PBS EOC Review
Assessment
•
Melanie Brooks
•
Other Sciences
•
9th - 11th Grade
•
2K plays
•
Medium
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
131 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
A single 5 carbon ring
A single 6 carbon ring
A double ring with one six carbon and one 5 carbon ring
A double ring with two four carbon rings
2.
Multiple Choice
Create a pattern of a person's DNA
Act as molecular scissors that cut DNA
Separate and compare different DNA sequences
Produce millions of copies of DNA
3.
Multiple Choice
adenine... purine
thymine... pyrimidine
cytosine.....purine
guanine....pyrimidine
4.
Multiple Choice

Suspect 1
Suspect 2
Suspect 3
Suspect 4
5.
Multiple Choice
heart rate
type of exercise
amount of exercise
time of day exercise occurs
6.
Multiple Choice
1
2
3
4
7.
Multiple Choice

What was the control?
The customers
The crabby patty
The colored buns
The number of customers
8.
Multiple Choice
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms
Restriction Fragmented Long Palindromes
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Polymorphic Fragment Chains
9.
Multiple Choice
negative, positive
positive, negative
negative, neutral
positive, neutral
10.
Multiple Choice
Phosphates and sugars
Basepairs
Deoxyribose
Hydrogen bonds
11.
Multiple Choice
triple... hydrogen
double... nitrogen
double... hydrogen
triple... nitrogen
12.
Multiple Choice
Shoeprint
Tabletop
Syringe
Blood
13.
Multiple Choice
Blood type
Weapon
Amount of blood lost
The height from which the blood fell
14.
Multiple Choice
Endocrine
Integumentary
Immune
Urinary
15.
Multiple Choice
Blood pressure
Fingerprints
Skin texture
Body Temperature
16.
Multiple Choice
Magnetism
Electricity
Hydrogen Bonds
Agarose
17.
Multiple Choice
Coroner
Toxicologist
Medical Examiner
Forensic Anthropologist
18.
Multiple Choice
100 bp
1,000 bp
5,000 bp
10,000 bp
19.
Multiple Choice
20%
10%
30%
60%
20.
Multiple Choice
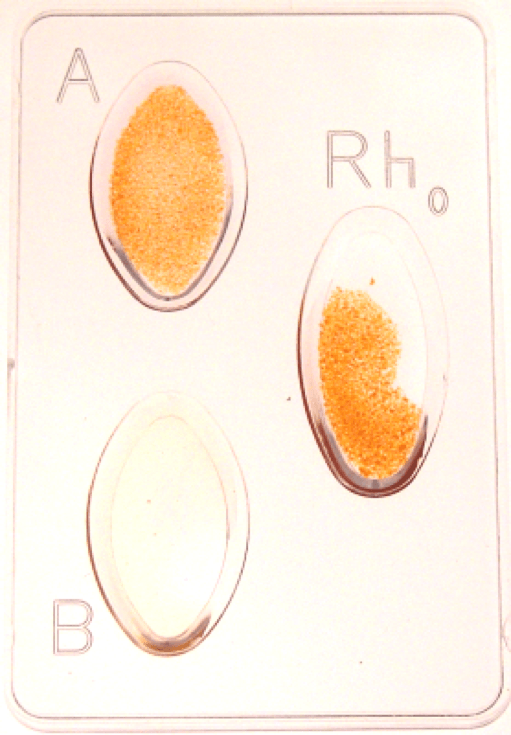
Type A
Type B
Type AB
Type O
21.
Multiple Choice
Immune
Nervous
Endocrine
Digestive
22.
Multiple Choice
Circulatory system
Respiratory System
Muscular System
Digestive System
23.
Multiple Choice
Muscular
Digestive
Immune
Endocrine
24.
Multiple Choice
The person is under 18
When the person cannot be reached by phone
When the person has given consent to the doctor
When the mother tells the doctor it is okay
25.
Multiple Choice
Yes, he is not entitled to know her information just because he came to the doctor's office.
No, He came with his wife to the doctor and she never told the nurse not to say anything.
Yes, because he should not be yelling at the nurse
No, husbands and wives are exempt from HIPAA
26.
Multiple Choice
Yes, the patient specifically asked her to protect his privacy.
No, measles is a public health concern and trumps the patient's entitlement to privacy
It depends on if the nurse has proper clearance from her boss.
27.
Multiple Choice
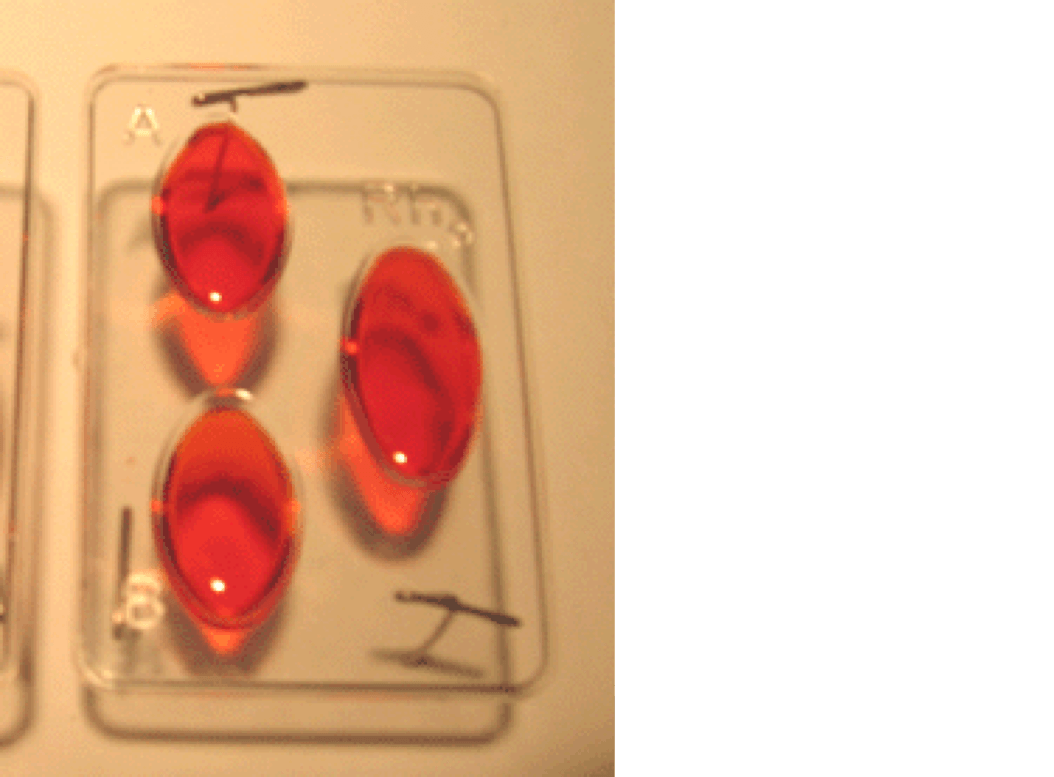

