
Unit 5 - Weathering, Erosion, Deposition
Assessment
•
Kenneth Andersen
•
Social Studies
•
8th - 12th Grade
•
12 plays
•
Medium
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
130 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
sand
silt
clay
pebble
2.
Multiple Choice
sand
silt
clay
pebble
3.
Multiple Choice
sand
silt
clay
pebble
4.
Multiple Choice
sand
silt
clay
pebble
5.
Multiple Choice
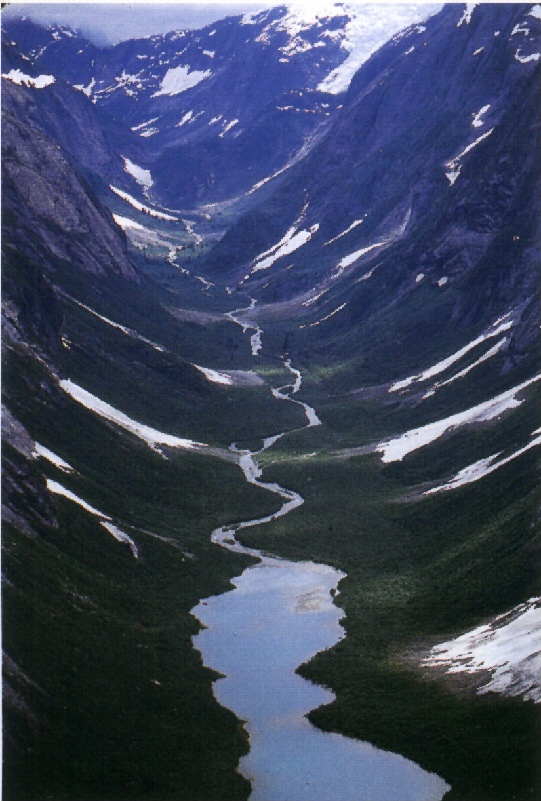
U-Shaped Valley
V-Shaped Valley
Kettle
Moraine
6.
Multiple Choice
U-Shaped Valley
V-Shaped Valley
Kettle
Moraine
7.
Multiple Choice
true
false
8.
Multiple Choice

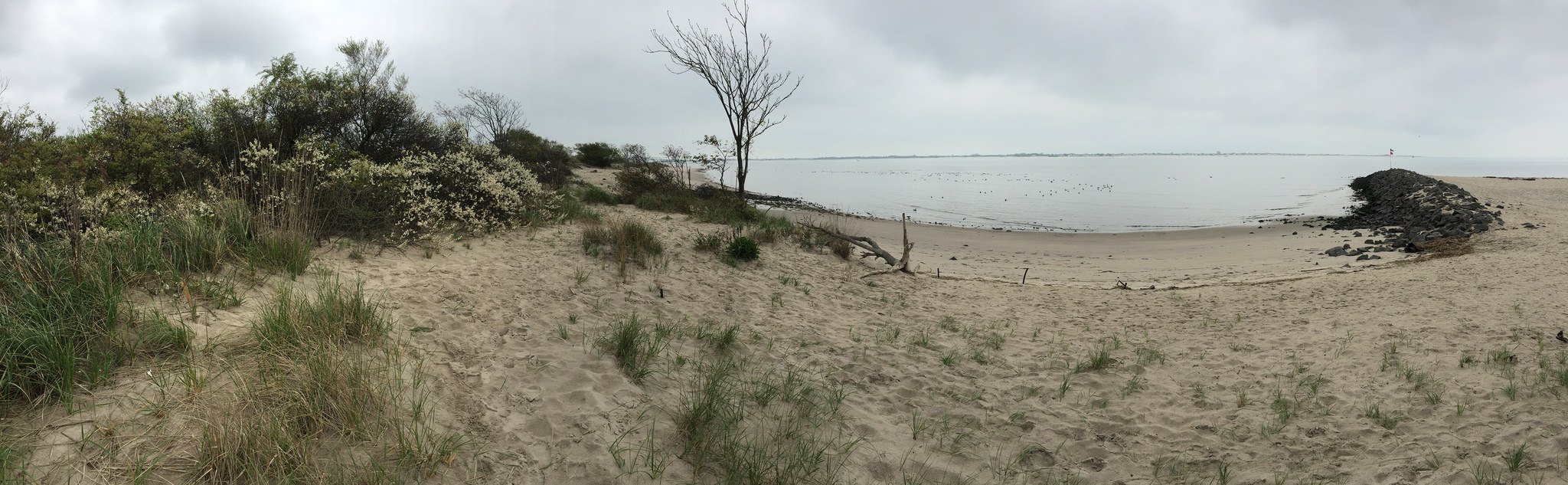
Which agent of erosion created this landform?
Ocean waves
Moving Ice
Wind
Gravity
9.
Multiple Choice
Glacial erosion causes ______ as it moves across the land.
plucking and striations
beaches and sand bars
sea caves and headlands
sand dunes and ventifacts
10.
Multiple Choice
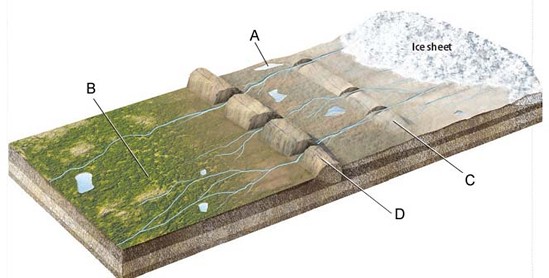
moraines
outwash plains
kettle lakes
ice sheets
11.
Multiple Choice

moraine
outwash plain
kettle lake
ice sheet
12.
Multiple Choice

moraine
outwash plain
kettle lake
ice sheet
13.
Multiple Choice
glacier
iceberg
ice wedging
dune
14.
Multiple Choice
drumlin
unsorted sediments
ice wedging
dune
15.
Multiple Choice
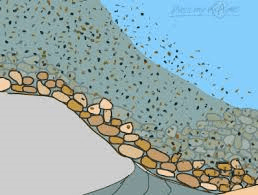
What is the laying down or settling of eroded material?
River Abrasion
Dunes
Deposition
Weathering
16.
Multiple Choice

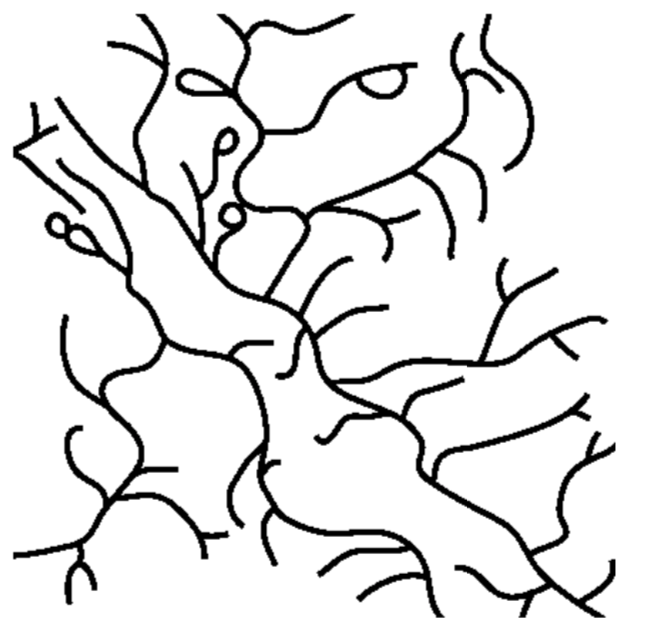
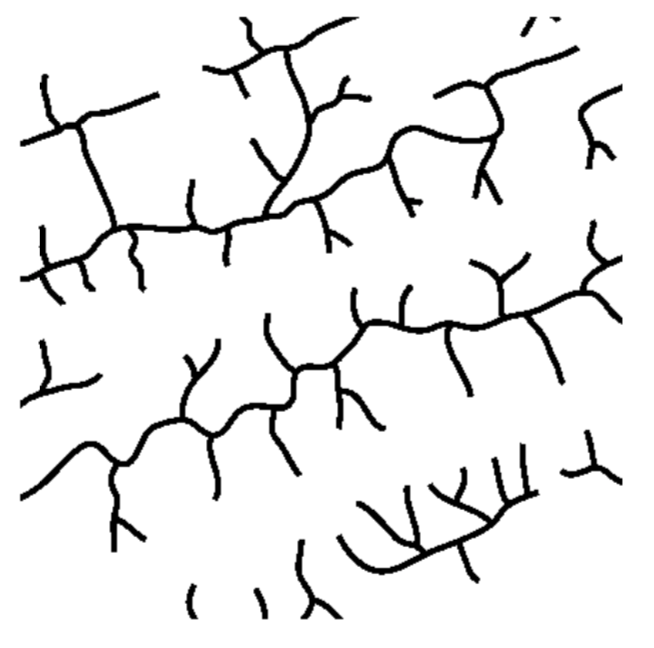
Plucking
Abrasion
Striations
Till
17.
Multiple Choice
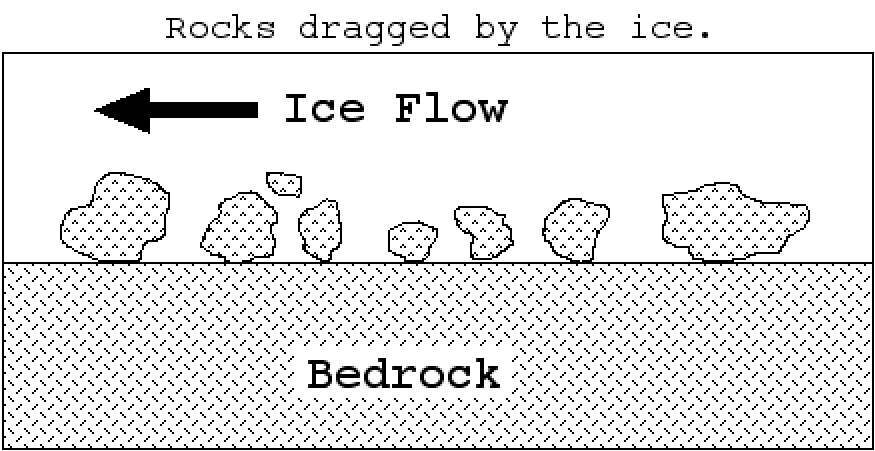
_____ happens when rocks stuck along the base of a glacier create polishing, grooves and striations.
Plucking
Abrasion
Weathering
Erosion
18.
Multiple Choice
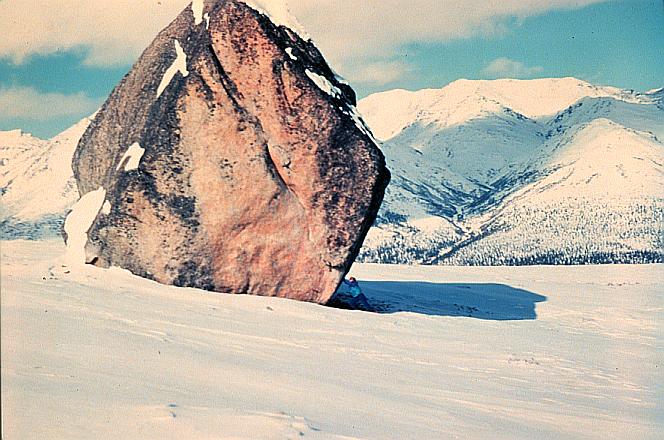

