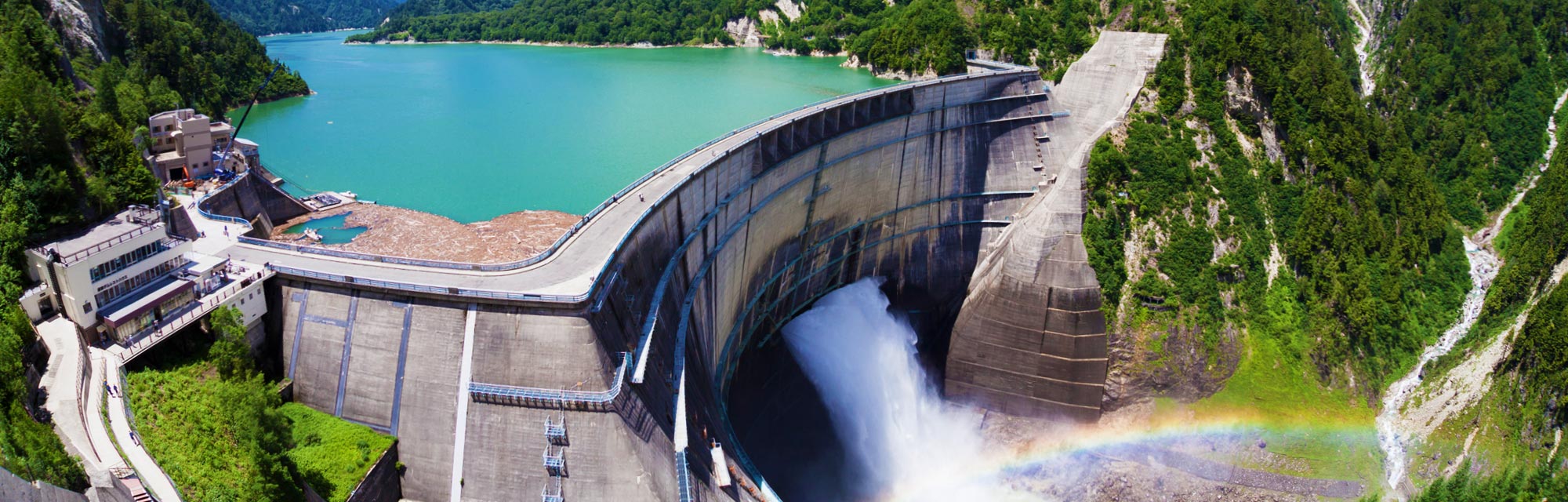

Wind
Hydro
Geothermal
Solar
61.
Multiple Choice

Hydro
Coal
Nuclear
Geothermal
62.
Multiple Choice
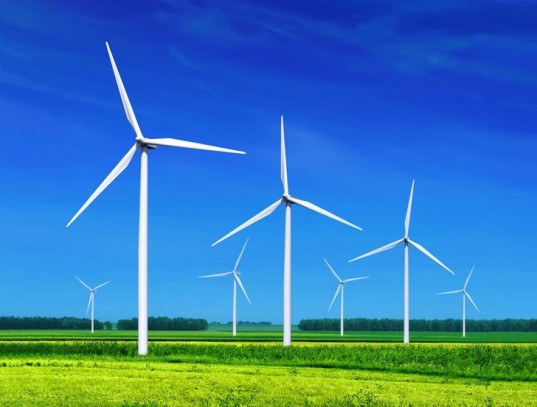

