
Moon Phases and Tides
Assessment
•

Antoinette Longino
•
Other Sciences
•
6th - 8th Grade
•
3K plays
•
Hard
Improve your activity
Higher order questions
Match
•
Reorder
•
Categorization
.svg)
actions
Add similar questions
Add answer explanations
Translate quiz
Tag questions with standards
More options
52 questions
Show answers
1.
Multiple Choice
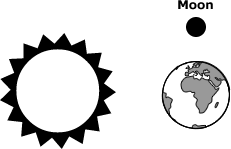
The Moon revolves around the Earth
The Moon revolves around the Sun
The Moon revolves around the Earth and rotates on it’s axis at the same rate
The Moon revolves around the Sun and rotates around the Earth at the same rate
2.
Multiple Choice
29.5 days
27.5 days
23.5 days
30 days
3.
Multiple Choice
29.5 days
23.5 days
27.5 days
Answer not shown
4.
Multiple Choice
Changing angles of the Earth, Moon, and Sun
Moon’s revolution around the Earth
The views of light and dark on the Moon as visible from Earth
All answer choices are correct
5.
Multiple Choice
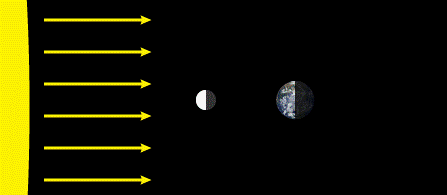
New Moon
First Quarter
Last Quarter
Full Moon
6.
Multiple Choice

Waxing Crescent
Waxing Gibbous
Waning Crescent
Waning Gibbous
7.
Multiple Choice
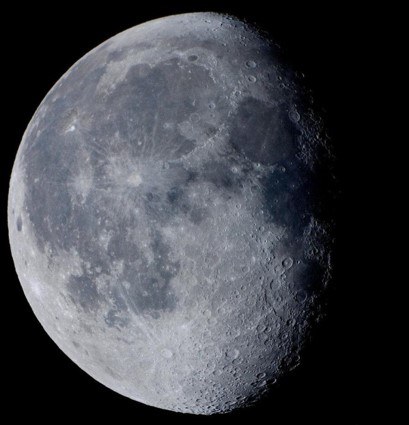

Waxing Crescent
Waxing Gibbous
Waning Crescent
Waning Gibbous
8.
Multiple Choice
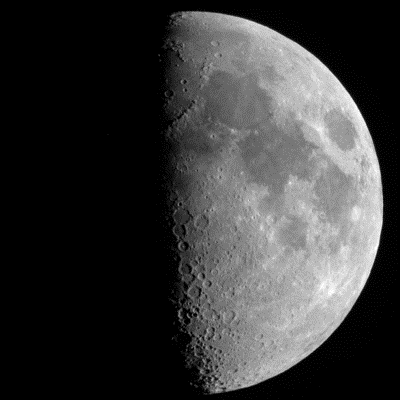