Till
Erratics
Moraines
Drumlins
19.
Multiple Choice
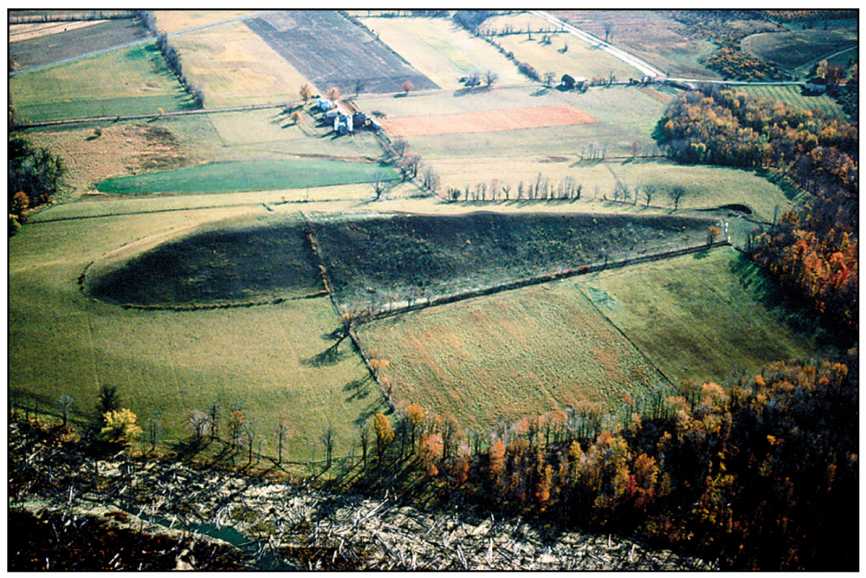

drumlin
esker
moraine
erratic
20.
Multiple Choice
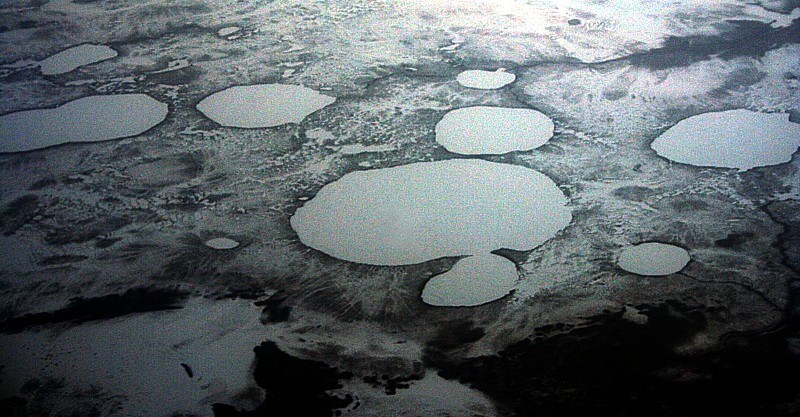

erratics
eskers
kettles
drumlin
21.
Multiple Choice
What are hills made of glacial till that point in the direction of glacier movement?
outwash plains
kettle lakes
drumlins
eskers
22.
Multiple Choice

blowing wind
ocean waves
moving ice
running water
23.
Multiple Choice
They block the wind from the soil.
They loosen soil.
They lift up sediment.
They hold sediment into place.
24.
Multiple Choice
Abrasion by wind-carried sand is the leading cause of erosion in New York.
True
False
25.
Multiple Choice
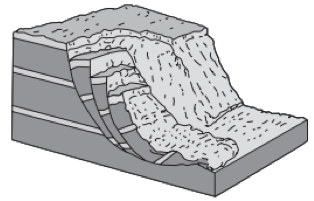
groundwater and abrasion
groundwater and gravity
prevailing wind and abrasion
prevailing wind and gravity
26.
Multiple Choice
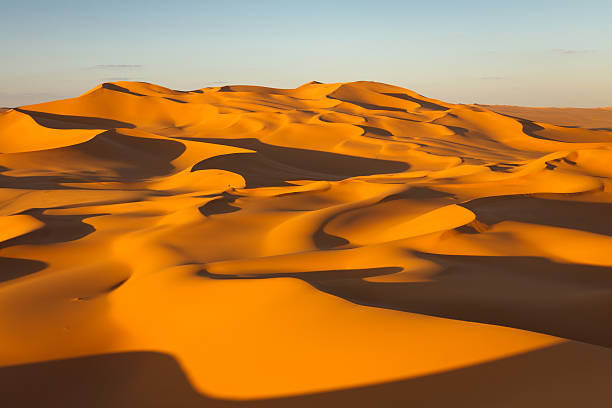

wind
ocean
stream river
gravity
27.
Multiple Choice
sorted and layered
sorted and not layered
unsorted and layered
unsorted and not layered
28.
Multiple Choice
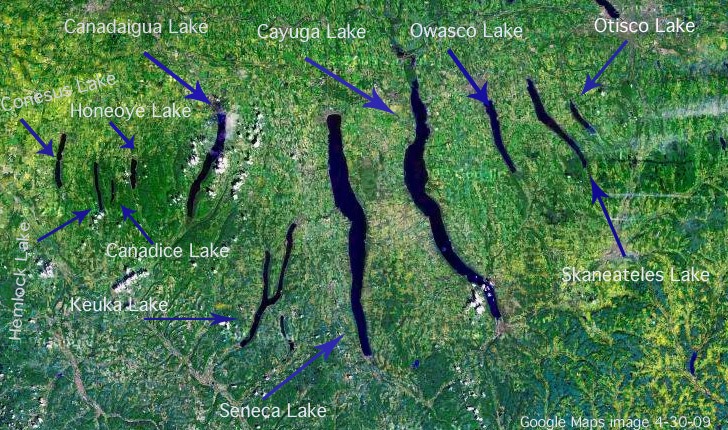
running water
moving ice
wave action
mass movement
29.
Multiple Choice
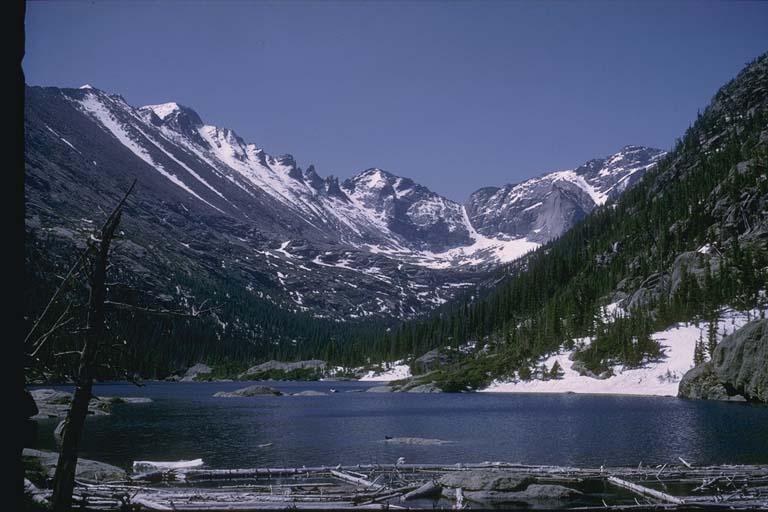

blowing wind
ocean waves
moving ice
running water
30.
Multiple Choice
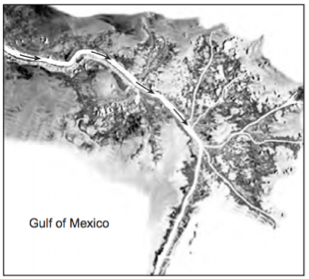
a delta
a sandbar
a barrier island
an outwash plain
31.
Multiple Choice
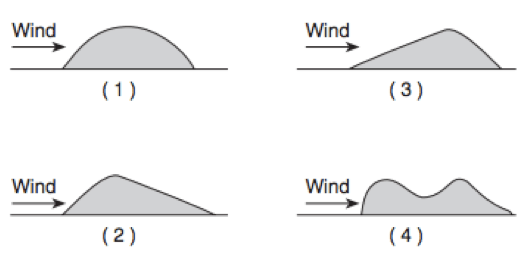
1
2
3
4
32.
Multiple Choice
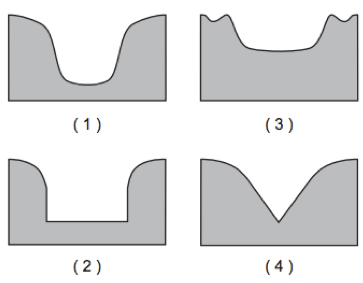
1
2
3
4
33.
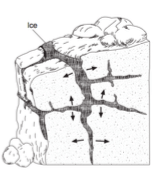
Multiple Choice
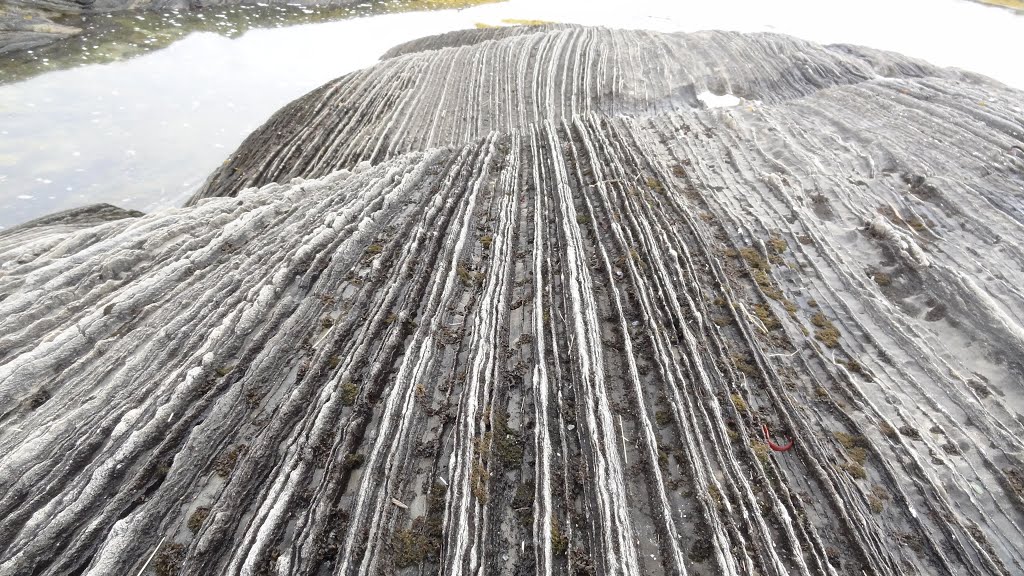