Type A
Type B
Type AB
Type O
28.
Multiple Choice
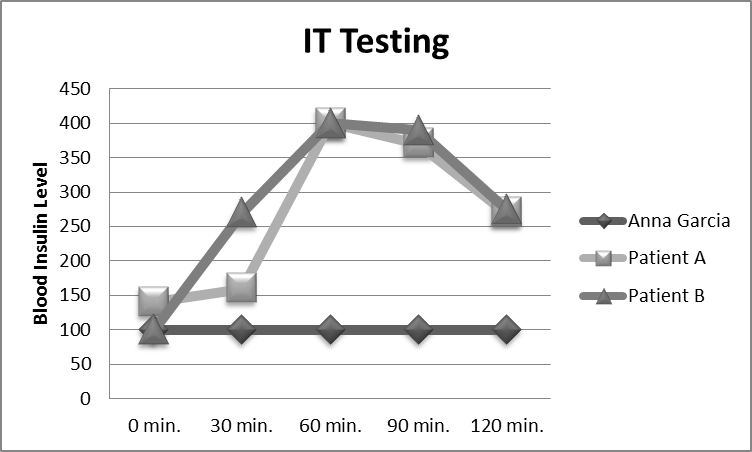
Anna only
Patient A
Patients A and B
Patient B and Anna
29.
Multiple Choice
glucagon
insulin
glucose
pancreasome
30.
Multiple Choice
hypoglycemia
hyperglycemia
31.
Multiple Choice
expand
shrink
not change
expand and then shrink
32.
Multiple Choice
positive feedback loop
negative feedback loop
neutral feedback loop
cause-effect feedback loop
33.
Multiple Choice
Spleen
Pancreas
Liver
Lungs
34.
Multiple Choice
Advanced age
obesity
poor foot care
physical inactivity
35.
Multiple Choice
30-69 mg/dL
70-130 mg/dL
160-280 mg/dL
425 mg/dL
36.
Multiple Choice
Blindness
Cardiovascular disease
kidney disease
genetic mutations
37.
Multiple Choice
hypoglycemia;hypertonic
hyperglycemia; hypotonic
hypoglycemia; hypotonic
hyperglycemia ;hypertonic
38.
Multiple Choice
alpha cells of pancreas
beta cells of pancreas
liver
brain
39.
Multiple Choice
I. Weight gain
II. Decreased urination
III. Feeling hungry
IV. Feeling thirsty
V. Weight loss
VI. Hyperactivity
All of these
I, III, V, VI
III, IV, and V
II, IV, VI
40.
Multiple Choice
Type I
Type II
41.
Multiple Choice
I. A diet low in carbs
II. Exercise
III. Insulin
IV. Anti-viral drugs
V. Warmer climates
All of these
I, II, III, and V
III
III and V
42.
Multiple Choice
positive feedback loops
negative feedback loops
external stimuli
internal stimuli
43.
Multiple Choice
balanced external environment
balanced internal environment
changing external environment
changing internal environment
44.
Multiple Choice
lack of internal balance
eventual death
difficulty carrying on metabolism
all three
45.
Multiple Choice
amplify processes
prevent small changes from getting larger
are initiated during childbirth
are found only in plants