Waxing Gibbous
First Quarter
Waning Gibbous
Last Quarter
9.
Multiple Choice
The Moon has a strong gravitational pull on the Earth
The Sun has a weak gravitational pull on the Earth
The Moon and Sun have the same gravitational pull on the Earth
Moon has a strong pull / Sun has a weak pull
10.
Multiple Choice
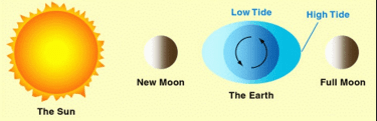
Spring Tide
Neap Tide
11.
Multiple Choice
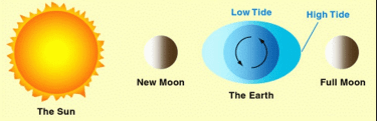
Lower high tides
Highest high tides
12.
Multiple Choice
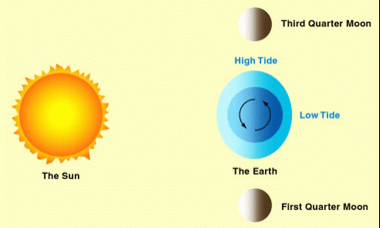
Spring Tide
Neap Tide
13.
Multiple Choice
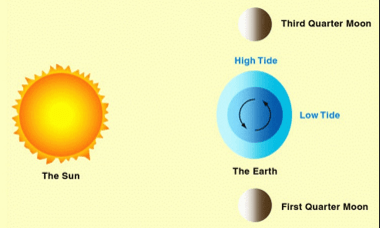
Highest high tide
Lower high tide
14.
Multiple Choice
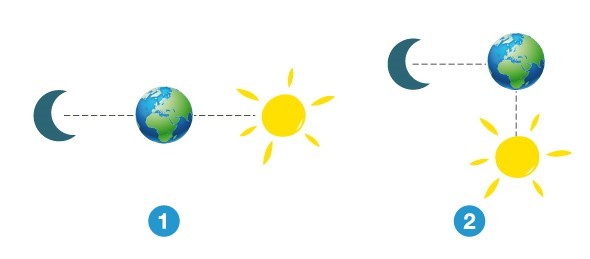
Picture 1
Picture 2
neither alignment produces highest tides
both alignments produce equally high tides
15.
Multiple Choice
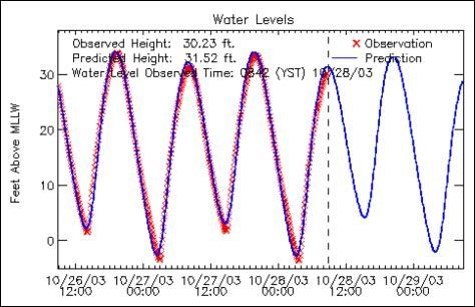
1 high and 1 low
2 high and 2 low
2 high and 1 low
2 high and 2 low
16.
Multiple Choice
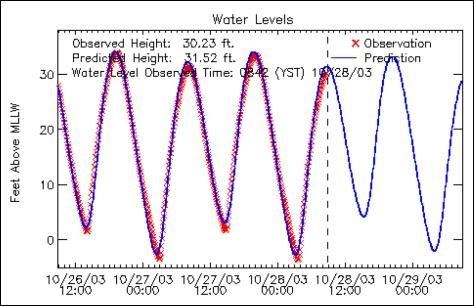
Red is interpolated and blue is extrapolated
Red is extrapolated and blue is interpolated
Both red and blue are interpolated
Both red and blue are extrapolated
17.
Multiple Choice
Waxing crescent
Waxing gibbous
Waning crescent
Waning gibbous
18.
Multiple Choice
Waxing crescent moon
Waning crescent moon
Waxing gibbous moon
Waning gibbous moon
19.
Multiple Choice
1
2
3
4
20.
Multiple Choice
1
8
15
23
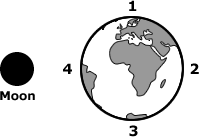
21.
Multiple Choice
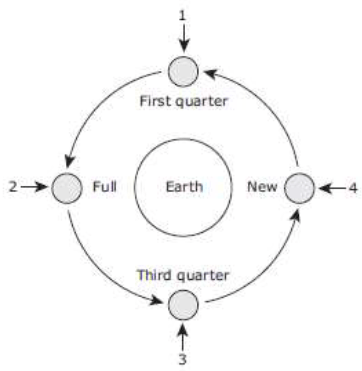
The diagram below shows four phases of the moon as it revolves around Earth.
A student builds a model based on this diagram. The student uses foam balls to represent the moon and Earth and a flashlight to represent the sun. The student should shine the flashlight on the model of Earth from Position—
1
2
3
4
22.
Multiple Choice
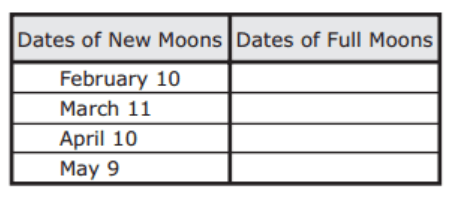
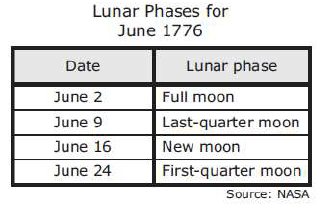
A student must complete the column of the table that lists the dates of the full moons.
What are the most likely dates of the full moons?
February 5, March 7, April 5, May 4
February 15, March 17, April 15, May 14
February 25, March 27, April 25, May 24
February 29, March 31, April 29, May 28
23.
Multiple Choice
A student uses paper and fasteners to create a model of Earth, the sun, and the moon. The sun and Earth are attached to the paper background, while the moon is free to revolve around Earth.
Which diagram shows the objects arranged so that a third/last quarter moon would be visible from Earth?
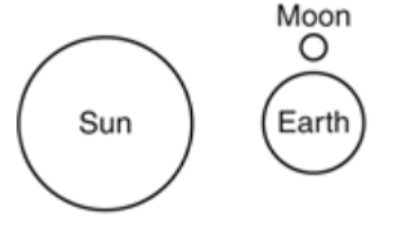