alternating thawing and freezing of water cracked the bedrock
flooding from a nearby lake covered the bedrock
a glacier dragged rocks over the bedrock
rocks from a landslide slid along the bedrock
34.
Multiple Choice
wind erosion
wave erosion
mass movement
chemical precipitation
35.
Multiple Choice

photograph A—glacier; photograph B—river
photograph A—river; photograph B—glacier
Both A and B—river
Both A and B—glacier
36.
Multiple Choice
running water
moving ice
wave action
mass movement
37.
Multiple Choice
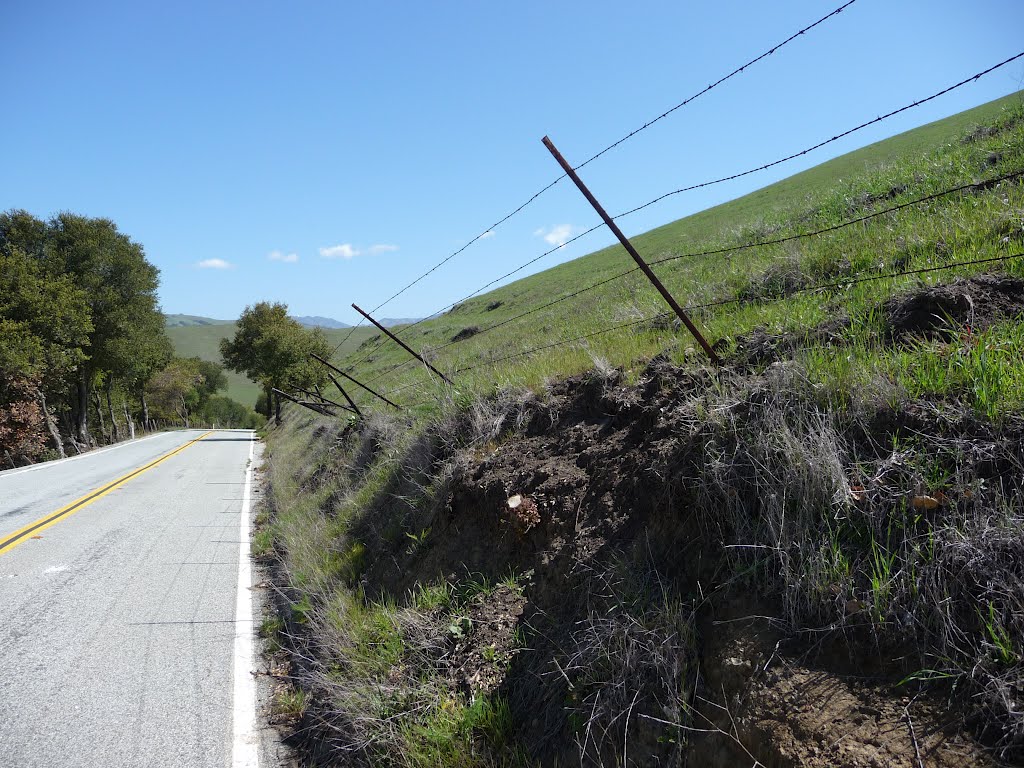

