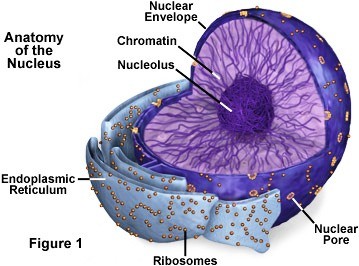
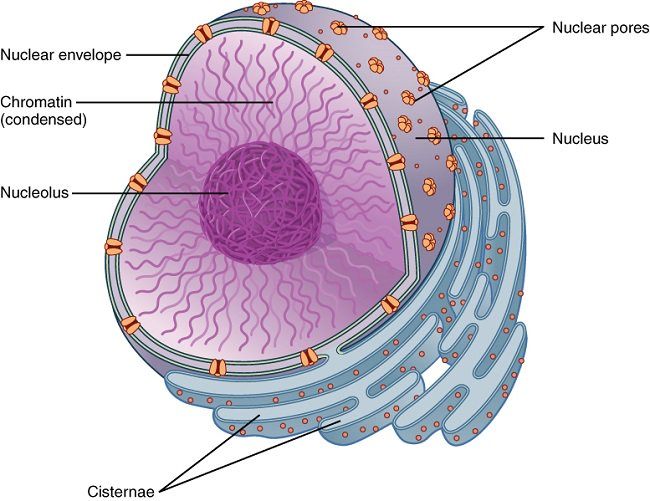
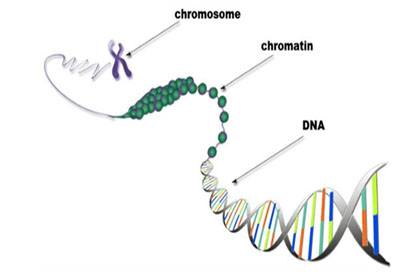
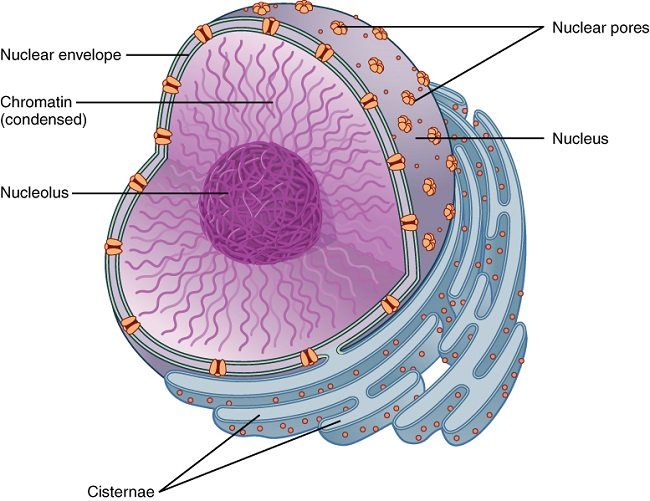
The Nucleus
Assessment
•
Kelly Fitz-Randolph
•
Science
•
6th - 8th Grade
•
952 plays
•
Medium
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
11 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
The control center of the cell.
cytoplasm
nucleus
nucleoplasm
chromatin
2.
Multiple Choice
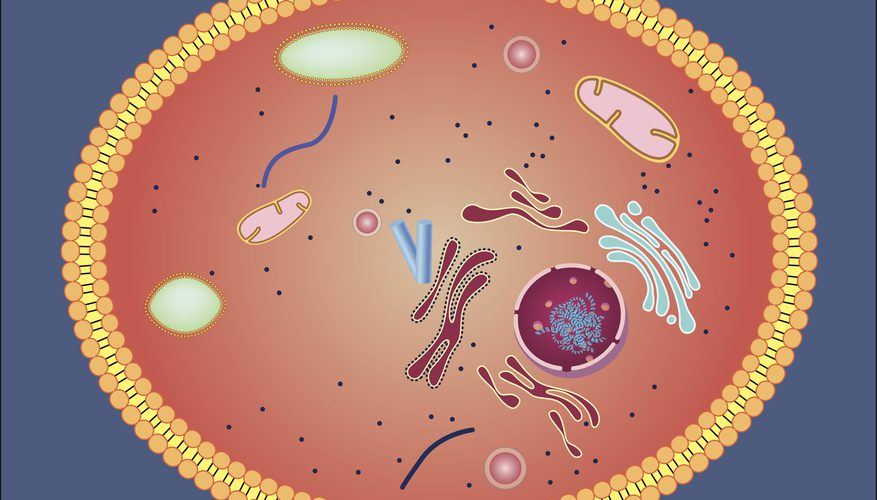
A jelly-like fluid that lls all the empty space in the cell, giving it shape and keeping everything in place.
chromatin
cytoplasm
nucleus
nucleoplasm
3.
Multiple Choice
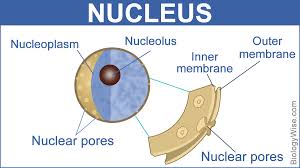
Made up of two layers (an inner and an outer), this acts like a cushiony outer shell of protection.
nucleoplasm
nuclear pores
nuclear membrane
nucleolus
4.
Multiple Choice
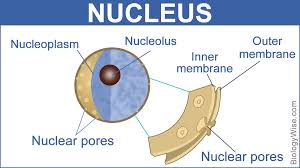
Tiny holes in the nuclear membrane that allow different cellular materials to come in and go out of the cell.
nucleus
nucleoplasm
nucleolus
nuclear pores
5.
Multiple Choice
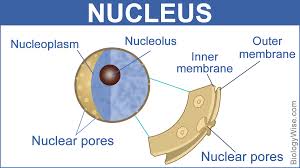
A gel-like fluid that holds things in place and helps to give the nucleus shape.
nuclear pores
nucleoplasm
nucleolus
nuclear membrane
6.
Multiple Choice
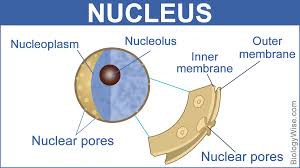
Helps transport essential materials throughout the nucleus.
nuclear membrane
nuclear pores
nucleoplasm
nucleolus

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Cells and Cell Organelles
•
7th Grade

Plant and Animal Cells
•
5th - 6th Grade

Plant and Animal Cells
•
6th Grade

Cell Organelles
•
7th Grade

Plant and Animal Cells
•
5th Grade

Cell Structure and Function
•
7th - 8th Grade

Plant and Animal Cells
•
6th - 8th Grade

Cells Cells and more Cells
•
1st - 3rd Grade