46.
Multiple Choice
negative feedback loop
positive feedback loop
47.
Multiple Choice
negative feedback loop
positive feedback loop
48.
Multiple Choice
kidneys
glands
brain
bones
49.
Multiple Choice
decreased
non existant
increased
changes constantly
50.
Multiple Choice
Positive Feedback Response
Negative Feedback Loop
51.
Multiple Choice
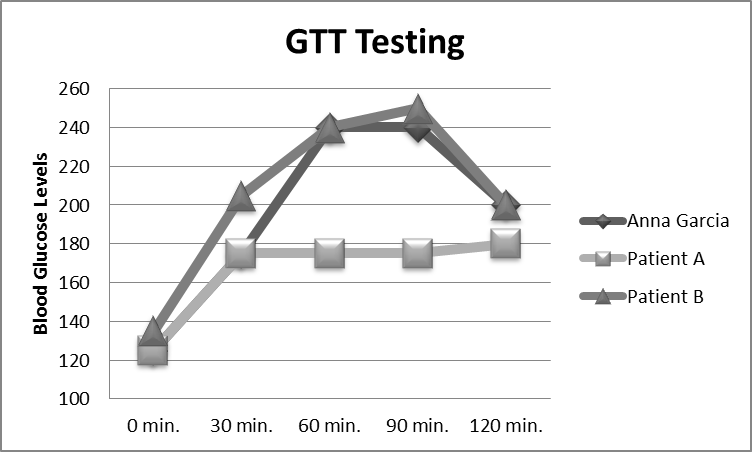
Anna and Patients A and B
Patient A only
Patient B and Anna
Patient A and Anna
52.
Multiple Choice
Take cholesterol to the liver
Take cholesterol to the cells
Take cholesterol to the pancreas
Take cholesterol to the blood
53.
Multiple Choice
Take cholesterol to the liver
Take cholesterol to the cells
Take cholesterol to the pancreas
Take cholesterol to the blood
54.
Multiple Choice
a fat that carries protein in the blood
a protein that carries cholesterol in the blood
a cell that carries blood to the liver
a cell that transforms cholesterol into protein
55.
Multiple Choice
Which lipoprotein takes up more room?
LDL
HDL
56.
Multiple Choice
HDL
LDL
PDL
BDL
57.
Multiple Choice
100
150
200
250
58.
Multiple Choice
50
100
150
200
59.
Multiple Choice
30
40
50
60
60.
Multiple Choice
Centrifuge
Transcription
Electrophoresis
Protein synthesis
61.
Multiple Choice
positive
negative
neutral
62.
Multiple Choice
Can someone be a carrier of the FH gene? Why or why not?
Yes, because it is recessive
Yes, because it is dominant
No, because it is recessive
No, because it is dominant
63.
Multiple Choice
Restriction Enzymes
Double Helix
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
Gel
64.
Multiple Choice
100%
75%
50%
25%
65.
Multiple Choice
Plaque build up in the inner walls of arteries
Plaque build up in the heart chambers
Quivering contraction of the ventricles