wind
gravity
glaciers
river
38.
Multiple Choice
gravity
running water
wind
ocean waves
39.
Multiple Choice
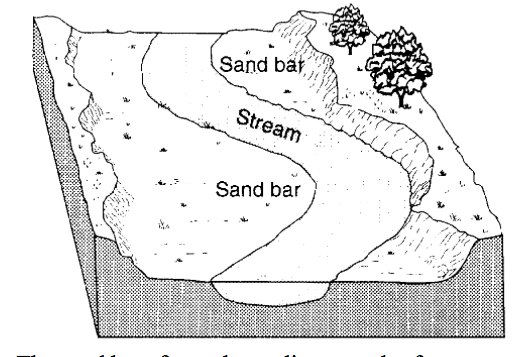
erosion due to a decrease in stream velocity
erosion due to an increase in stream velocity
deposition due to a decrease in stream velocity
deposition due to an increase in stream velocity
40.
Multiple Choice
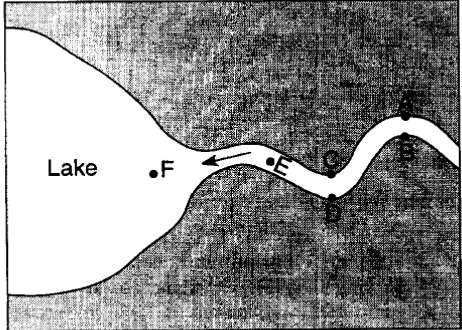
At which locations is the amount of deposition greater than the amount of erosion?
A,C and E
B, D and F
B, C, and F
A, D and E
41.
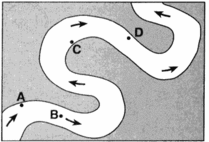
Multiple Choice
A
B
C
D
42.
Multiple Choice
velocity of the river decreased
force of gravity decreased
volume of the river increases
gradient of the river increases
43.
Multiple Choice
A
B
C
D
44.
Multiple Choice
deposition on the inside of the meander
deposition on the outside of the meander
erosion on the inside of the meander
erosion on the outside of the meander
45.
Multiple Choice
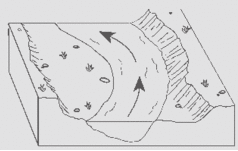
Slower, causing deposition
Faster, causing deposition
Slower, causing erosion
Faster, causing erosion
46.
Multiple Choice
A
B
C
D
47.
Multiple Choice
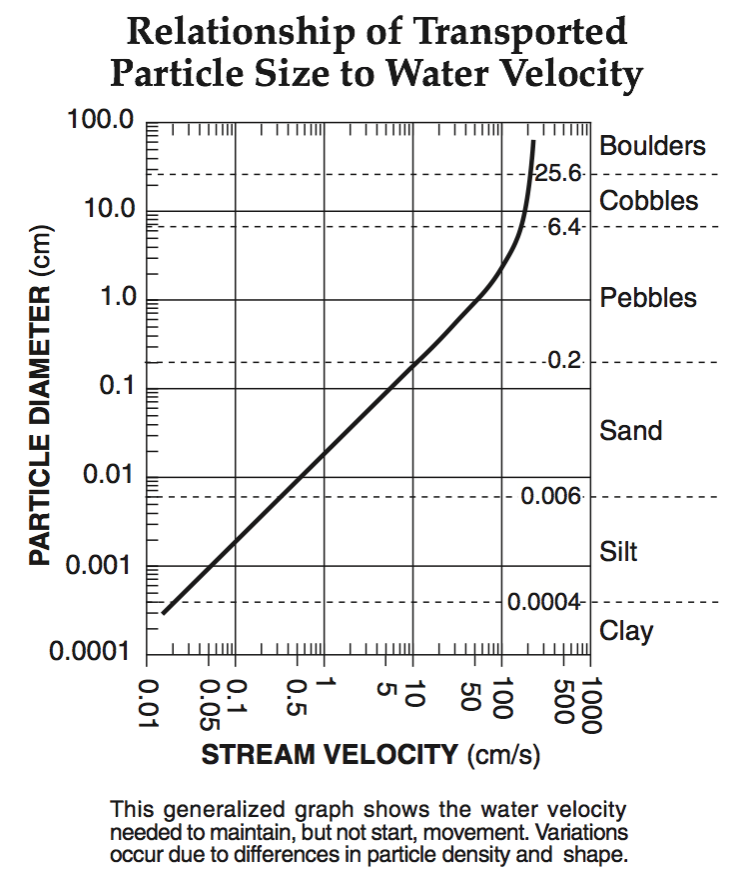
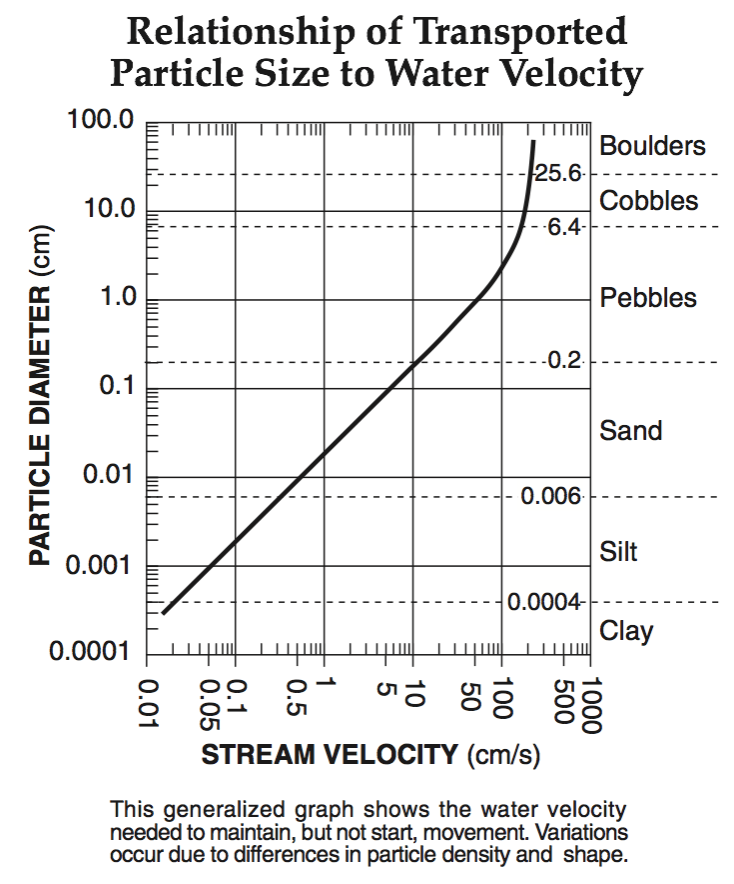
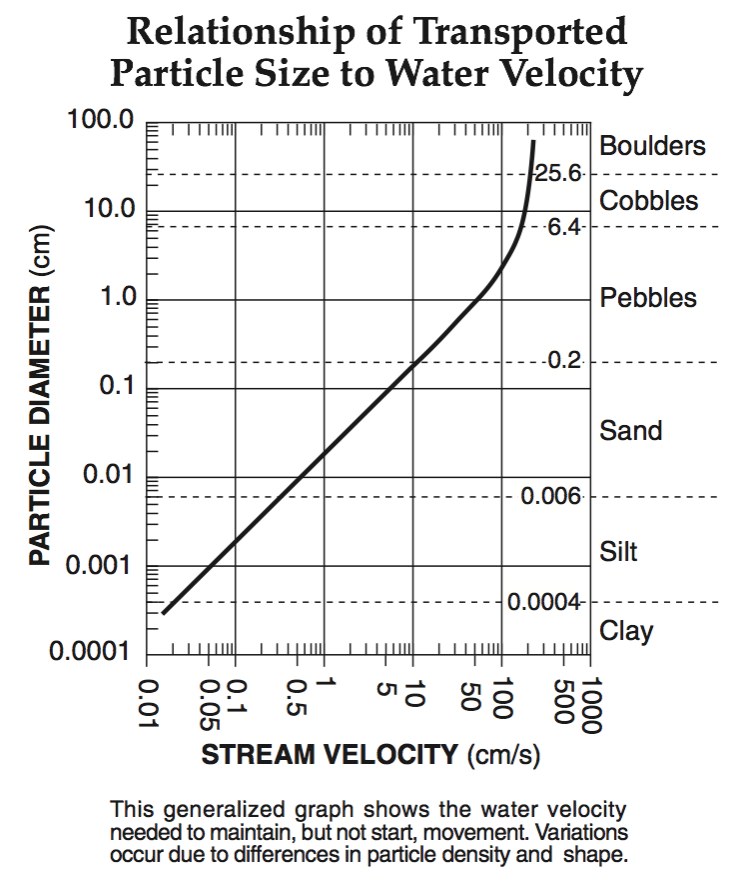
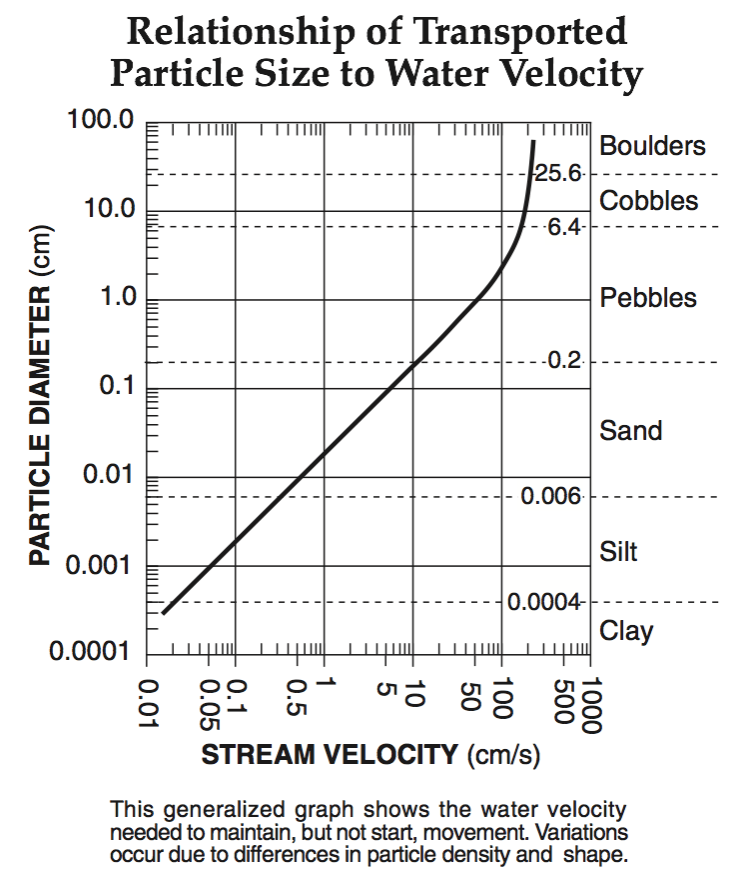
A stream’s velocity decreases from 100 cm/s to 5 cm/s. Which size sediment particles will still be transported by the stream?
pebbles, sand, silt and clay
sand, silt and clay only
silt and clay only
clay only
48.
Multiple Choice
runoff decreases during preciptiation
ground water storage is usually very large
roads, pavements and buildings reduce the infiltration of water into the ground
the heat generated by the city areas decreases actual evapotranspiration
49.
Multiple Choice
decreases and runoff decreases
decreases and runoff increases
increases and runoff decreases
increases and runoff increases
50.
Multiple Choice
a loose sand and strong wind
pressure in the Earth
ice glaciers
Gravity
51.
Multiple Choice
What is a landform that forms when rivers or glaciers wear away rock and soil?
valley
hoodoo
sand dune
ventifact
52.
Multiple Choice
What is a hill of sand that is deposited by the wind?
valley
sand dune
hoodoo
canyon
53.
Multiple Choice
What is the movement of weathered materials by water, wind, or ice?
weathering
deposition
landform
erosion
54.
Multiple Choice
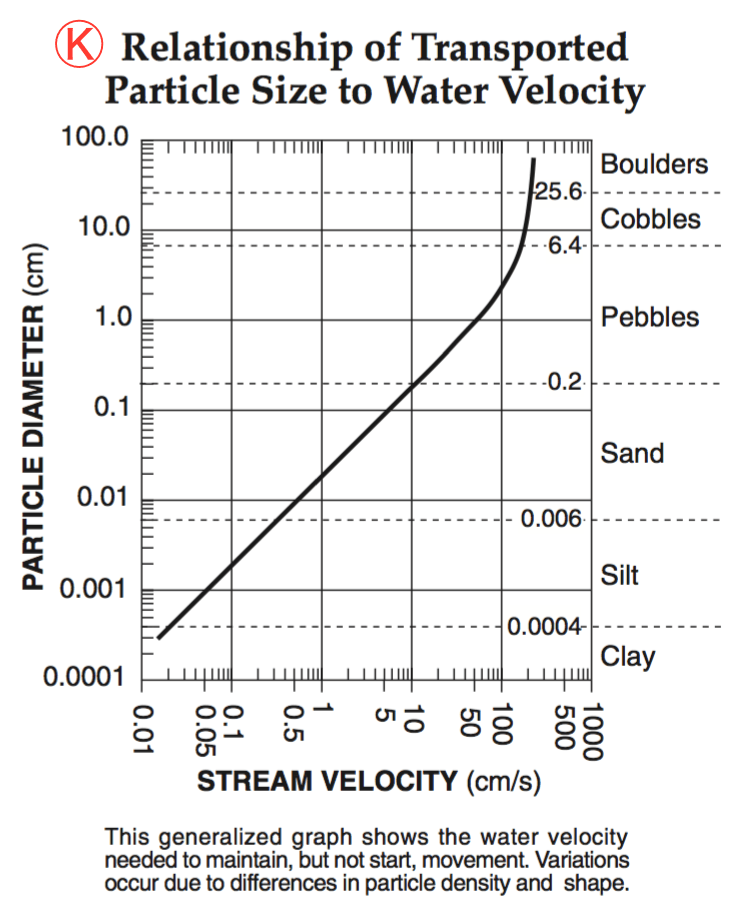
5.0 cm/s
0.02 cm/s
0.5 cm/s
20.0 cm/s
55.
Multiple Choice
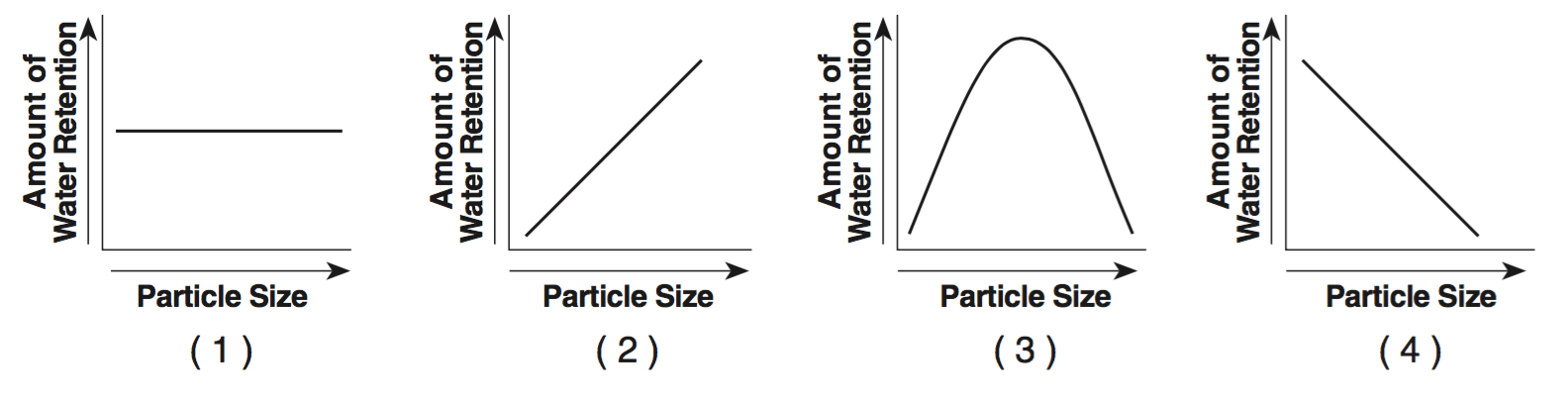
GRAPH 1
GRAPH 2
GRAPH 3
GRAPH 4
56.
Multiple Choice
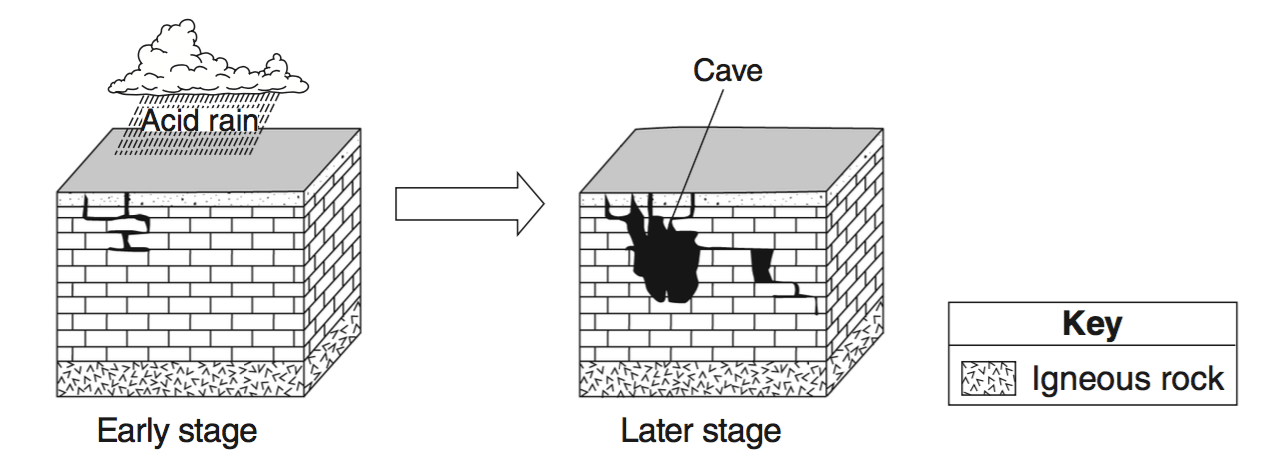
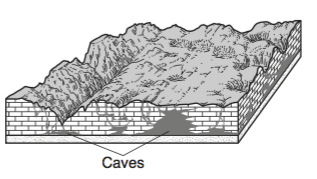
The two block diagrams below represent the formation of caves. Which types of weathering and erosion are primarily responsible for the formation of caves?
chemical weathering and groundwater flow
chemical weathering and runoff
physical weathering and groundwater flow
physical weathering and runoff
57.
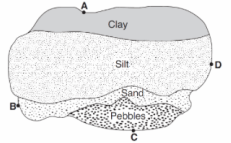
Multiple Choice
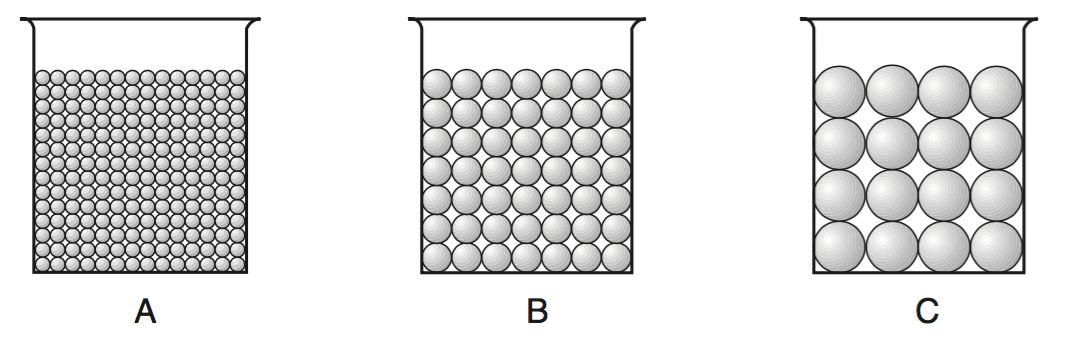
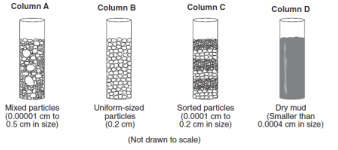
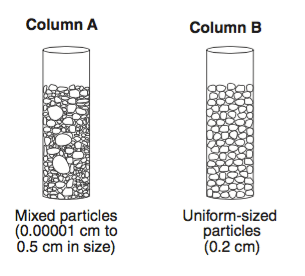
Which statement best describes the porosity that was found for these three samples?
A had a greater porosity than B and C.
B had a greater porosity than A and C.
C had a greater porosity than A and B.
All three samples had the same porosity.
58.
Multiple Choice
inside of meanders where the stream flows faster
inside of meanders where the stream flows slower
outside of meanders where the stream flows faster
outside of meanders where the stream flows slower
59.
Multiple Choice
velocity of the river decreases
force of gravity decreases
volume of water increases
slope of the river increases
60.
Multiple Choice
110 cm/s
190 cm/s
325 cm/s
425 cm/s
61.
Multiple Choice
It is located at a high elevation in a mountainous area.
It is less than 25 centimeters in diameter.
Its composition is different from that of the bedrock under it.
It appears to have been intensely metamorphosed.
62.
Multiple Choice
It will become jagged and its mass will decrease.
It will become jagged and its volume will increase.
It will become rounded and its mass will increase.
It will become rounded and its volume will decrease.
63.
Multiple Choice
Boulder
Cobble
64.
Multiple Choice
Pebble
Sand
65.
Multiple Choice
Sand
Silt
66.
Multiple Choice
Pebble
Cobble
67.
Multiple Choice
Clay
Silt
Sand
68.
Multiple Choice
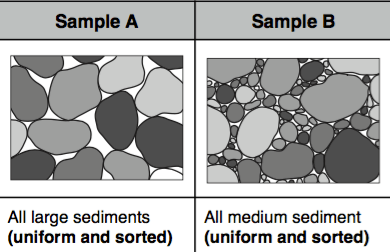
Sample A
Sample B
They have the same porosity
69.
Multiple Choice
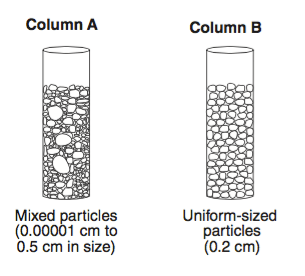
it will have faster rates of infiltration
it will have slower rates of infiltration
It will have the same rate of infiltration
It will have a longer time needed to infiltrate
70.
Multiple Choice
The process of water soaking into a soil sample
The ability of a soil sample to permit water to flow through it
The percentage of empty space in a soil sample
What happens to water that cannot soak through a soil sample
71.
Multiple Choice
Sample A
Sample B
They have the same retention
72.
Multiple Choice
The amount of water that is kept within soil after it is drained
The ability of a soil sample to permit water to flow through it
The percentage of empty space in a soil sample
What happens to water that cannot soak through a soil sample
73.
Multiple Choice
This means that there is a(n) ________ relationship between these two variables.
direct
inverse
74.
Multiple Choice
This means that there is a(n) ________ relationship between these two variables because ____ _________________________.
direct - an increase in one causes a decrease in the other
inverse - an increase in one causes a decrease in the other
direct - an increase in one causes an increase in the other
inverse - an increase in one causes an increase in the other
75.
Multiple Choice
Physical weathering is best defined as...
Mechanical changes to a rock by a variety of forces.
Compositional changes to a rock by a variety of forces.
Changes to a rock caused by the weather.
All of the above.
76.
Multiple Choice