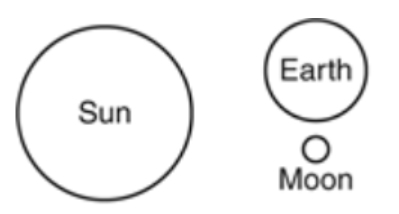
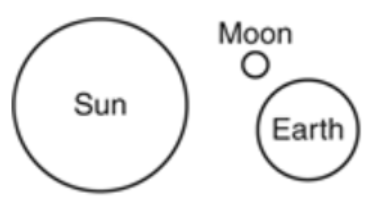
24.
Multiple Choice
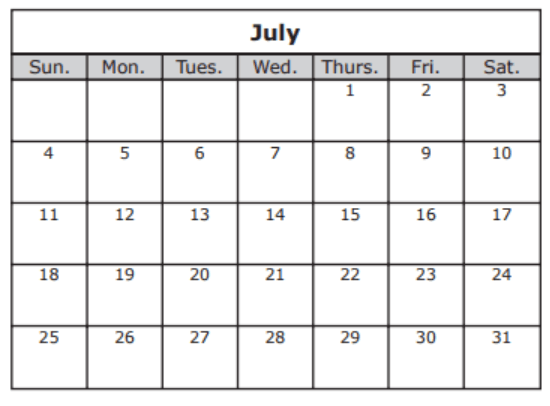
Two friends want to go for a night hike when there is a full moon in July.
If there is a third-quarter moon on July 2, what is the approximate date of the next full moon?
July 9
July 16
July 23
July 30
25.
Multiple Choice
The appearance of the moon changes in a predictable way in a pattern that lasts approximately 28 days. The changes in appearance are called phases of the moon. What is the main cause of moon phases?
The distance between the Earth and the moon.
The tilt of Earth on its axis compared to the tilt of the moon on its axis.
The amount of sunlight the Earth’s surface is exposed to.
The position of the moon in relationship to the Earth and Sun.
26.
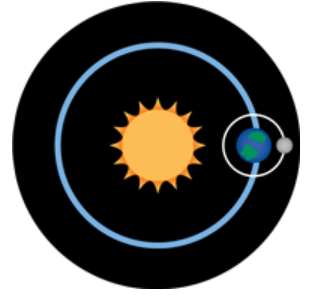
Multiple Choice
Which diagram BEST represents the relationship of the Earth, moon, and sun during the new moon phase?
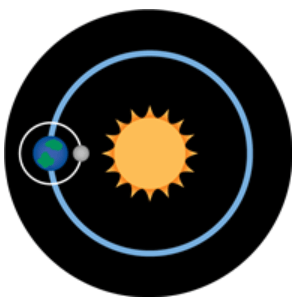
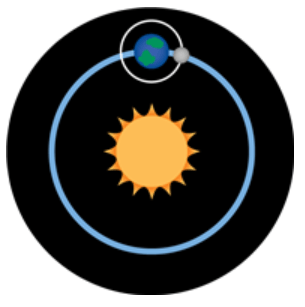
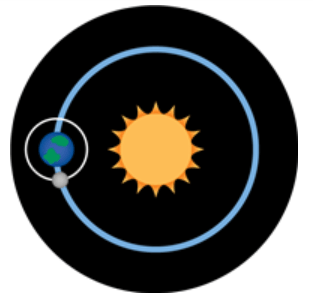
27.
Multiple Choice

Susan is sketching the appearance of the moon each night. Below is her entry for last night.
What will Susan’s entry look like in 14 days?