Quivering contraction of the atria
66.
Multiple Choice
Use of a balloon & stent to move plaque and reinforce the wall
Use of a balloon to move plaque to clear pathway
Use of new vessel to go around the blocked section of blood flow
67.
Multiple Choice
Use of a balloon & stent to move plaque and reinforce the wall
Use of a balloon to move plaque to clear pathway
Use of new vessel to go around the blocked section of blood flow
68.
Multiple Choice
Supply blood to the lungs
Supply blood to the brain
Supply blood to the heart
Supply blood to the Aorta
69.
Multiple Choice
Myocardial infarction
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Commotio cordis
Myocardial difibrilation
70.
Multiple Choice
Right
Left
71.
Multiple Choice
Right
Left
72.
Multiple Choice
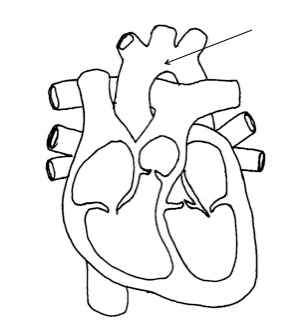
Pulmonary vein
Right atrium
Aorta
Pulmonary artery
73.
Multiple Choice
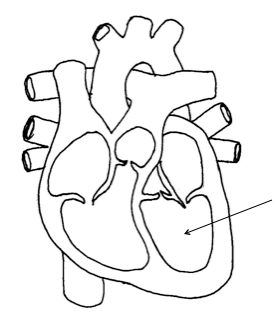
Left ventricle
Vena cava
Right atrium
Right ventricle
74.
Multiple Choice
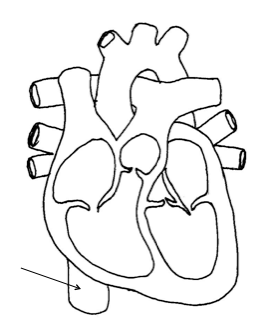
Superior vena cava
Right ventricle
Inferior vena cava
Pulmonary vein
75.
Multiple Choice
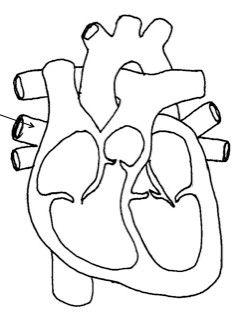
Pulmonary veins
Left atrium
Aorta
Pulmonary artery
76.
Multiple Choice
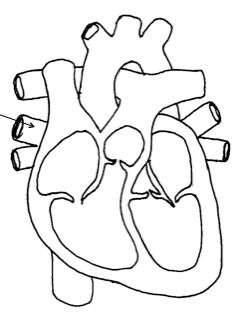
Pulmonary veins
Left atrium
Aorta
Pulmonary artery
77.
Multiple Choice
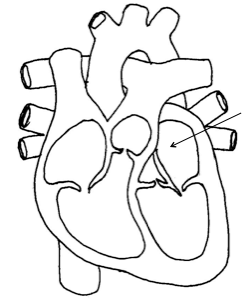
Right atrium
Left ventricle
Right ventricle
Left atrium
78.
Multiple Choice
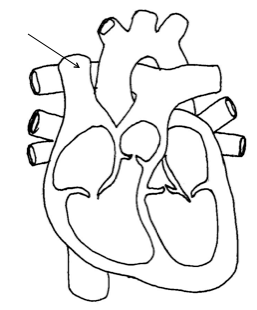
Superior vena cava
Right ventricle
Right atrium
Inferior vena cava
79.
Multiple Choice
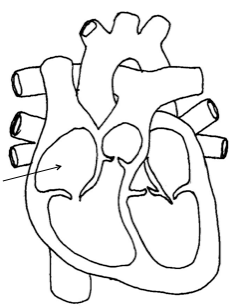
Right ventricle
Aorta
Right atrium
Atrium
80.
Multiple Choice
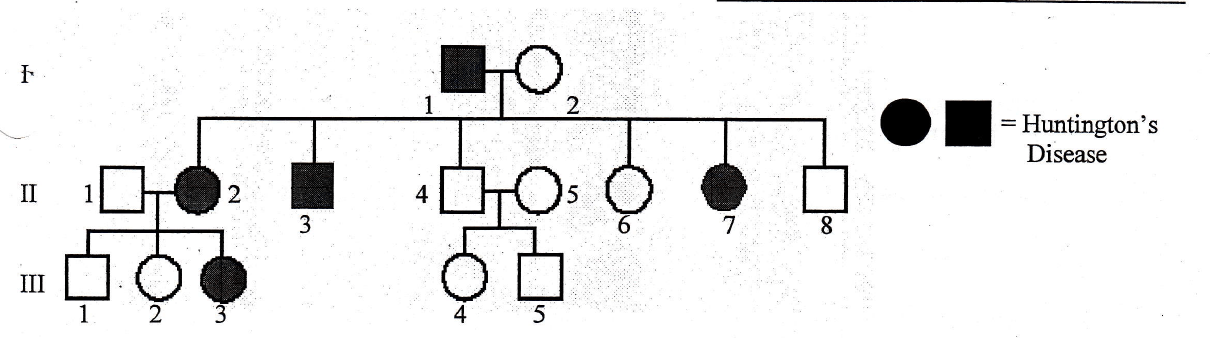
Dominant
Recessive
81.
Multiple Choice