Physical - Root Action
Physical - Abrasion
Chemical - Root Action
Chemical - Abrasion
77.
Multiple Choice

The picture shows a cave created out of limestone from acidic rainwater. This is an example of what type of weathering?
Physical - Oxidation
Physical - Carbonation
Chemical - Oxidation
Chemical - Carbonation
78.
Multiple Choice
Physical - Frost Action
Physical - Carbonation
Chemical - Frost Action
Chemical - Carbonation
79.
Multiple Choice

The picture shows rocks falling down a cliff. This is an example of what type of erosion?
Ocean Waves
Gravity
Running Water
Wind
80.
Multiple Choice

Physical - Oxidation
Physical - Carbonation
Chemical - Oxidation
Chemical - Carbonation
81.
Multiple Choice
the shape AND the composition of rocks.
the shape BUT NOT the composition of rocks.
the composition BUT NOT the shape of rocks.
NEITHER the shape NOR the composition of rocks.
82.
Multiple Choice
the shape AND the composition of rocks.
the shape BUT NOT the composition of rocks.
the composition BUT NOT the shape of rocks.
NEITHER the shape NOR the composition of rocks.
83.
Multiple Choice
water
carbon dioxide
oxygen
methane
84.
Multiple Choice

Arid environments usually have
BOTH chemical and physical weathering
some physical BUT NOT chemical weathering
some chemical BUT NOT physical weathering
NEITHER chemical nor physical weathering
85.
Multiple Choice

The picture shows a limestone statue that has been weathered. This is an example of what type of weathering?
Physical - Carbonation
Physical - Abrasion
Chemical - Carbonation
Chemical - Abrasion
86.
Multiple Choice

Physical - Carbonation
Physical - Abrasion
Chemical - Carbonation
Chemical - Abrasion
87.
Multiple Choice
air temperature increases and precipitation decreases
air temperature decreases and precipitation also decreases
air temperature decreases and precipitation increases
air temperature increases and precipitation also increases
88.
Multiple Choice
air temperature increases and precipitation decreases
air temperature decreases and precipitation also decreases
air temperature decreases and precipitation increases
air temperature increases and precipitation also increases
89.
Multiple Choice
cool and dry
warm and dry
cool and wet
warm and wet
90.
Multiple Choice
cool and dry
warm and dry
cool and wet
warm and wet
91.
Multiple Choice
chemical weathering of limestone
physical weathering of limestone
chemical weathering of sandstone
physical weathering of sandstone
92.
Multiple Choice
freezing of water in the cracks of a sandstone sidewalk
rusting of iron particles in soil
grinding a sediment into powder
abrasion in a stream by tumbling sediments
93.
Multiple Choice
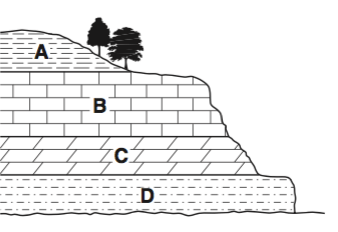
Layer A
Layer B
Layer C
Layer D
94.
Multiple Choice