28.
Multiple Choice
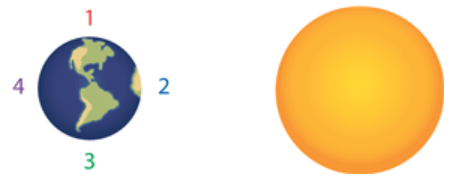
A student is drawing a diagram to show the positions of Earth, the moon, and the sun during a full moon.
Where on the diagram should the student place the moon to accurately show its position relative to the Earth and the sun during a full moon?
1
2
3
4
29.
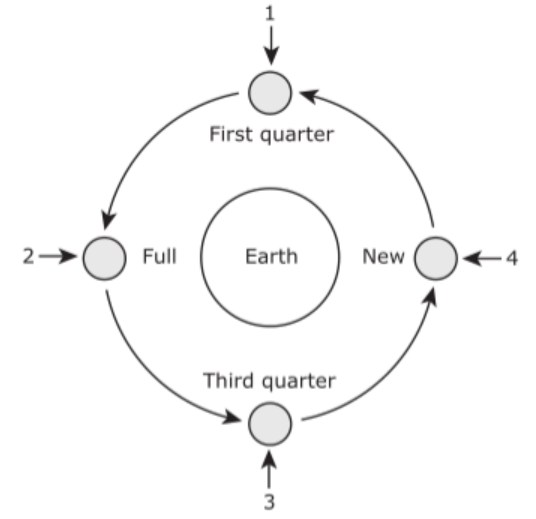
Multiple Choice
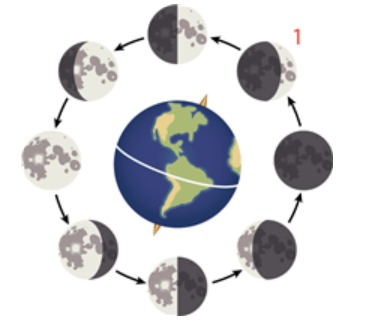
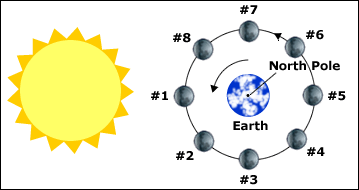
What is the phase of the moon indicated by the 1 in the diagram shown above?
waning crescent phase
waning gibbous phase
waxing crescent phase
waxing gibbous phase
30.
Multiple Choice
The alignment of the Moon and Sun has an affect on Earth’s ocean tides. What force causes this effect?
sun spots
magnetic fields
gravity
air resistance
31.
Multiple Choice
Which moon phases are associated with the highest tides?
full and three quarter
new and first quarter
new and full
first quarter and three quarter
32.
Multiple Choice
The appearance of the moon changes in a predictable pattern that lasts approximately 28 days. The changes in appearance are called phases of the moon. What is the main cause of moon phases?
The distance between the Earth and the moon.
The tilt of Earth on its axis compared to the tilt of the moon on its axis.
The amount of sunlight the moon’s surface is exposed to.
The position of the moon in relationship to the Earth and Sun.
33.
Multiple Choice
Mrs. Gupta is the Cub Scout den mother. She is taking a troop of boys on a camp out and believes it will be easier if she schedules the outing to happen during the full moon. Last night she observed a waning gibbous moon. Approximately how many days will she have to wait before the next full moon?
7
14
24
28
34.
Multiple Choice
Which diagram shows the position of the Moon, Earth and Sun, when the Moon appears full on Earth?
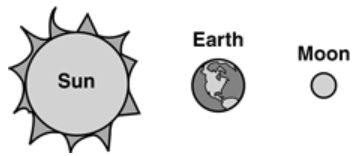
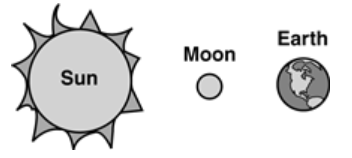
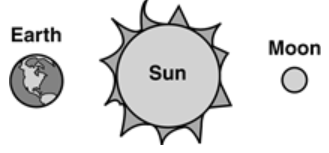
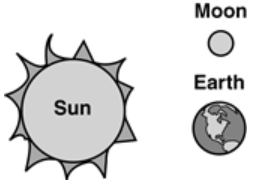
35.
Multiple Choice
A student viewed the moon through binoculars one week after a new moon. Which image shows the phase of the moon that the student observed?