Not affected Female (doesn't have the trait)
Not affected Male (doesn't have the trait)
Affected Male (has the trait)
Affected Female (has the trait)
82.
Multiple Choice
Not affected male (doesn't have the trait)
Not affected female (doesn't have the trait)
Affected male (has the trait)
Affected female (has the trait)
83.
Multiple Choice
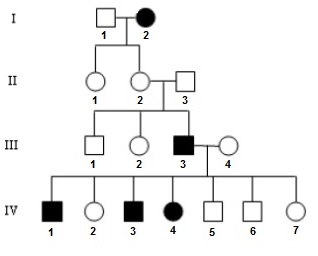
XBXb
XbXb
XBY
XbY
84.
Multiple Choice
True
False
85.
Multiple Choice
sterile
aseptic
antiseptic
clean
86.
Multiple Choice
True
False
87.
Multiple Choice
aspirin
radiation
antibiotics
ibuprophen
88.
Multiple Choice
sunny, cold and dry
hot and dry
warm, dark and moist
cold and wet
89.
Multiple Choice
plasma membrane
fimbriae
peptidoglycan
pilus
90.
Multiple Choice
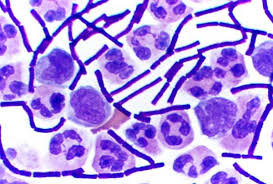
gram positive
gram negative
nonliving
viral
91.
Multiple Choice
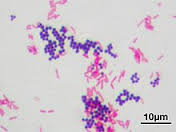
nonliving
gram positive
gram negative
gram positive and gram negative
92.
Multiple Choice
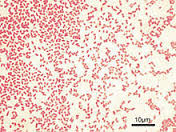
gram positive and negative
gram positive
gram negative
viral
93.
Multiple Choice
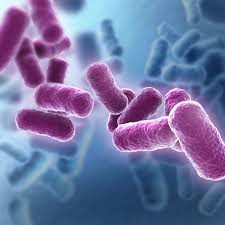
coccus
bacillus
spirilla
none of these
94.
Multiple Choice
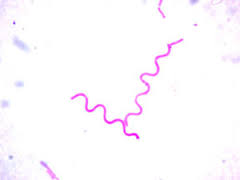
coccus
bacillus
spirilla
none of these
95.
Multiple Choice
alcohol
grams iodine
crystal violet
safranin
96.
Multiple Choice
alcohol
crystal violet
safranin
grams iodine
97.
Multiple Choice
shape
gram staining + or -
both of these
98.
Multiple Choice
A non-infectious disease
A Bacterial Infection
An infectious disease
A virus
99.
Multiple Choice
T-Cells
Memory Cells
White Blood Cells
Antibodies
100.
Multiple Choice
Saliva
B Cells
Tears
Skin
101.
Multiple Choice
Viruses can only kill bacterial cells
Humans have 100 trillion cells; viruses can't infect enough to kill
Our immune cells hunt and kill viruses
We have vaccines for all viruses
102.
Multiple Choice
everyone under 18 is vaccinated
a high proportion of all people are vaccinated
factory farming is outlawed
antibiotic are used to treat viral infections
103.
Multiple Choice
mosquitoes biting an infected person and flying to the next victim
viral particles left on surfaces where they can picked up on people's hands
viral particles are carried through the air in droplets when people sneeze
bodily fluids containing virus are exchanged through skin-to-skin contact
104.
Multiple Choice
They need host genetic material
They need a host cell
They need bacteria
They need insulin
105.
Multiple Choice
They are not cellular
They cannot reproduce on their own
They cannot make proteins
all of the above
106.
Multiple Choice
a structure that directly causes cell lysis
the type of virus that attacks bacteria
the genetic material of a virus
the protein coat of a virus
107.
Multiple Choice
viroid
prion
bacteriophage
protista
108.
Multiple Choice
droplet infection
direct contact
blood and bodily fluids
109.
Multiple Choice
to prevent antibiotic resistance
so you do not waste drugs
because antibiotics are good for you
110.
Multiple Choice
bind and flag infectious agents
destroys infectious agents
recognizes infectious agents
111.
Multiple Choice
Airborne
Dropletborne
Bareborne
Waterborne
112.
Multiple Choice
White blood cells that eat pathogens.
B cells
T cells
phagocytes
amoeboids
113.
Multiple Choice
B cells
T cells
Skin
Phagocytes
114.
Multiple Choice
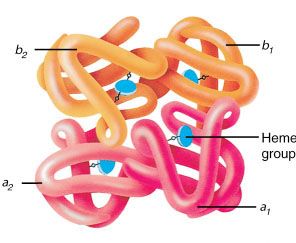
protein
parasite
plasma
115.
Multiple Choice
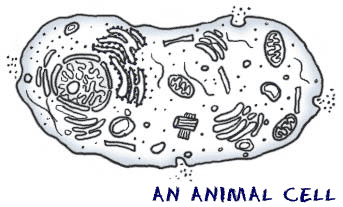
hemoglobin
mitochondria
cytoplasm
membrane
116.
Multiple Choice
blood
oxygen
water
117.
Multiple Choice
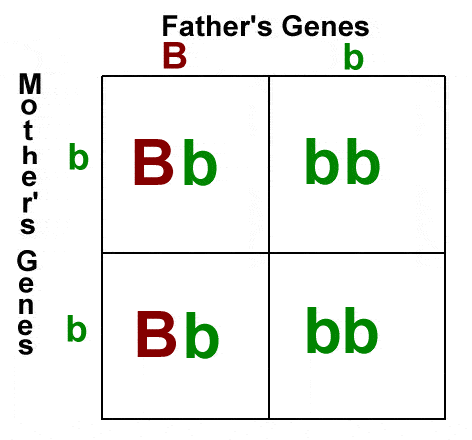
recessive
dominant
118.
Multiple Choice
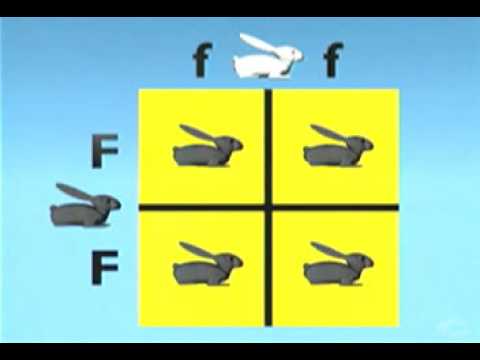
recessive
dominant
119.
Multiple Choice
If you have type B- blood, who can be your donor?
B- only
A- and AB-
O- and B-
AB+
120.
Multiple Choice
The Antibodies do not bind with the antigen.
Nothing happens.
The immune system will attack the blood cells.
The antigens change shape.
121.
Multiple Choice