Renewable
Nonrenewable
63.
Multiple Choice
Any environment where a large number of plants and animals died.
A swamp with many generation of plants that died and couldn't decompose naturally.
A sea where many plants and animals died and couldn't decompose.
A desert environment where no living things ever existed.
64.
Multiple Choice
Heat homes directly
Heat water
Generate electricity
Heat food
65.
Multiple Choice
that the clouds can block the sunlight
it is not available at night
that the clouds can block the sunlight and it is not available at night
the sun is too hot to be absorbed in solar panels
66.
Multiple Choice
the practice of increasing the use of natural resources in order to use them
the practice of increasing the use of natural resources in order to save them
the practice of decreasing the use of natural resources in order to use them
the practice of decreasing the use of natural resources in order to save them
67.
Multiple Choice
to find a common ancestor
to show the evolution of organisms
to show relationships between organisms
to identify organisms
68.
Multiple Choice
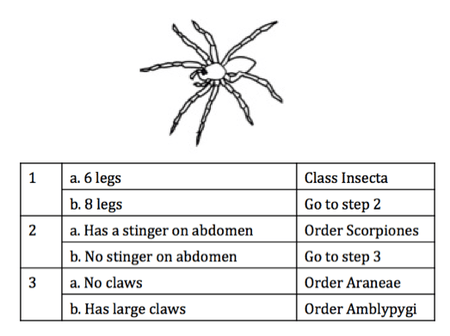
Class Insecta
Order Amblygygi
Order Araneae
Order Scorpiones
69.
Multiple Choice
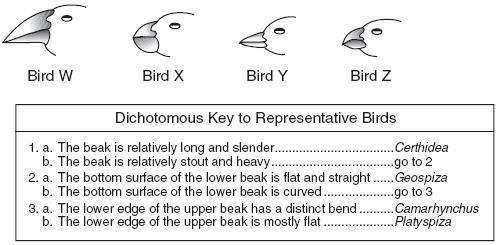
Certhidea
Geospiza
Camarhynchus
Platyspiza
70.
Multiple Choice
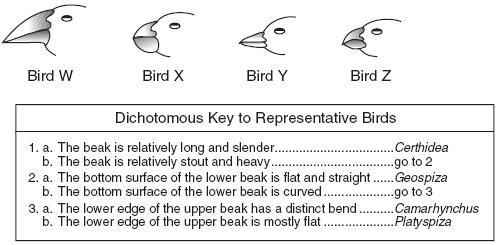
Certhidea
Geospiza
Camarhynchus
Platyspiza
71.
Multiple Choice
To organize biomes
Classify organisms
Identify bacteria only
None of these
72.
Multiple Choice
A nonliving element in an ecosystem is a/an ---
biotic factor.
abiotic factor.
73.
Multiple Choice
A living, or once-living, organism in an ecosystem is a/an ---
abiotic factor.
biotic factor.
74.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT an abiotic factor?
sun
temperature
soil
grass
75.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a biotic factor?
mushroom
air
elephant
coyote
76.
Multiple Choice
Which kind of factor is this? a fern
abiotic
biotic
77.
Multiple Choice
Which kind of factor is this? weather
abiotic
biotic
78.
Multiple Choice
Which kind of factor is this? sunlight
abiotic
biotic
79.
Multiple Choice
Temperature, light, air, water, and soil are all _____ parts of the environment
abiotic
biotic
80.
Multiple Choice

What are the biotic factors in this image?
sunlight, elephants, and grasses.
sunlight, water, and air.
elephants, plants, and trees .
81.
Multiple Choice
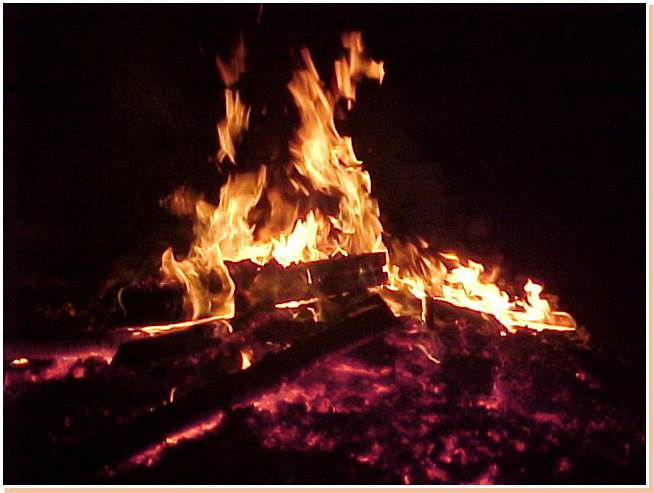

Fire
Oxygen
Heat
All of the Above

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Producers and Consumers
•
9th Grade

Ecosystems
•
3rd - 6th Grade

Food Chains
•
3rd - 4th Grade

Food Chains & Food Webs
•
5th Grade

Ecosystems
•
5th - 8th Grade

Ecosystems
•
7th Grade

Food Chains and Webs
•
5th - 7th Grade

Relationships in Ecosystems
•
9th Grade