Layer A
Layer B
Layer C
Layer D
95.
Multiple Choice
Which characteristics best distinguish one landscape region from another?
human population density and types of environmental pollutants
stream gradients and soil types
bedrock structure and elevation of land surfaces
composition of bedrock and variety of fossils
96.
Multiple Choice
In which New York State landscape region is Niagara Falls located?
Tug Hill Plateau
St. Lawrence Lowlands
Allegheny Plateau
Erie-Ontario Lowlands
97.
Multiple Choice
Which sequence shows the order in which landscape regions are crossed as an airplane flies in a straight course from Albany, New York to Massena, New York?
plateau → plain → mountain
plateau → mountain → plain
plain → mountain → plain
mountain → plain → plateau
98.
Multiple Choice
Landscapes characterized by gentle slopes and meandering streams are most often found in regions with
steep mountian cliffs
sediment-covered bedrock
recently active faults and folds
high volcanic activity
99.
Multiple Choice
Which New York State landscape region is composed mainly of metamorphosed surface bedrock?
Taconic Mountains
Allegheny Plateau
Atlantic Coastal Plain
Erie-Ontario Lowlands
100.
Multiple Choice
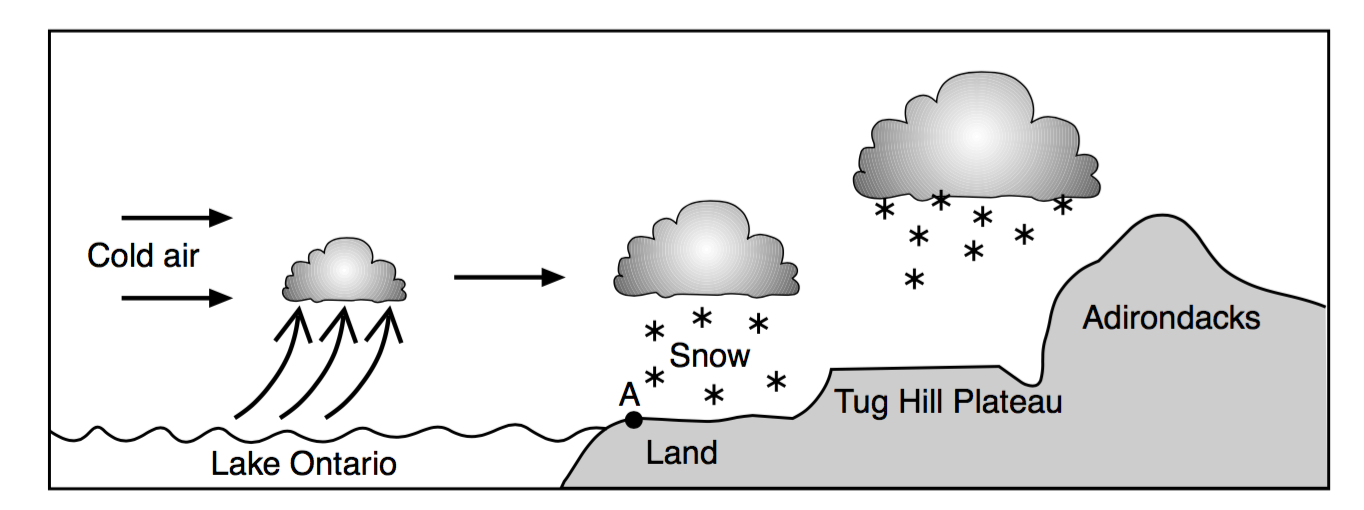
State the name of the New York State landscape region that includes location A shown in the diagram.
Erie-Ontario Lowlands
the Catskills
Taconic Mountains
Allegheny Plateau
101.
Multiple Choice
Chemical weathering is best defined as...
Mechanical changes to a rock by a variety of forces.
Compositional changes to a rock by a variety of forces.
Changes to a rock caused by the weather.
All of the above.
102.
Multiple Choice
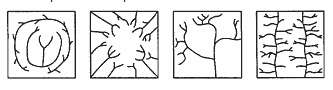
Which factor most likely caused the differences in these stream drainage patterns?
Time
Climate
Human activities
Bedrock structure
103.
Multiple Choice
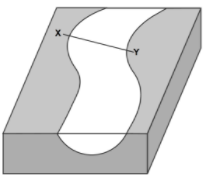
Which cross section best represents the shape of the stream channel at line XY?
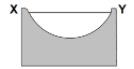
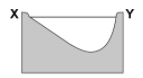
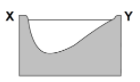
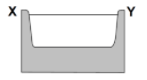
104.
Multiple Choice
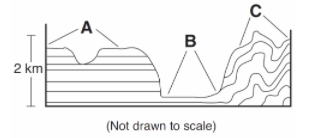
Which list correctly identifies the type of landscapes represented by letters A, B, and C?
A = plain, B = plateau, C = mountain
A = plateau, B = plain, C = mountain
A = mountain, B = plateau, C = plain
A = plain, B = mountain, C = plateau
105.
Multiple Choice
The narrow, sandy, barrier islands in the ocean along the south coast of Long Island were deposited by
wave action
glaciers
wind
streams
106.
Multiple Choice
Which type of landscape region is found at 44º North latitude and 75º West longitude?
mountains
plains
plateau
lowlands
107.
Multiple Choice
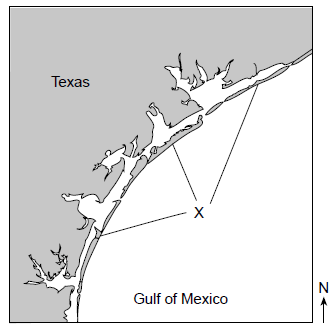
The feature labeled "X" was created by wave action. What is the name of the feature indicated by the letter X?
barrier islands
island arc
delta
morain
108.
Multiple Choice
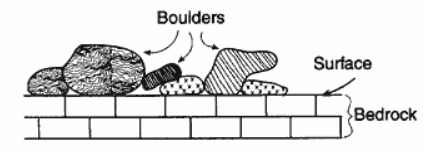
The cross section below represents large boulders made of granite, gneiss, and quartzite that are found lying on limestone bedrock near Oswego, New York.
If no overturning of bedrock has occurred, which statement correctly explains the source of the boulders?
The limestone was changed by contact metamorphism caused by a lava flow.
The limestone bedrock formed under conditions of high heat and pressure.
Older igneous and metamorphic bedrock that once covered the limestone eroded away, forming the boulders.
The boulders were transported and deposited on the limestone bedrock by a glacier.
109.
Multiple Choice
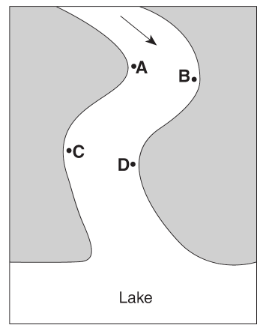
The greatest stream velocities are found closest to points
A and B
B and C
C and D
D and A
110.
Multiple Choice
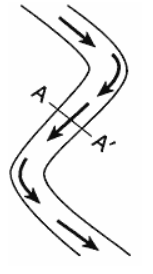
Which stream profile best represents the cross section from A to A' ?

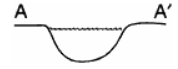

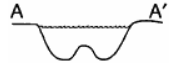
111.
Multiple Choice
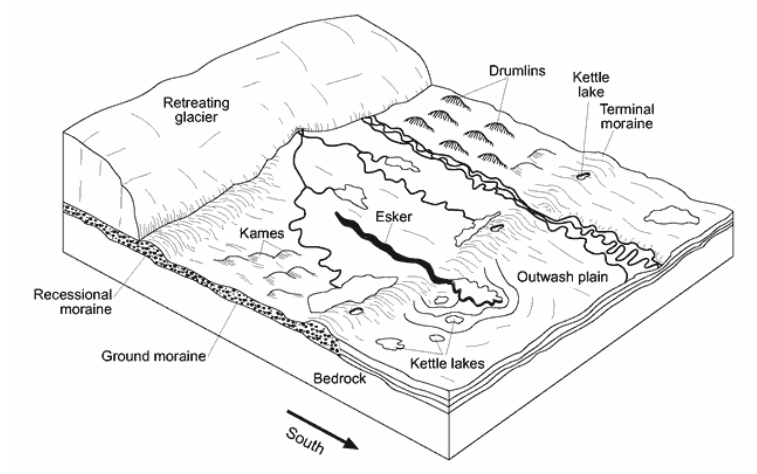
The shape of elongated hills labeled drumlins is most useful in determining the
direction of glacial movement
age of the glacier
thickness of the glacial ice
rate of glacial movement
112.
Multiple Choice
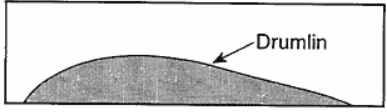
The diagram below represents a side view of a hill (drumlin) that was deposited by a glacier on the Atlantic coast.
This hill is most likely composed of
cemented sediments
unsorted sediments
vertically layered sediments
horizontally layered sediments
113.
Multiple Choice
Which cross section best represents the valley shape where a rapidly flowing stream is cutting into the bedrock in a mountainous area?
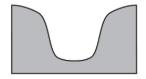
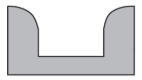
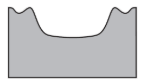
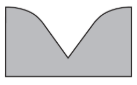
114.
Multiple Choice
Which profile best shows the general depositional pattern that occurs when water from a stream enters the ocean?
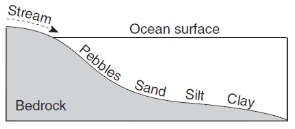
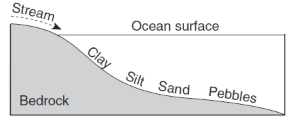
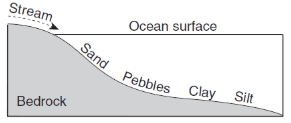
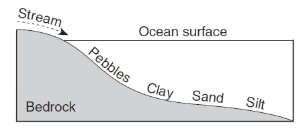
115.
Multiple Choice
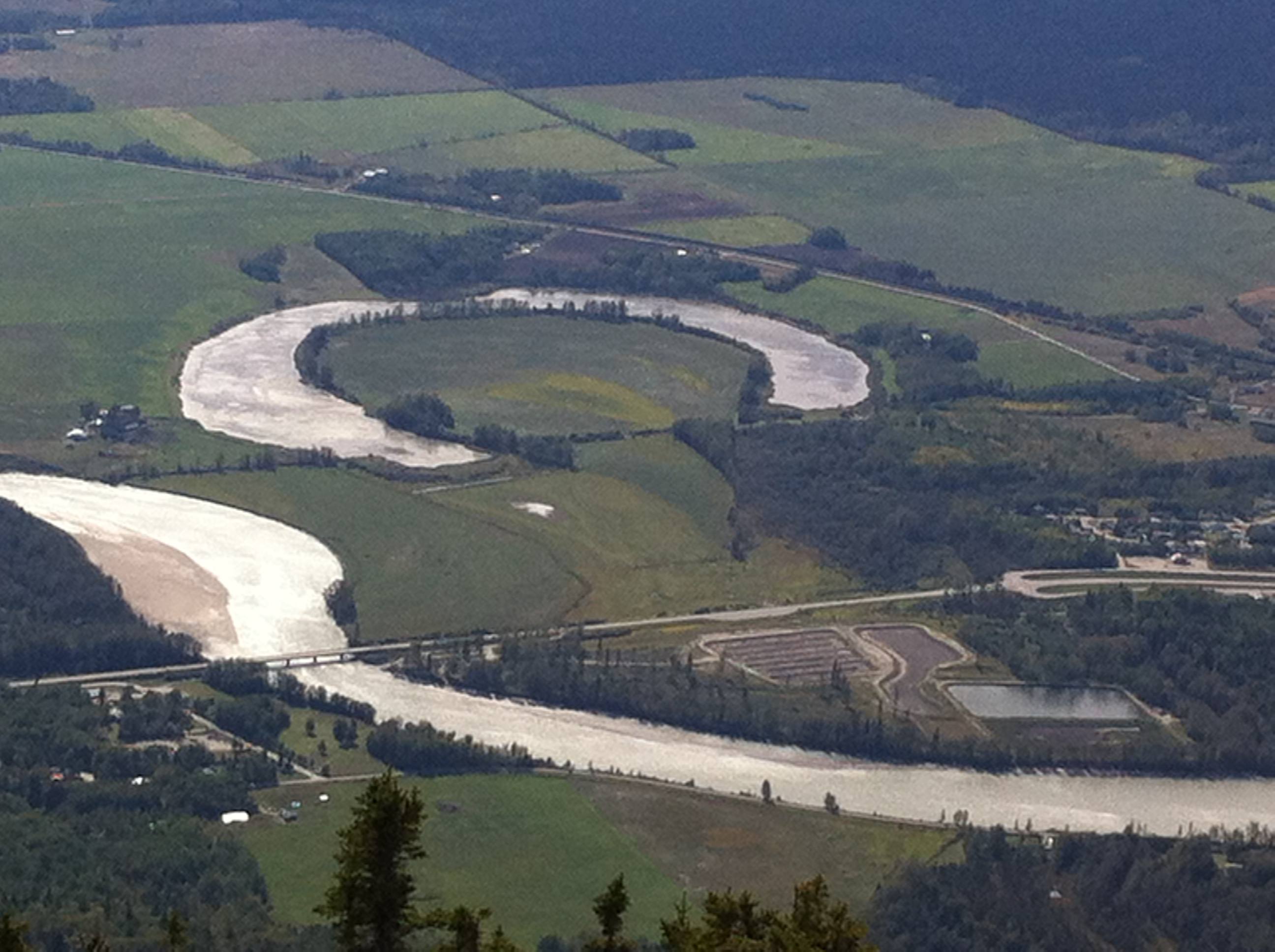