36.
Multiple Choice
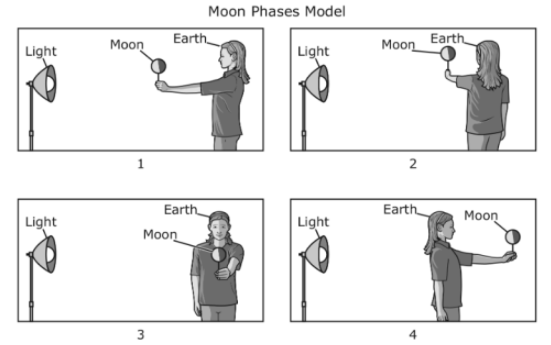
A student models moon phases. She holds a foam ball on a stick in front of her body and then stands in front of a light as shown. The student uses herself to represent Earth. She turns her body slowly to represent four different moon phases.
Which numbered diagram represents the student modeling a full moon?
Diagram 1
Diagram 2
Diagram 3
Diagram 4
37.
Multiple Choice
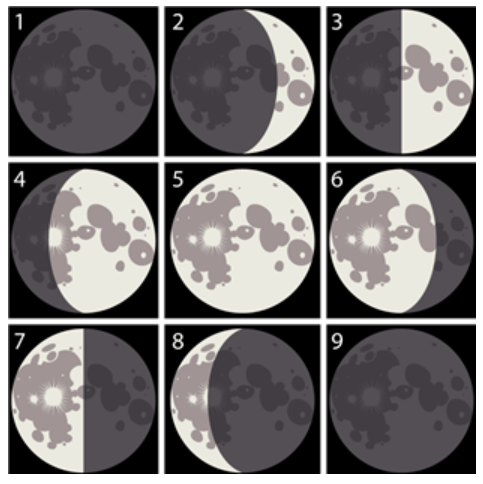
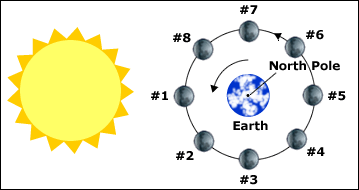
The diagram above represents the phases of the moon. Position 1 represents the new moon. Positions 2 through 8 represent the phases of the moon that follow.
Which phase does position 6 represent?
Full moon
Waning crescent
Waning gibbous
Quarter moon
38.
Multiple Choice
A father wanted to explain how the moon shines to his five-year-old child by comparing it to an object that the child uses. Which statement below is the best explanation?
The moon is like a flashlight. It produces its own light.
The moon is like a mirror. It reflects light produced by the sun.
The moon is like a glow-in-the-dark sticker. It absorbs light during the day and glows at night.
The moon is like a burner on a stove. When it reaches a certain temperature, it glows.
39.
Multiple Choice
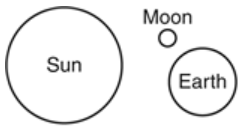
Which model of the Sun, Earth, and the Moon represents the positions that would result in the highest tides occurring on Earth?
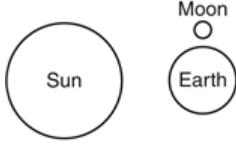
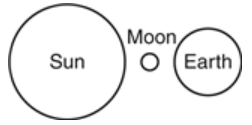
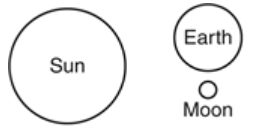
40.
Multiple Choice
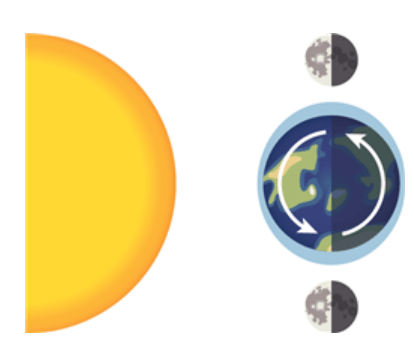
The gravitational impact of the moon and the sun can be seen when observing the Earth’s tides. The diagram shows a snapshot of where the high tides can occur due to the moon's alignment with the Earth at that moment.
Why are the tides more affected by the moon’s gravitational pull than the sun’s?
The moon is larger than the sun, giving it a stronger gravitational pull on the Earth.
The moon is closer to the Earth, giving it a stronger gravitational pull on the Earth.
The sun’s gravitational pull is spread evenly among all planets in the solar system, but the moon’s gravity only affects the Earth.