Which of the following is not true about Sickle Cell Anemia?
It is most common among those of African descent.
It is caused by the genetic mutation that replaces GLU with VAL in the hemoglobin protein
It is caused by a frame shift mutation
It has a protective factor for malaria
122.
Multiple Choice
azuritis
cyanosis
psoriasis
anemia
123.
Multiple Choice
25.2%
15.4%
21.25%
18.75
124.
Multiple Choice
Erythrocytes
Thrombocytes
Leukocytes
Erytropoietin
125.
Multiple Choice
platelets
leukocytes
blood vessels
erythrocytes
126.
Multiple Choice
oxygen
protein
carbon dioxide
platelets
127.
Multiple Choice
Plasma
Leukocytes
Anemia
Erythropoietin
128.
Multiple Choice
Decomposition
Mummification
Rigor mortis
None of the above
129.
Multiple Choice
liver
mouth
stomach
underarm
130.
Multiple Choice
homicide
accidental
undetermined
natural
131.
Multiple Choice
The reason someone dies is called the:
type of death
manner of death
cause of death
mechanism of death

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Blood Review
•
11th - 12th Grade

Cardiovascular System
•
11th - 12th Grade

The Circulatory System
•
7th Grade

Solar System
•
5th - 8th Grade

Mixtures and Solutions
•
4th Grade

Morris Heart Anatomy
•
10th - 12th Grade

Anatomy of the Heart
•
11th - 12th Grade

Paraphrasing
•
4th Grade