What feature is pictured?
oxbow lake
braided river
U-shaped valley
landslide
116.
Multiple Choice
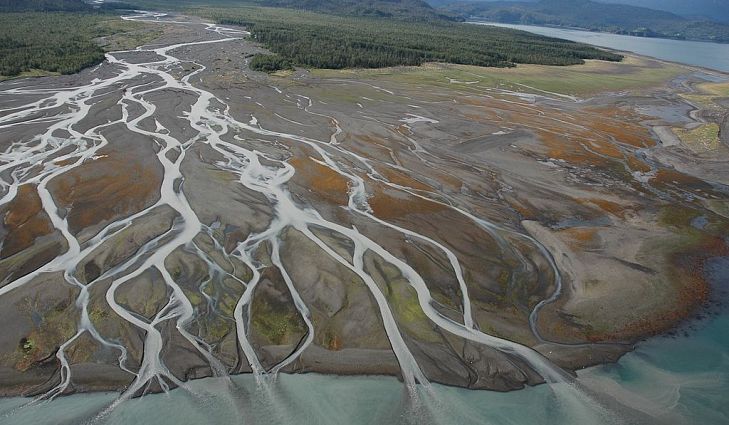

When a river meets a large body of water...
it speeds up, picking up more material
it continues at the same speed
it slows down, depositing material
it makes a whirlpool
117.
Multiple Choice
Organic material would be near the ______________ of a section of soil
top
middle
bottom
118.
Multiple Choice
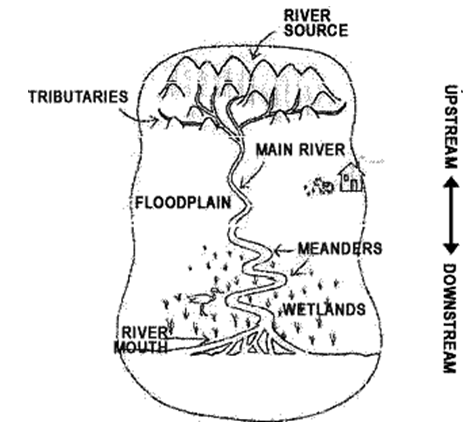
What is a watershed?
a shed with water
rivers and streams
land area that drains tributaries and rivers into it
wetlands and marshes
119.
Multiple Choice
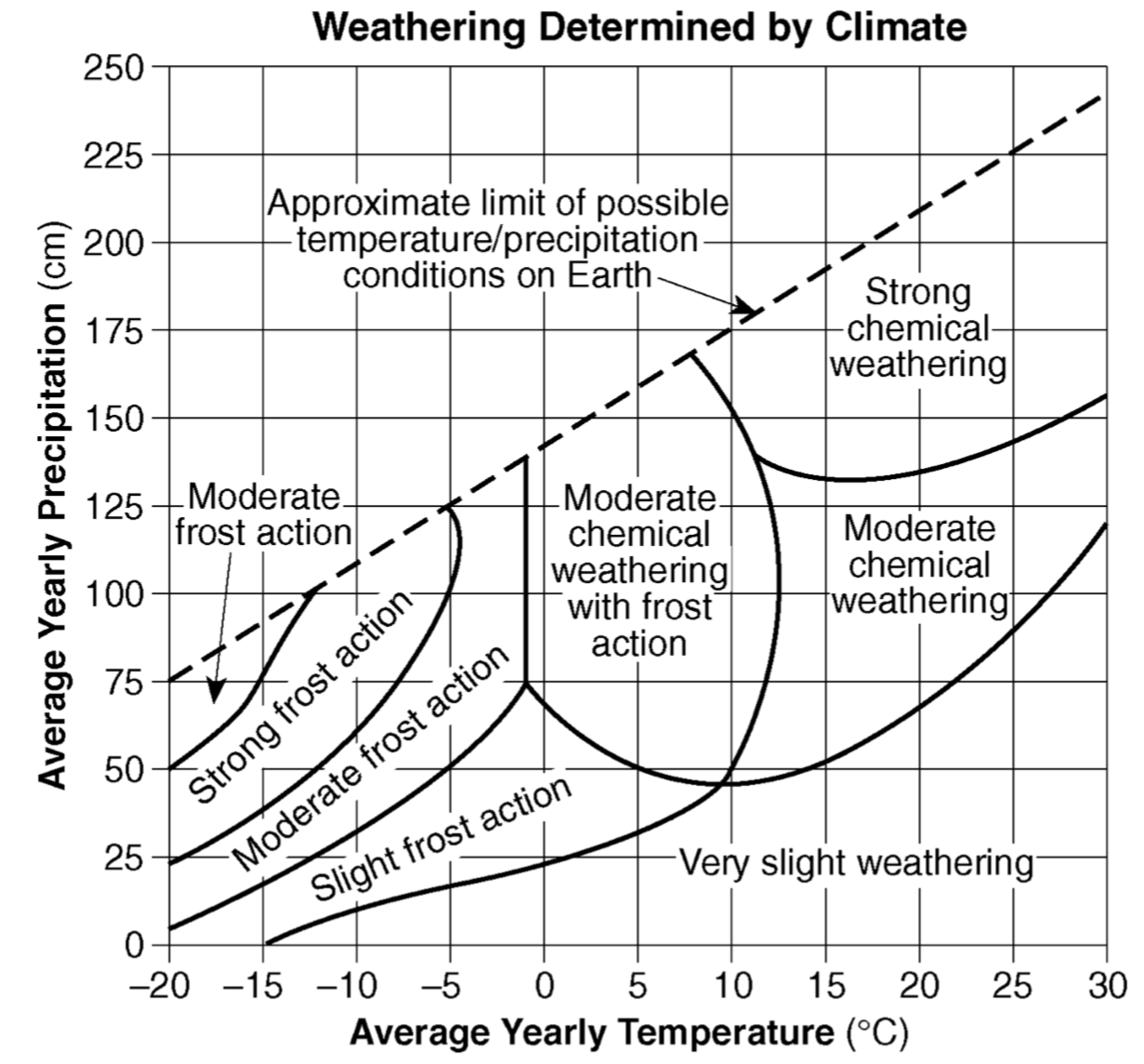
The amount of chemical weathering will increase if
air temperature decreases and precipitation decreases
air temperature increases and precipitation decreases
air temperature decreases and precipitation increases
air temperature increases and precipitation increases
120.
Multiple Choice
Which factor has the most influence on the development of soil?
climate
longitude
amount of eroded sediment
slope of the landscape
121.
Multiple Choice
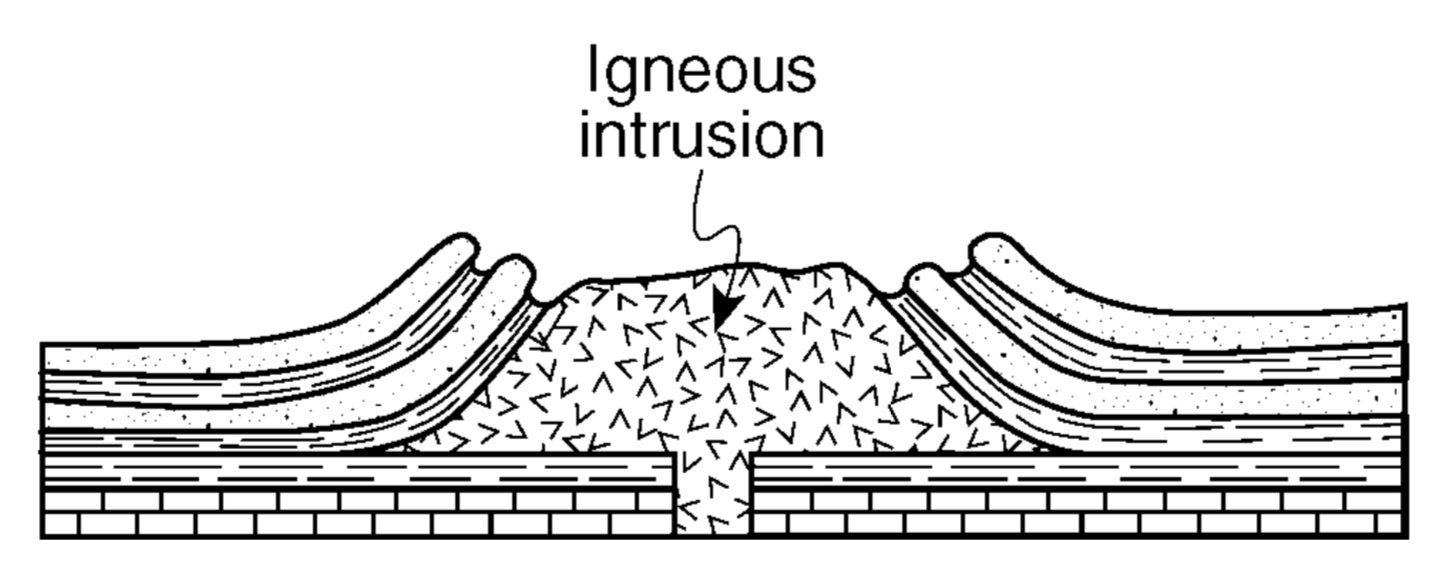
The cross section above shows the rock structure of a deeply eroded, domed mountain region. Which map shows the stream drainage pattern that will most likely develop as the bedrock is weathered and eroded from this igneous dome?
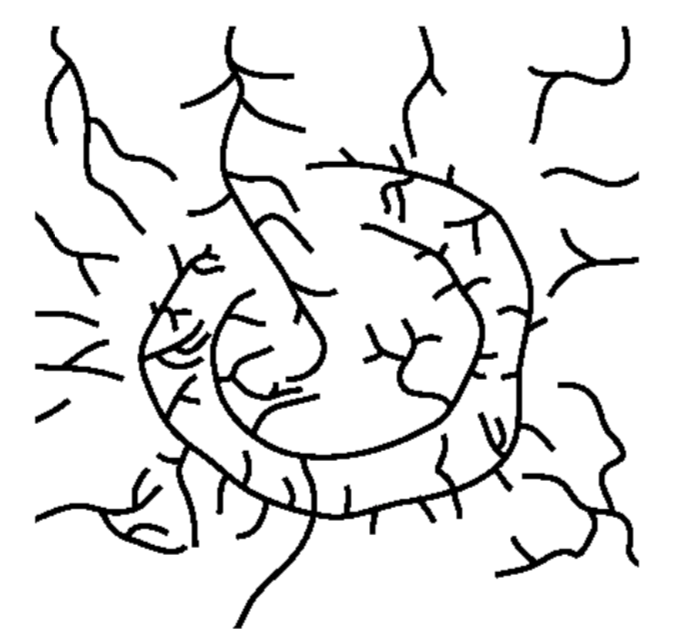
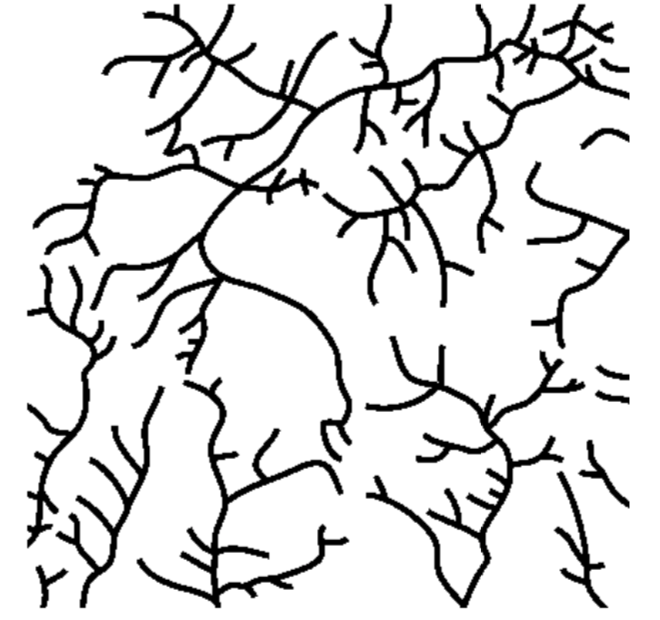