The rock that composes the moon creates a special gravitational pull that affects the liquids found on the Earth.
41.
Multiple Choice
The moon phases occur because...
the sun, the earth, and the moon do a dance and create shadows
the moon grows and shrinks
the moon revolves around the earth
the moon produces its own light
42.
Multiple Choice
The moon goes through every phase..
once a month
twice a month
once a year
the moon doesn't have phases, it has seasons
43.
Multiple Choice
The Moon revolves around the Earth
The Moon revolves around the Sun
The Moon revolves around the Earth and rotates on it’s axis at the same rate
The Moon revolves around the Sun and rotates around the Earth at the same rate
44.
Multiple Choice
New Moon
First Quarter
Full Moon
Third Quarter
45.
Multiple Choice
Waning Gibbous
Waxing Gibbous
Waning Crescent
Waxing Crescent
46.
Multiple Choice
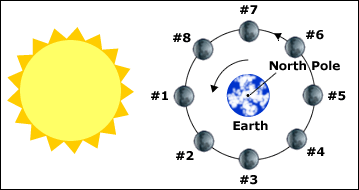
First Quarter
New Moon
Waxing Gibbous
Waning Crescent
47.
Multiple Choice
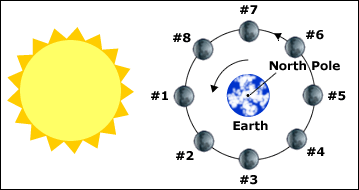
Waning Crescent
Waning Gibbous
Waxing Crescent
Waxing Gibbous
48.
Multiple Choice
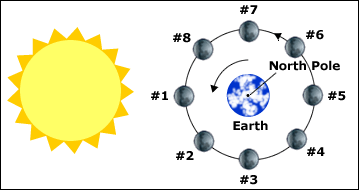
Waning crescent
First Quarter
Waxing crescent
Third Quarter
49.
Multiple Choice
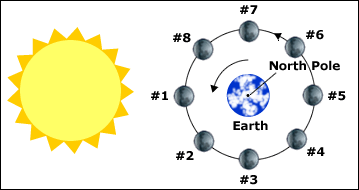
Waxing crescent
Waning crescent
Waxing Gibbous
First Quarter
50.
Multiple Choice
Reverse tide
Quarter tide
Neap tide
Spring tide
51.
Multiple Choice
4 only
1 and 4
3 and 4
2 and 4
52.
Multiple Choice
A tidal bulge occurs at Earth's north pole when the moon is farthest from the sun and at the south pole when the moon is closest to the sun.
A tidal bulge occurs at Earth's south pole when the moon is farthest from the sun and at the north pole whe the moon is closest to the sun.
Tidal bulges occur on the sides of Earth that are at right angles to the position of the moon.
A tidal bulge occurs on the side of Earth closest to the moon, as well as on the side farthest from the moon.

Explore this activity with a free account
Find a similar activity
Create activity tailored to your needs using
.svg)

Moon Phases
•
6th Grade

Moon Phases Quiz
•
4th Grade

Tides
•
6th Grade

Phases of the Moon
•
5th - 7th Grade

Mixtures and Solutions
•
4th Grade

Moon Phases
•
5th - 8th Grade

Moon Phases and Tides
•
8th Grade

Seasons
•
8th Grade