122.
Multiple Choice
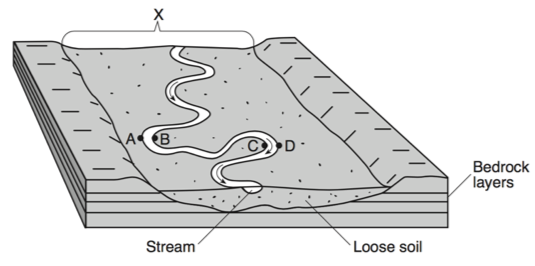
The landscape feature labeled X is best described as
a flood plain
a sand bar
a delta
an escarpment
123.
Multiple Choice
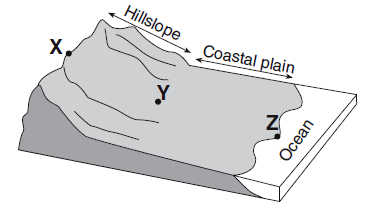
Compared to the stream velocity between point X and point Y, the stream velocity between point Y and point Z is most likely
greater, since the slope of the land decreases
greater, since the slope of the land increases
less, since the slope of the land decreases
less, since the slope of the land decreases
124.
Multiple Choice
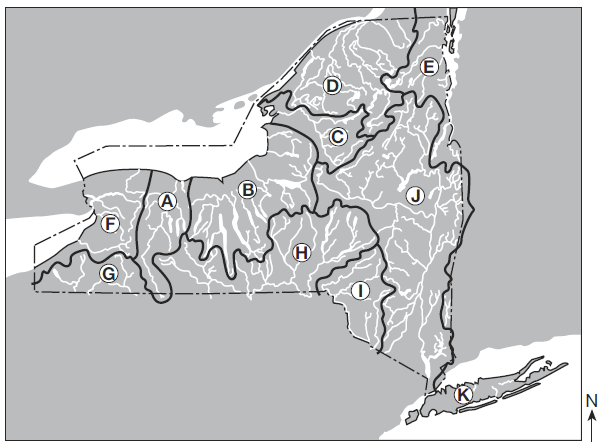
Over which two landscape regions do the streams in watershed D flow?
Tug Hill Plateau and the Catskills
Tug Hill Plateau and Erie-Ontario Lowlands
Adirondack Mountains and Champlain Lowlands
Adirondack Mountains and St. Lawrence Lowlands
125.
Multiple Choice
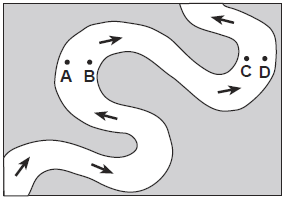
Which two locations have the greatest stream velocities?
A and B
B and C
C and D
D and A
126.
Multiple Choice
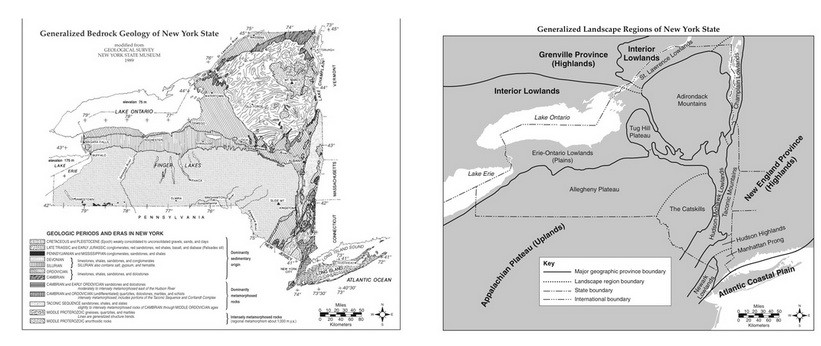
Which two cities are located in the Interior Lowlands?
Elmira and Binghamton
Riverhead and New York City
Massena and Old Forge
Buffalo and Watertown
127.
Multiple Choice
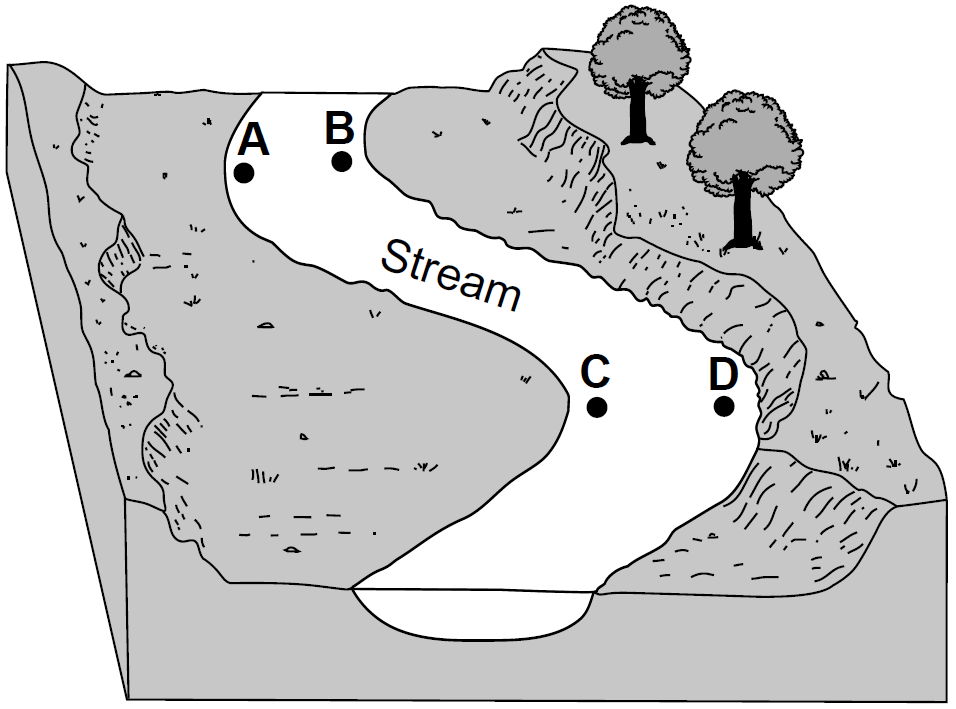
At which two locations would the stream most likely be the deepest?
A and B
B and C
C and D
D and A
128.
Multiple Choice
climate variations
bedrock structure
vegetation type
bedrock age
129.
Multiple Choice
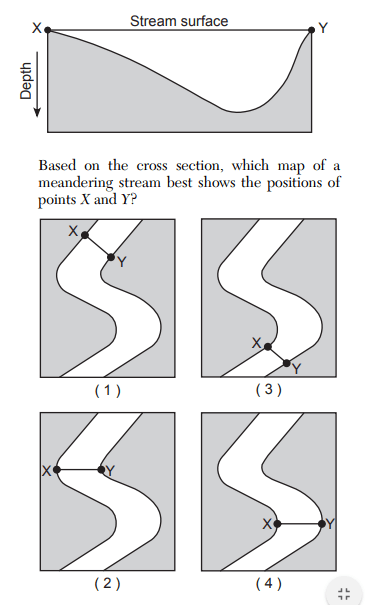
Based on the cross section, which map of a meandering stream best shows the positions of points X and Y?
map 1
map 2
map 3
map 4
130.
Multiple Choice
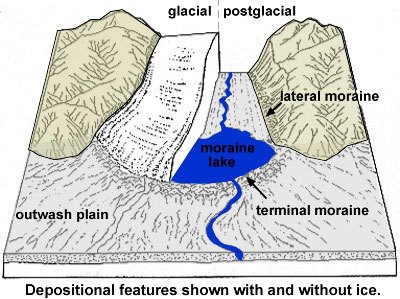
How does the sediment compare at the moraines and the outwash plain?
The moraine and outwash plain are both sorted
The moraine is sorted and the outwash plain is unsorted
The moraine is unsorted and the outwash plain is sorted
The moraine and outwash plain are both unsorted

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Glaciers
•
9th - 12th Grade

Weathering and Mass Movements
•
9th - 11th Grade

Urban, Suburban, and Rural Communities
•
1st - 2nd Grade

Glaciers
•
9th Grade

Glaciers Deserts and Wind
•
11th - 12th Grade

First Amendment
•
2nd Grade

Quick Changes to Earth
•
2nd Grade

Abraham Lincoln
•
KG